INTRODUCTION
TO VISUAL COMMUNICATION
PART
– A
·
Communication is the transfer of information
form one person to another.
·
It is the process of sending and receiving
messages
2. Visual communication
·
Visual communication is the conveyance of ideas and information through
visuals.
·
Visual communication in part or whole relies
on eyesight.
·
Visual communication includes signs, typography, drawing, graphic design, illustration, industrial design, advertising, animation, color, and electronic resources
3. Gestures
·
It is a non-verbal communication.
·
It is communication through body movement.
·
Especially hand or head to express an idea.
Eg – saying bye
4. Kinesics
·
It is a non-verbal communication.
·
Interpretation of body motion communication
such as facial expression, gestures are kinesics.
5. Noise
·
The sound which disturbs the communication
processes is noise.
·
Because of noise the receiver is not able to
receive message properly.
6. Feedback
·
It is respond to the communicated message.
·
The communication process is completed once
the feedback is reached to the sender
·
It completes the communication cycle
7. Visual language
·
Visual language is defined as a system of communication using visual elements.
·
Visual expression in these forms can cross over
traditional language barriers
and serve as a universally understood language.
8. Psychological noise
·
Psychological noise is a type of interference that occurs within our minds
as we try to communicate with others.
·
Example - Hunger, fatigue, headaches, pain, and physiological effects from
medicine that affect the way you think or feel.
9. Semantics
·
·
Example: A child could be called a child, kid, boy, girl, son,
daughter.
·
A message is defined as information
conveyed by words (in speech or writing), and/or other signs and symbols.
·
A message (verbal or nonverbal, or
both) is the content of the communication process.
The sender conveys the message to
a receiver.
·
Converting
our idea or thoughts into symbol, such as text, audio, video, etc.
·
In
a communication process the sender encodes the message.
·
Ex
– A person encodes his friend’s birthday wishes in the form of text, visual
(greeting card), voice message, etc.
·
Converting
symbols such as text, audio, video, etc. into meaningful message is called
decoding.
·
In
a communication process the receiver decodes information
·
Ex
– A person understand his birthday wishes message from the received text,
visuals, voice message, etc.
·
The pattern of gaze movement describes the moving directions of eyes
·
The gaze movement of viewers may vary depends on their cultural
backgrounds
·
Balance in design is the distribution of elements of the design.
·
Large, dense elements appear to be heavier
while smaller elements appear to be lighter.
15.
Symmetrical
balance / formal balance
·
Symmetrical balance refers to balance that
is achieved by arranging elements on either side of the center of a composition
in an equally weighted manner.
·
·
Asymmetrical balance results from unequal visual weight on each side of the
composition.
·
Designers can use asymmetry to create balance and harmony even though two sides
of the design do not
mirror one another
·
It refers to the misunderstanding of message by
the receiver
·
The meaning of words, signs and symbols might
be different from one person to another and the same word might have hundreds
of meanings.
·
Body language is a type of nonverbal communication that relies on body movements (such as gestures, posture, and facial expressions) to
convey messages.
·
Body language may be used consciously or unconsciously.
·
It may accompany a verbal message or serve as a
substitute for speech.
·
An optical
illusion is something that tricks your eyes so that what you think
you sees is different from what is really there.
·
Ghost image is an optical illusion that refers to an image continuing to appear
in one's vision after the exposure to the original image has ceased
·
Color saturation refers to the intensity of color in an image.
·
It refers to the dominance of hue in the color.
·
On the outer edge of the hue wheel are the
'pure' hues.
·
The elements that your user needs to see should
be classified as primary information.
·
These elements should have the most emphasis.
·
Ex – the name of the organization in a visiting
card
·
The elements that you want your users to see
(but aren't required to) should be classified as secondary information.
·
They should not stand out more than the primary information.
·
Ex – the address of an organization in a
visiting card
·
A logo is
a graphic mark, emblem, symbol or stylized name used to identify a company,
organization, product, or brand.
·
It may take the form of an abstract or
figurative design, or it may present as a stylized version of the company's
name
·
Human communication is the
field dedicated to understanding how humans communicate.
·
Humans communicate to share
information’s, thoughts, feelings, etc
·
Visual thinking, also called
picture thinking is the phenomenon of thinking through visual processing.
·
Visual thinking has been
described as seeing words as a series of pictures.
26.
Colour
management
·
In digital imaging systems, color management is the
controlled conversion between the color representations
of various devices, such as image scanners, digital cameras, monitors, TV
screens, computer printers, etc.
·
Color management prevents color variations.
·
The ability to see, hear, smell, taste, touch
and become aware of something.
·
Eg- when we see the object, we perceive the
shape and color of the object.
·
An individual or organism must be capable of
performing neurophysiological processing of the stimuli in their environment
for them to possess what is called a sensory perception.
·
·
Linear perspective, a system of creating an illusion of depth on a flat
surface.
·
All parallel lines in a painting or drawing
using this system converge in a single vanishing point on the composition's
horizon line.
·
Color theory is the study of color in art and design, their relationships with each other
and principles used to create harmonious color schemes.
·
In order to choose the right colors and color combinations, it is important that the graphic
designer has a basic understanding of color theory.
·
Visual power is the force in the visual process enabling one to see equally well in reading a
sign at twenty feet and in the next split- second reading a paragraph in a book
at twenty inches or less and do both in comfort.
·
Sets of colors that can be combined to make a useful
range of colors.
·
Red, yellow, and blue are the primary colors.
·
A colour resulting from the mixing of two
primary colours is called secondary colors.
·
Violet, orange, and green are the secondary
colors.
·
It is the literal (direct)
meaning of a word
·
Example - the denotation for “blue” is the color blue.
·
Rose is a flower
·
It is the indirect
meaning of a word
·
For example, blue is a color, but it is also a word used to describe a
feeling of sadness
·
Rose
is a symbol of love
·
The term "decision making" refers to the
process that groups go
through to identify alternative choices and appropriate way to select an
alternative to implement.
·
The advantage is that the
idea that the whole (group members) is greater than the sum (individual) of its
parts.
·
It refers to the arrangement of opposite
elements (light vs. dark colors, rough vs. smooth textures, large vs. small
shapes, etc.) in a design so as to create visual interest, excitement and
drama.
·
Contrast helps organize the design and establish a hierarchy which simply shows which
parts of the design are
most important.
38.
Visual
culture
·
Visual culture is a term that refers to the visible expressions by a
people, a state or a civilization, and collectively describes the
characteristics of that body as a whole.
·
Visual culture, a field of academic study that emphasizes the cultural meaning of a work of art
rather than its aesthetic value.
·
Visualization is any technique for creating images, diagrams, or
animations to communicate a message.
·
Visualization through visual imagery has been an effective way to
communicate both abstract and concrete ideas
·
Skills management is the
practice of understanding, developing and deploying people and their skills.
·
Well-implemented skills
management should identify the skills that job roles require, the skills of
individual employees, and any gap between the two
·
·
Sender starts the communication process and
encode the message
·
It is a medium which carries information to
receiver.
·
Eg – TV, radio, newspaper, magazine, cinema,
poster, painting, etc
·
If any signal problem in TV or radio or
printing problem in newspaper or magazine it is called as channel noise.
43.
Popular
culture
·
Popular culture is generally
recognized by members of a society as a set of the practices, beliefs, and
objects
·
The most common pop-culture categories are: entertainment (such as film, music,
television and video games), sports, news (as in people/places in the news),
politics, fashion, technology, and slang.
·
A line is
a form with width and length, but no depth.
·
Artists use lines to create edges, the outlines of objects.
·
The horizontal, vertical and diagonal directions
of a line can convey
different moods.
·
Texture refers to the surface quality in a work of art.
·
We describe things as being rough, smooth,
silky, shiny, fuzzy and so on.
·
Some things feel just as they appear; this is
called real or actual texture.
·
It is defined as anything that prevents
effective exchange of information, thought and ideas.
·
Physical, emotional, cultural, language,
gender are some of the examples of barriers to effective communication
·
Sign is a form of language that directly communicates with
the targeted audiences.
·
·
Color creates ideas, expresses messages, spark interest, and
generate certain emotions.
·
Within the psychology of colors, warm colors show excitement, optimism,
and creativity; cool colors symbolize
peace, calmness, and harmony.
·
Perception
is the ability to see, hear, or become aware of something through the senses
·
Visual perception refers to the brain's ability to make sense of what the
eyes see.
·
It
is also the way in which something is regarded, understood or interpreted
·
A text is any object that
can be "read".
·
Text messages are used for personal, family, business and social purposes.
·
Governmental and non-governmental organizations
use text messaging for
communication between colleagues.
·
It transmits some kind of
informative message.
·
Abstractions are ideas that are not described in specifics.
·
They cannot be physically sensed (seen, heard,
felt, touched, or smelled).
·
Examples of abstractions can
be feelings such as sadness or happiness.
·
Visual impact means how something you see affects you, or a given public
who would be viewing
an image.
·
So, the stronger an impact the greater the influence.
·
Value is one of the elements of art.
·
Value deals with the lightness or darkness of a color.
·
Since we see objects and understand objects
because of how dark or light they are, value is incredible important to art.
·
Perspective is a technique for depicting three-dimensional volumes
and spatial relationships in two dimensions
·
The main characteristic of perspective is that objects
appear smaller if it is in long distance from the observer.
·
A visual
narrative (also visual storytelling)
is a story told primarily through the use of visual media.
·
The story may be told using still photography, illustration,
or video, and can be enhanced with graphics, music, voice and other audio.
56.
Ideograms
·
An ideogram or ideograph is
a graphic symbol that represents an idea or concept
·
Good examples of ideogram are the red circle that
means “not allowed”, or the orange or yellow triangle that means “attention” or
“danger”.
57. Symbolic
·
Symbols take the form of words, sounds,
gestures, ideas, or visual images and are used to convey other ideas and
beliefs.
·
For
example, a red octagon may be a symbol
for "STOP". On a map, a blue line might represent a
river.
58.
Visual
literacy
·
Visual literacy is the
ability to interpret and make meaning from information presented in the form of
an image
·
Visual
literacy concerns how meaning
is made in still and moving images.
·
It includes non-fiction,
textbooks, picture books, art, advertisements, posters, graphic novels, comic
strips, animations, film clips, web pages, etc.
·
Proxemics is the study of how people use and perceive the
physical space around them.
·
The space between the sender and the receiver
of a message influences the way the message is interpreted.
·
The perception and use of space varies
significantly across cultures
·
Harmony can be described as sameness, the belonging of one
thing with another.
·
·
Analogous colours are groups
of three colours that are next to each other on the colour wheel
·
Red, orange, and red-orange
are examples.
·
An analogous color scheme
creates a rich, monochromatic look
·
A pictogram is
a symbol that conveys meaning through its resemblance to a physical object.
·
Examples of pictograms include way finding signage, such as in airports
and other environments where many people may not be familiar with the language
of the place they are in
·
Perceptual learning process by which the ability of sensory systems to respond
to stimuli is improved through experience.
·
Perceptual learning occurs through sensory interaction with the environment
as well as through practice in performing specific sensory tasks.
64.
Rhythm
·
Rhythm is a principle of design that suggests
movement or action.
·
Rhythm is usually achieved through repetition of lines, shapes,
colors, and more.
·
It creates a visual tempo in artworks and
provides a path for the viewer's eye to follow
·
The principle of dominance applied
to how the different elements of design can
be adjusted to give emphasis to an object.
·
If a design does not have a form of dominance will make the art work feel boring, monotonous and
confusing.
·
Pragmatic language refers to the social language skills that we
use in our daily interactions with others.
·
·
The phrase cool color is used to describe any
color that is calm or peaceful in nature.
·
Cool colors typically make a space seem larger.
·
Examples of cool colors include green, blue and violet.
68.
Warm
color
·
The phrase warm color is used to describe any
color that is vivid or bold in nature.
·
Warm colors are those that tend to advance in
space and can be overwhelming.
·
Examples of warm colors include red, yellow and orange (Ex-fire and volcanoes).
·
It focuses on public speaking : speaker –
speech – occasion - audience – effect.
·
Ex : Speaker is Alexander, his speech about
invasion, in the occasion of war field, to his soldiers (audience), to defeat
Persia (effect) is an example for this model.
70.
Design
element
·
The Elements of Design are the language of the visual arts.
·
These elements are
most relevant to two-dimensional (flat) art works.
·
Other elements related to three-dimensional art such as mass and
volume.
·
Graphic design is the
process of visual communication through the use of typography, photography,
iconography and illustration.
·
The field is considered a
subset of visual communication and communication design
·
A shape is a two- or
three-dimensional object
·
A shape can live in
different areas in space, and have other elements like line, color, texture, or
movement.
·
Shapes come in two
different types: geometric and organic.
·
Design Execution is the last long mile of any User Centered Design
project
·
Design Execution is a skill based activity where the designer
collaborates with various skill disciplines like Graphic Design, Animation, Illustration,
Packaging, Product Styling, Brand Identity etc.
·
Intercultural communication is the exchange of cultural information between
people with significantly different cultures.
·
Intra - cultural
communication is the exchange of meaningful messages
between members of the same cultural group.
·
The primary purpose of intercultural communication is to increase
understanding of culturally mediated communication phenomena.
·
"The design" is the output of the process of "Designing a thing".
·
"Implementing a design" means actually doing the
work to convert the idea (the design)
into something real.
·
It’s a systematic series of steps that helps to
define, plan and produce a creative design.
·
It allows us to be efficient, transparent and focused
on creating the best design.
·
Complementary colors are any two colors which
are directly opposite each other, such as red and green and red-purple and yellow-green.
·
Complementary colors may also be called
"opposite colors."
·
There are many visual forms such
as painting, drawing, printmaking, sculpture, ceramics, photography, video,
filmmaking, design, crafts, and architecture.
·
These forms are used to communicate the
information visually
PART
- B & C
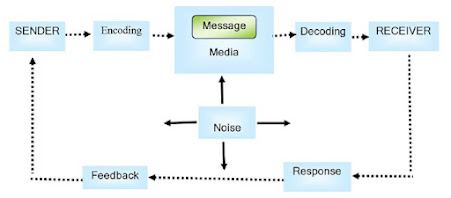
1. Elements of communication
1. Sender
He is the person who
sends his ideas to another person. For example, if a manager wants to inform
his subordinates about the introduction of a new product, he is the sender.
2. Message
The idea, feeling,
suggestion, guidelines, orders or any content which is intended to be
communicated is message. For example, message is the introduction of new
product.
3. Encoding
It is the process of
converting the idea, thinking or any other component of message into symbols,
words, actions, diagram etc. For example, message is connected in words and
actions.
4. Media (Channel)
It is the medium,
passage or route through which encoded message is passed by the sender to the
receiver. There can be various forms of media-face to face communication,
letters, radio, television, e-mail etc. For example manager inform about the
introduction of a new product in a meeting through presentation.
5. Decoding
It means translating
the encoded message into language understandable by the receiver. That means
the symbols, words, actions, etc are understand by the receiver as message.
6. Receiver
He is the person to
whom the message has been sent. For example, subordinates are receivers.
7. Feedback
It is the response by
the receiver. It marks the completion of the communication process.
8. Noise
Survival –
Communication is useful for a person to survive because he is depending on
others
Relationship –
Communication is used to build relationship. It is to identify relationship
among people to accomplish different task
Persuasion –
Communication is used to influence others. Advertisement, political meetings
are used to influence public
Power – It is used in
business organization to command power over others
Social need –
Communication used to fulfill one’s desire in the society
Information – It is
exchange of information from one person to another. It can be news, ideas,
entertainment.
Decision making –
Communication is used to take decision on various matters among family / in
society
Publicity –
Communication is used to announce message to public. Advertisements are used to
announce about the product
· Denotation is the literal meaning of a word.
· Denotation is the standard definition of a word
· For example, take the word "rose."
· The picture heart is parts of our body
Connotation
·
Connotation
is an indirect meaning of a word.
·
Connotation
is the feeling evoked by a word.
·
Example
– rose is the symbol of love
·
It
is also symbol of love
· A word has two different meanings depending upon what words are around it.
4. User interface design
A user interface (UI) is how a user interacts with a device or application. UI design is the process of designing interfaces to make them easy to use and provide a user-friendly experience. A UI includes all of the things a user interacts with—the screen, keyboard and mouse—but in the context of graphic design, UI design focuses on the user’s visual experience and the design of on-screen graphic elements like buttons, menus, micro-interactions, and more. UI designers specialize in desktop apps, mobile apps, web apps and games.
Examples
of user interface graphic design
·
Web
page design
·
Game
interfaces
·
App
design
5. Visual perception and its significance
· Visual perception is the ability to perceive our surroundings through the light that enters our eyes.
· The visual perception of colors, patterns, and structures has been of particular interest in relation to graphical user interfaces (GUIs) because these are perceived exclusively through vision.
· Physiologically, visual perception happens when the eye focuses light on the retina.
· Within the retina, there is a layer of photoreceptor (light-receiving) cells which are designed to change light into a series of electrochemical signals to be transmitted to the brain.
· Visual perception occurs in the brain’s cerebral cortex
· Different attributes of visual perception are widely used in GUI design
· Many designers apply Gestalt principles (i.e. how humans structure visual stimuli) to the design of GUIs so as to create interfaces that are easy for users to perceive and understand
Importance
·
The
visual perception skill of visual attention is what allows us to cut out
distractions in the environment in order to focus on what is important.
·
Reading
is one of the main ways that we acquire knowledge, it is evident how important
visual processing is to learning.
·
Perception
is how we draw conclusions from sensory experiences. Two people may perceive
the same sensory experience differently.
6. Characteristics of an effective graphic design
· Good graphic design is innovative.
· Good design makes a product useful. A product is bought to be used. It has to satisfy certain criteria, not only functional, but also psychological.
· Good design is aesthetic.
· Good design makes a product understandable. It clarifies the product’s structure.
· Good design is honest. It does not make a product more innovative, powerful or valuable than it really is.
· Good design is long-lasting
· Good design is thorough down to the last detail. Nothing must be left to chance.
· Good design is environmental-friendly. It conserves resources and minimizes physical and visual pollution throughout the lifecycle of the product.
7. Visual literacy
· Visual literacy is the ability to interpret, negotiate, and make meaning from information presented in the form of an image
· It commonly signifies interpretation of a written or printed text.
· Visual literacy is based on the idea that pictures can be "read" and that meaning can be through a process of reading
· Visual literacy, otherwise known as visual skill, is the foundation of learning.
· Children read pictures before they master verbal skills.
· Visual literacy allows individual learners to interpret art and visual media as they come into contact with them.
· Visual literacy is a skill and a necessary ability to interpret what is shared online and distributed in any other form of visual media.
· A perfect example of this are road and safety signs. If you know how to read road signs in your local area, then you can be confident that even if you are new to a place
· Visual literacy offers a deeper connection with all kinds of texts and encourages analytical interpretations of what is represented and their hidden meanings.
· It is a skill that eliminates barriers to learning.
· Example - Stories of ancient history made it to our books and online media distribution databases
· Visual literacy guides consumers in their buying decisions.
8. Semiotics
· Semiotics is an investigation into how meaning is created and how meaning is communicated.
· Its origins lie in the academic study of how signs and symbols (visual and linguistic) create meaning.
· A sign is defined as anything that communicates a meaning
· Signs can communicate through any of the senses, visual, auditory, tactile, etc.
· Semiotics includes the study of signs and sign processes (semiosis)
· A sign is a mark or shape that always has a particular meaning, for example in mathematics or music.
· It is the smallest unit of meaning.
· It is able to communicate information to the one interpreting or decoding the sign.
· It can work through any of the senses, visual, audio, touch or taste.
Signs
In each case, the sign can be broken into two parts, the signifier and the signified. The signifier is the thing, item, or code that we ‘read’ – so, a drawing, a word, a photo. Each signifier has a signified, the idea or meaning being expressed by that signifier. Only together do they form a sign.
A good example is the word ‘cool.’
The
word ‘Cool’ – Signifier.
Temperature
– Signified.
Types of signs
(i) Iconic sign
The icon is the simplest pattern that physically resembles what it stands for. Example picture of a computer on the desktop screen is an icon for the my computer
My computer (word) – Signifier
My computer (picture) - Signified
(ii) Indexical sign
Dark cloud – Signifier
Rain – Signified
Indexical signs have a cause-and-effect
relationship between the sign and the meaning of the sign. There is a
direct link between the two. Dark cloud might be the indexical sign of rain
(iii) Symbolic sign
No parking (text) – Signifier
Symbol - Signified
Symbol is an object that represents idea, visual image.
They take the form of words, sounds, visual images and are used to convey
ideas.
A Symbolic sign has no resemblance between the signifier and the signified. The connection between them must be culturally learned. Numbers and alphabets are good examples. There’s nothing inherent in the number 9 to indicate what it represents. It must be culturally learned.
·
Symbols are representations of an event, action, object,
person, or place that can be used to communicate about the event, action,
object, person or place
·
A symbol is a something that is accepted by certain
group of people or general population.
·
It can be interpreted differently by people from
different backgrounds.
· A cross is an example of symbol that has been universally accepted as representing Christianity.
· Symbol is a form of a sign that may have deep meaning. It can be interpreted in different ways since its meaning may not be universally shared by different people.
· Without symbols we cannot transport an idea from our environment to our brain, from one part of our brain to another, or from one person to another.
9. Design (in Visual Communication)
·
Visual
communication design is a creative process that combines the visual arts and
technology to communicate ideas.
·
It
begins with a message that, in the hands of a talented designer, is transformed
into visual communication that transcends mere words and pictures.
·
By
controlling color, type, movement, symbols, and images, the visual
communication designer creates and manages the production of visuals designed
to inform, educate, persuade, and even entertain a specific audience.
· Communication design is a mixed discipline between design and information-development
· It is concerned with how media intervention such as printed, crafted, electronic media or presentations communicate with people.
10. Design principles
The principles of
design are the rules a designer must follow to create an effective composition
that cleanly delivers a message to the audience. The following are the
principles of design
Balance
Every element of a design – typography, colors, images, shapes, patterns, etc. carriers a visual weight. Some elements are heavy and draw the eye, while other elements are lighter. The way these elements are laid out on a page should create a filing of balance. Balance is either symmetrical or asymmetrical. Symmetrical balance is when the weight of elements is evenly divided on either side of the design, whereas asymmetrical balance uses scale, contrast, and colour to achieve the flow in design.
Proximity
Proximity helps in creating a relationship between similar or related elements. These elements need not be grouped; instead, they should be visually connected by way of font, colour, size, etc.
This image is an
example of ‘Proximity.’ Here, a consistent shape (circle) and colours create an
organized design.
Alignment
Alignment plays a pivotal role in creating a seamless visual connection with the design elements. It gives an ordered appearance to images, shapes, and blocks of texts by eliminating elements placed in an inappropriate manner. The text, shape and image have been lined up in the middle, creating an ‘Alignment.’
Repetition
Contrast
Contrast happens
when there is a difference between the two opposing design elements. The most
common types of contrast are dark vs. light, contemporary vs. old-fashioned,
large vs. small, etc. Contrast guides a viewer’s attention to the key elements,
ensuring each side is legible.
Emphasis
Emphasis deals with the parts of a design that are meant to stand out. In most cases, this means the most important information the design is meant to convey. It can also be used to reduce the impact of certain information.
Proportion
Proportion is the visual size and weight of elements in a composition and how they relate to each other. It often helps to approach the design in section, instead of as a whole. It is the size of the elements in relation to one another. Larger elements are more important than smaller elements.
Movement
Movement is controlling the elements in a composition so that the eye is led to move from one to the next and the information is properly communicated to the audience.
Rhythm
The space between repeating elements can
cause a sense of rhythm to form, similar to the way the space between notes in
a musical composition create a rhythm. Rhythms can be used to create a number
of feelings. They can create excitement and consistency.
Unity
Unity is achieved when each individual element within a design comes together to reveal a singular cohesive vision. Unity allows each individual element to coexist with one another to form an aesthetically pleasing design despite its internal components differing in scale, contrast, or style.
11. Process of understanding gestures
·
Gestures
can be some of the most direct and obvious body language signals.
·
Waving,
pointing, and using the fingers to indicate numerical amounts are all very
common and easy to understand gestures.
·
Some
gestures may be cultural
The following examples are common
gestures and their possible meanings:
· A clenched fist can indicate anger in some situations or unity in others.
· A thumbs up and thumbs down are often used as gestures of approval and disapproval.
· The "okay" gesture, made by touching together the thumb and index finger in a circle while extending the other three fingers can be used to mean "okay" or "all right."
· The V sign, created by lifting the index and middle finger and separating them to create a V-shape, means peace or victory in some countries.
· The communication model refers to the visual representation of the communication process.
· The communication model performs certain functions in developing communication skills and efficiency.
· Communication model represents various elements involved in sending and receiving message.
· Communication model is to help in conducting research in the field of communication.
· It is to predict or forecast the success or failure of a particular communication process. One can find out the causes of success or failure of communication.
· Communication model helps to understand the communication process easily and logically.
· It shows how information flows form one person to another in the organization.
· Communication process is a complex issue. Through a model, this complex issue can be presented easily.
Gains attention :The first and foremost thing that a customer looks for is the design of a product. For e.g. - a person went to a shop to buy a pair of shoes will first look the design of the shoes. If the design stands out well among others then it definitely has to be his choice.
Increasing sales :A good design will lead to increased sales as it will be appreciated and practiced by more number of users. The most remember able product is chosen by maximum users and the product is remembered if it is more appealing and attractive through its design.
Ensure trust :Trust is very important in order to get the buyers for your product and convince them about the quality of the product. A professional and a good design help to generate trust among the customers, as it promises to give something new to them.
Builds a professional image :A good design, logo drawings or pictures can help to create a better professional image which could be a good and unbeatable advantage over others.
Provides a better world :Building a good design creates an impact on the user’s mind. We may emphasize to create a better planet by creating a better product through fresh designs and thoughts.
Brings out innovation :Each time a person has to come up with some new ideas and thoughts. It motivates them to look around the things in a creative manner and get the best out of them. Thus it makes the person more innovative and brings its artistic skills from within
Design elements are the basic units of any visual design which form its structure and convey visual messages. The elements of design as line, shape, size, texture, value and colour are the materials from which all designs are built.
Dot
Point or dot is the smallest element of graphic design. Designing with dots or points can create a wide variety of visual effects. There are various associations that can be made with positioning a single dot in different areas of a page. Single point in a center of an area can convey calm. Dots form together and create shapes.
Line
Line is
an element of art defined by a point moving in space. Lines can be vertical,
horizontal, diagonal or curved. They can be any width or texture. And can be
continuous, implied, or broken. Different lines create different moods; it all
depends on what mood you are using a line to create.
Shape
A
shape is defined as a two dimensional area that stands out from the space
next to or around it due to a defined or implied boundary, or because of
differences of value, color, or texture. Shapes are recognizable objects
and forms and are usually composed of other elements of design. Geometric
shapes are shapes that can be drawn using a ruler or compass, such as square,
circle, triangle, ellipse, parallelogram, star and so on.
Circle has
no end-point and thus a symbol of infinity. It conveys less tension than any
other areas and is not pulling in any direction. It’s static, balanced and
harmonious. The eye is always drawn to the center.
Ellipse – more dynamic than circle. If placed upright it suggests movement upwards, but also instability. Placed horizontally it becomes more static and relaxes.
Square –
a rectangle whose sides are parallel, the same length. When the square is on
one of its sides – the perception is of calm, stability, functionality. When turned
on its point, it becomes more dynamic and playful and unstable.
Triangle –
has the strongest directional component of all. When used in design or
composition, it is always dynamic, with most acute angle as focal point and
lesser angled base as a ground of composition/information. A triangle is used
most widely in portraiture paintings.
Color
Color
is often deemed to be an important element of design as it is a universal
language which presents the countless possibilities of visual communication.
Hue, saturation and brightness are the three characteristics that describe
colour. Hue can simply be referred to as “colour” as in red, yellow, or green.
Saturation gives a colour brightness or dullness. Brightness refers
to how much white (or black) is mixed in the color
Type
Type is an important element of design because it literally conveys the message we want to communicate. It provides structure between the content and the visuals. Type can also be a striking visual element or shape. Type when used well does not need a photograph or illustration to back it up. The font you choose can convey a lot of emotion.
Texture
Texture refers to the physical and visual qualities of a surface. Texture can be used to attract or repel interest to an element, depending on how pleasant the texture is perceived to be. Texture can also be used to add complex detail into the composition of a design.
Pattern
When a design is repeated over and over again in a surface, it results in a pattern. Patterns are frequently used in fashion design or textile design. Patterns are also used in architectural design, where decorative structural elements such as windows, columns are incorporated into building design.
Space
Space can be used to both
separate and connect elements in a design. Wider spaces separate elements from
each other and narrower spaces connect elements to reveal relationships between
them. We create design flow through the use of space.
Form
In
visual design, form is described as the way an artist arranges elements in the
entirety of a composition. It may also be described as any three
dimensional object. Form can be measured, from top to bottom (height),
side to side (width), and from back to front (depth). Form is also defined by
light and dark.
APPLICATIONS OF
GRAPHIC DESIGN
Graphic design uses visual compositions to communicate
ideas through typography, imagery, color and form. There’s no one way to do
that, and that’s why there are several types of graphic design, each with
their own area of specialization.
Visual identity graphic design
A brand is a relationship between a business or
organization and its audience. A brand identity is how the organization
communicates its personality, tone and essence, as well as memories, emotions
and experiences. Visual identity graphic design is exactly that: the
visual elements of brand identity that act as the face of a brand to
communicate those intangible qualities through images, shapes and color.
Marketing & advertising graphic
design
Companies depend on successful marketing efforts to tap into their target audience’s decision-making process. Great marketing engages people based on the wants, needs, awareness and satisfaction they have about a product, service or brand. Since people will always find visual content more engaging, graphic design helps organizations promote and communicate more effectively.
Examples
of marketing graphic design
·
Postcards
and flyers
·
Magazine
and newspaper ads
·
Posters,
banners and billboards
·
Infographics
·
Brochures
(print and digital)
·
Signage
and trade show displays
·
Email
marketing templates
·
PowerPoint
presentations
·
Social
media ads, banners and graphics
A user interface (UI) is how a user interacts with a
device or application. UI design is the process of designing interfaces to make
them easy to use and provide a user-friendly experience. A UI includes all of
the things a user interacts with—the screen, keyboard and mouse—but in the
context of graphic design, UI design focuses on the user’s visual experience
and the design of on-screen graphic elements like buttons, menus,
micro-interactions, and more. UI designers specialize in desktop apps, mobile
apps, web apps and games.
Examples of user interface graphic design
·
Web
page design
·
Game
interfaces
· App design
Publications are long-form pieces that communicate with an audience through public distribution. They have traditionally been a print medium such as books, newspapers, magazines and catalogs. Graphic designers that specialize in publications work with editors and publishers to create layouts with carefully selected typography and accompanying artwork, which includes photography, graphics and illustrations.
Examples
of publication graphic design
·
Books
·
Newspapers
·
Newsletters
·
Directories
·
Annual
reports
·
Magazines
· Catalogs
Packaging graphic design
Most products require some form of packaging to protect and prepare them for storage, distribution, and sale. But packaging design can also communicate directly to consumers, which makes it an extremely valuable marketing tool. Every box, bottle and bag, every can or container is a chance tells the story of a brand. Packaging designers create concepts, develop mockups and create the print-ready files for a product.
Motion graphic design
Simply put, motion graphics are graphics that are in
motion. This can include animation, audio, typography, imagery, video and other
effects that are used in online media, television and film. “Motion graphics
designer” is a somewhat new specialty for designers. Formally reserved for TV
and film, technological advances have reduced production time and costs, making
the art form more accessible and affordable.
Examples
of motion graphic design
·
Title
animation
·
Advertisements
·
Animated
logos
·
Trailers
·
Presentations
·
Promotional
videos
·
Tutorial
videos
·
Websites
·
Apps
·
Video
games
·
Banners
·
GIFs
Environmental graphic design
Environmental graphic design visually connects people to
places to improve their overall experience by making spaces more memorable,
interesting, informative or easier to navigate. Environmental graphic design is
a multidisciplinary practice that merges graphic, architectural, interior,
landscape and industrial design. Designers collaborate with people in any
number of these fields to plan and implement their designs. Because of
that, designers typically have education and experience in both graphic design
and architecture. They must be familiar with industrial design concepts and
able to read and sketch architectural plans.
Examples
of environmental graphic design
·
Signage
·
Wall
murals
·
Museum
exhibitions
·
Office
branding
·
Public
transportation navigation
·
Retail
store interiors
·
Stadium
branding
·
Event
and conference spaces
Art and illustration for graphic design
Examples
of art and illustration for graphic design
·
T-shirt
design
·
Graphic
patterns for textiles
·
Graphic
novels
·
Video
games
·
Websites
·
Comic
books
·
Album
art
·
Book
covers
·
Picture
books
·
Infographics
· Concept art
16.
Communication
is a process
- The process of communication refers to the transmission or passage of information or message from the sender through a selected channel to the receiver overcoming barriers that affect its pace.
- The process of communication is a cyclic one as it begins with the sender and ends with the sender in the form of feedback.
- It takes place upward, downward and laterally throughout the organization.
- The process of communication as such must be a continuous and dynamic interaction.
- Communication process consists of certain steps where each step constitutes the essential of an effective communication.
The following is a brief analysis of the important steps of the process of communication.
1. Sender
He is the person who
sends his ideas to another person. For example, if a manager wants to inform
his subordinates about the introduction of a new product, he is the sender.
2. Message
The idea, feeling,
suggestion, guidelines, orders or any content which is intended to be
communicated is message. For example, message is the introduction of new
product.
3. Encoding
It is the process of
converting the idea, thinking or any other component of message into symbols,
words, actions, diagram etc. For example, message is connected in words and
actions.
4. Media (Channel)
It is the medium, passage or route through which encoded message is passed by the sender to the receiver. There can be various forms of media-face to face communication, letters, radio, television, e-mail etc. For example manager inform about the introduction of a new product in a meeting through presentation.
5. Decoding
It means translating
the encoded message into language understandable by the receiver. That means
the symbols, words, actions, etc are understand by the receiver as message.
6. Receiver
He is the person to
whom the message has been sent. For example, subordinates are receivers.
7. Feedback
It is the response by
the receiver. It marks the completion of the communication process.
8. Noise
It is the hindrance
in the process of communication. It can take place at any step in the entire
process. It reduces the accuracy of communication e.g. 1) Disturbance in the
telephone lines, 2) An inattentive receiver 3) Improper Decoding of Message
etc.
17. Colour Psychology
Colour
psychology is the study of colours in relation to human behavior. It aims to
determine how colours affect our day to day decisions such as the items we buy.
Yellow
It is associated with happiness, warmth and energy.We can use it for various purposes like, to produce children’s product, in the items related to leisure or in the restaurant interior. However, it should be avoided if you want to represent stability and safety. E.g.- yellow is used in sign boards since it highlights the instruction and important information. It attracts the eye thus promotes the message very well.
Red
Red is the color of blood thus it signifies energy, danger, strength, desire and love. It enhances human metabolism and raises the blood pressure. It allows a person to make quick decision and it’s a perfect choice for ‘buy now’ button on the web. E.g.- red is usually used with yellow by the fast food industry because it triggers stimulation, appetite and hunger.
Green
Green color belongs to the nature. It has a great healing
power, moreover it’s the most relaxing color for the human eye. It indicates
growth and hope. It can be used to promote green products since it has a direct
connection to nature. E.g.- it is usually used in hospitals since it doesn’t shout
for attention and also gives a calming effect.
Blue
It is related to the sky therefore it’s often associated with depth and stability. It produces calming effect and slows human metabolism. It is also considered to be a masculine color and it is widely accepted among males. E.g.- blue is the most popular color on internet. It is a comparatively modern invention which also symbolizes trust, confidence and faith.
White
It is used to represent peace and purity. It is also considered to be color of perfection. White is the color of snow therefore it is used in advertising to signify coolness and cleanliness. E.g – it is the most desirable when it comes to cars because it denotes luxury, status and quality.
Orange
Orange represents
creativity, adventure, enthusiasm, success, and balance. The color orange adds
a bit of fun to any picture, website, or marketing material. Despite it is
attracting color, it’s not as commanding as the color red. Many marketers still
use the color for call to actions or areas of a website that they want to draw
the eye too.
Pink
Pink is a popular
color for brands that primarily serve a female audience. In color psychology,
pink’s color meaning revolves around femininity, playfulness, immaturity and
unconditional love. Some brands have chosen to use the color pink for the
product packaging especially for girl’s toys. Whereas other brands highlight
the pink color in their logo, website design, or to highlight key messages.
Purple
Purple is a royal
color. The color meaning for purple is connected to power, nobility, luxury,
wisdom, and spirituality. But avoid using the color too much as it can cause
feelings of frustration. Some perceive its overuse as arrogant.
Black
Black is a popular
color in retail. In color psychology, black color meaning is symbolic of
mystery, power, elegance, and sophistication. In contrast, the color meaning
can also evoke emotions such as sadness and anger. Many fashion retailers have
used black in their logos. Black is also a popular color for text as it’s an
easy color to read.
Grey
Grey color represents
neutrality and balance. Its color meaning likely comes from being the shade
between white and black. However, grey does carry some negative connotations,
particularly when it comes to depression and loss. Its absence of color makes
it dull. Grey can be used for font color, headers, graphics, and even products
to appeal to a mass audience.Apple is an example of a brand who uses the color
grey in their branding.
Brown
Brown is an earthy color. After all, it’s the color of earth, wood and stone. So naturally, color psychology highlights that the color meaning for brown relates to comfort, security and a down to earth nature. In marketing, you’ll find that brown is often used for natural products and food. Brown is a color that shows up in logos, banner images, and sometimes even text due to its contrast on a white background.
18. Importance of colour in visual communication
1 Color creates ideas, expresses messages, spark interest, and generate certain emotions. Within the psychology of colors, warm colors show excitement, optimism, and creativity; cool colors symbolize peace, calmness, and harmony.
Color is used to attract attention, group related elements, convey meaning, and generally enhance the aesthetics of the design.
. It can be used to organize the design elements and create a visual hierarchy in design. A small dose of color that contrasts with the main color will draw attention. It will give emphasis.
It has the power to create an emotion as powerful as music can. Color helps us instantly understand our environment. It is intrinsically important to our everyday life. It is all around us all the time and helps us to relate and to respond to our world, even if we generally take it for granted.
. Color can sway thinking, change actions, and cause reactions. It can irritate or soothe our eyes, raise your blood pressure or suppress your appetite. When used in the right ways, color can even save on energy consumption.
Symbolism of color: It is common knowledge that colors represent meaning. There are however standard universal color meanings. For eg: Red can communicate many different ideas depending on its context. Because red is associated with fire, it can represent warmth or danger. Since red is also the color of blood, it’s considered an energetic, lively color and is also associated with matters of the heart, and sometimes violence. In some Eastern cultures, red symbolizes good fortune and prosperity and is the color worn by brides on their wedding day. Worldwide, red has been associated with various political movements and has symbolized revolution.
Color in design: Design, be it in the use of color or layout, is all about balance. The more complicated the colors and the scheme, the more difficult it is to achieve balance. Pay attention to how the colors interact with each other especially when it comes to the ease of reading text and the mood you are creating with the color choices.60-30-10 is a basic, three-color palette rule that is sometimes applied to design which helps to create this harmony. Basically the dominant color is used 60% of the time, the accent color 30% and the balancer hue 10%. Another way to keep your color palette simple and balanced is using shades and tints of one Hue.
Color in marketing :The first impact a consumer has to a brand is visual and a consumer’s initial judgment of a product is largely to do with color and harmony. Thus the choice of color is not so much an artistic one as it is a business one and can affect every aspect from the consumers’ perception to the number of sales.We place a lot of emphasis on the harmonious juxtaposition of all design elements, including color, to create a unique personality for a specific brand. Each element is considered through experience, theory and a natural talent and design intuition. In design, the wrong colors can cripple marketing, even if all other elements are perfect.
19. Kinesics
Kinesics is the interpretation of body motion communication such as facial expressions and gestures, nonverbal behavior related to movement of any part of the body or the body as a whole.
Facial
expressions
It is
communication through face. The human face can produce thousands of different
expressions such as happy, sadness, anger, angry, etc. Happiness is associated
with an upturned mouth and slightly closed eyes; fear with an open mouth and
wide-eyed stare. The effect of facial expressions in conversation is
instantaneous.
Posture
The position in which someone holds their body when standing or sitting is posture. The position of our body relative to a chair or another person is another powerful silent messenger that conveys interest, aloofness, professionalism—or lack thereof. Head up, back straight (but not rigid) implies an upright character.
Gestures
Communication takes
place through the movement of part of the body such as hand, leg, head is
called gestures. Arms crossed over the chest, nail biting, head tilted to one
side, hand placed on the cheek are the examples of gestures. However, the
meaning of some gestures can be very different across cultures. While the OK
sign made with the hand, for example, conveys a positive message in
English-speaking countries, it’s consider offensive in countries such as
Germany, Russia, and Brazil. So, it’s important to be careful of how you use
gestures to avoid misinterpretation.
Eye contact
Since the visual sense is dominant for most people, eye contact is an especially important type of nonverbal communication. The way you look at someone can communicate many things, including interest, affection, hostility, or attraction. Eye contact is also important in maintaining the flow of conversation and for gauging the other person’s interest and response.
Handshake
It is
the movement of hands used to communicate information. A firm handshake, given
with a warm, dry hand, is a great way to establish trust. A weak, clammy
handshake conveys a lack of trustworthiness.
Crossing your Arms
Crossing
your arms could imply that a person is not open to new ideas / opinion
especially in case of giving a presentation. However, in a one-on-one interview
if the interviewer has his / her arms crossed, the candidate could do the same.
20. Importance of eye contact in communication
·
It
is a sign for good listening.
·
It
ensures that the receiver is paying attention on the sender’s content.
·
It
builds connection between the sender and receiver
·
Sender
feel comfortable talking and communicating with the receiver
·
Avoiding
eye contact represents that the person is not interested in listening
·
A
big part of eye contact is building trust.
·
Eye
contact indicates an openness in communication
·
It
is a sign of good conversation
·
If people need to get a
very important point across, eye contact is the best way to communicate that
importance.
·
Direct eye contact is
so powerful that it increases empathy (understanding) and links together
emotional states.
·
We have countless ways
of describing eyes including “shifty-eyed,” “kind-eyed,” “bright-eyed,” “glazed
over,” and more. Eye contact is also a powerful form of simultaneous
communication meaning you don’t need to communicate using words.
·
By looking the persons
eye we can understand what they are thinking
· Eye contact evokes (remind) presence and projects confidence, self-esteem, and boldness while speaking.
21. Importance of facial communication
· It is a form of non verbal communication
·
Eyes, mouth, eyebrows, and forehead are
involved in facial expression
·
Smiling is a positive emotion that tells the
receiver happy
·
Eyebrows are brought together, forehead is
rinkled indicating worry
·
Eye contact is an important sign of
confidence and respect
·
Opening one’s eyes or mouth widely,
indicating excitement and shock
·
Blinking eyes could signal that we are joking
· Raising our eyebrows communicate that we are surprised
22. Relationship between messages and meaning
Messages
·
In
rhetorical and communication studies, a message is defined as information
conveyed by words (in speech or writing), and/or other signs and symbols.
·
A
message is the content of the communication process.
·
The
originator of the message in the communication process is the sender. The
sender conveys the message to a receiver.
· A message may include verbal content, such as written or spoken words, sign language, email, text messages, phone calls, snail-mail, and even sky-writing
· Both verbal and nonverbal content is part of the information that is transferred in a message.
· If nonverbal cues do not align with the verbal message, ambiguity is introduced.
·
A
message will also include nonverbal content, such as body movement and
gestures, eye contact, artifacts, and clothing, as well as vocal variety,
touch, and timing
· Communication refers to the process of sending
and receiving messages, which can also be referred to as encoding and decoding
messages
· Depending on the receiver level of literacy in the medium in which the message is being encoded.
Meaning
·
Meaning is what a word, action, or concept is all about its
purpose, significance, or definition.
·
Meaning represents something's intent or purpose.
·
That
something can be a book, a conversation, a television show, or life itself.
·
When
you read a poem, you try to figure out the author's intended meaning by
interpreting the words he has chosen.
· For example, if a poet describes love as "a prison," you might interpret the meaning as his feeling limited by his love.
23. Visual form (visual aid)
Chalkboard or whiteboard
·
Chalkboards
and whiteboards are very useful visual aids, particularly when more advanced
types of media are unavailable.
·
They
are cheap and also allow for much flexibility.
·
The
use of chalkboards or whiteboards is convenient, but they are not a perfect
visual aid.
Poster
board
·
A
poster is a very simple and easy visual aid.
·
Posters
can display charts, graphs, pictures, or illustrations.
· Since a poster board paper is relatively flimsy, often the paper will bend or fall over.
Handouts
·
Handouts
can also display charts, graphs, pictures, or illustrations.
·
An
important aspect of the use of a handout is that a person can keep a handout
with them long after the presentation is over.
·
This
can help the person better remember what was discussed.
Video
excerpts
·
A
video can be a great visual aid and attention grabber, however, a video is not
a replacement for an actual speech.
·
Video
is very exciting and interesting
Projection
equipment
·
These
include slide projectors, PowerPoint presentations, overhead projectors, and
computer projectors.
·
PowerPoint
presentations are very popular and are used often. Overhead projectors are
still used but are somewhat inconvenient to use.
Computer-assisted
presentations
·
PowerPoint
presentations can be an extremely useful visual aid.
·
For
longer presentations, however, PowerPoints can be a great way to keep the
audience engaged and keep the speaker on track.
Social
media
·
Social
media is one of the most effective ways to communicate.
·
The
incorporation of text and images deliver messages quicker and more simplistic
through social media platforms.
24. Visual elements
Objects
·
The
use of objects as visual aids involves bringing the actual object to
demonstrate on during the speech.
·
For
example, a speech about tying knots would be more effective by bringing in a
rope.
Models
·
Models
are representations of another object that serve to demonstrate that object
when use of the real object is ineffective for some reason.
·
Examples
include human skeletal systems, the solar system, or architecture.
Graphs
·
Graphs
are used to visualize relationships between different quantities.
·
Various
types are used as visual aids, including bar graphs, line graphs, pie graphs,
and scatter plots.
Maps
·
Maps
show geographic areas that are of interest to the speech.
·
They
often are used as aids when speaking of differences between geographical areas
or showing the location of something.
Tables
·
Tables
are columns and rows that organize words, symbols, and/or data.
Photographs
· A photograph is also good to use when the actual object cannot be viewed.
· For example, in a health class learning about cocaine, the teacher cannot bring in cocaine to show the class because that would be illegal
Drawings or diagrams
· Drawings or diagrams can be used when photographs do not show exactly what the speaker wants to show or explain.
· For example, a drawing or diagram of the circulatory system throughout the body is a lot more effective
25. Visual culture
· Visual culture is a way of studying a work that uses art history, humanities, sciences, and social sciences.
· It is intertwined with everything that one sees in his day to day life - advertising, landscape, buildings, photographs, movies, paintings - anything within our culture that communicates through visual means.
· When looking at visual culture, one must focus on production, reception, and intention, as well as economical, social, and ideological aspects.
· It reflects the culture of the work and analyzes how the visual aspect affected it.
· It focuses on questions of the visible object and the viewer - how sight, knowledge and power all are related.
Some of the Indian visual cultures are
· Indian visual culture
has its roots in the cave paintings at Ajanta, the sculptures in Ellora and
Khajuraho, and in the mix of architectural styles of hundreds of temples,
mosques and churches and other types of shrines and pilgrim centers around the
country.
· Further, the many
forms of dance, theatre and music, have contributed to the national, regional
and local visual cultures.
· In Indian visual
culture, there has always been a search for "the sense of the
beautiful", results from a devotee's meditation and finds expression in
"rasa".
· For Indian aesthetes
like Jagannatha of the 17th century, the "beautiful" was that which
induced a unique feeling of pleasure, "an emotional thrill", "a
particular type of harmony".
· For example, Durga has
ten hands, Siva and Brahma have five faces, and Ganesh has an elephant's face
and trunk.
· This approach to
representations in art shaped the evolution of popular visual culture in the
technological media such as the press, photography, cinema, television,
recorded music, etc.
· Much before the
arrival of the cinema in India, shadow puppetry and the folk tradition of pat painting
demonstrated that the illusion of moving images could be created.
26. Describe Graphic Design
Graphic
design is the process of
visual communication through the use of typography, photography, and illustration.
The field is considered a subset of visual communication and communication
design. Graphic designers create and combine symbols, images and text to form
visual representations of ideas and messages. They use typography, visual arts
and page layout techniques to create visual compositions. Common uses of
graphic design include corporate design, editorial design, environmental
design, advertising, web design, communication design and product package
design.
HISTORY OF GRAPHIC DESIGN
In graphic design, "the essence is to give order to information, form to ideas, expression, and feeling to artifacts that document human experience." The term graphic design was coined by William Addison Dwiggins in 1922. However, the origins of graphic design can be traced from the origins of human existence, from the cave paintings, manuscripts, inscriptions, etc. In "Babylon, artisans pressed cuneiform inscriptions into clay bricks or tablets which were used for construction. The bricks gave information such as the name of the reigning monarch, the builder, or some other dignitary". The Egyptians developed communication by hieroglyphics that used picture symbols dating as far back as 136 B.C. The Egyptians also invented papyrus, paper made from reeds found along the Nile, on which they transcribed advertisements more common among their people at the time. From 500 AD to 1450 AD, monks created elaborate, illustrated manuscripts.
NATURE OF GRAPHIC DESIGN
Graphic design is an important tool that enhances how
you communicate with
other people. It serves to convey your ideas in a way that is not only
effective, but also beautiful. Graphic design is an art with
a purpose. It involves a
creative and systematic plan to solve a problem or achieve certain objectives,
with the use of images, symbols or even words. It is visual communication and
the aesthetic expression of concepts and ideas using various graphic elements
and tools. Graphic designers create
visual concepts, by hand or using computer software, to communicate ideas that
inspire, inform, or captivate consumers. They develop the overall layout and
production design for
advertisements, brochures, magazines, and corporate reports.
27. Role of graphic designer
Graphic designers create visual concepts, using computer software or by hand, to communicate ideas that inspire, inform, and captivate consumers. He develops the overall layout and production design for various applications such as advertisements, brochures, magazines, and corporate reports. His duties are
- Meet with clients or the art director to determine
the scope of a project
- Advise clients on strategies to reach a particular
audience
- Determine the message the design should portray
- Create images that identify a product or convey a
message
- Develop graphics for product illustrations, logos,
and websites
- Select colors, images, text style, and layout
- Present the design to clients or the art director
- Incorporate changes recommended by the clients into
the final design
- Review designs before printing or publishing them
Berlo’s SMCR Model of Communication includes four
components that describe the communication process. The different components in
the model are influenced by various factors.
Sender
The
sender of the message is the source who creates and sends the message to the
receiver. The source is the start of the communication process and is the
person who encodes the message. Factors that may influence the sender are also
applicable to the receiver. Berlo’s SMCR Model of Communication identifies the
following factors that affect the source:
·
Communication skills - Communication
skills include: reading, listening, speaking etc.
·
Attitude - One’s attitude in
relationship to the audience, receiver and subject changes the meaning and
consequence of the message.
·
Knowledge - Familiarity with
the subject of the message makes communication more effective.
·
Social systems - Values, beliefs,
religion and rules influence the way in which the sender communicates the
message, alongside location and circumstances.
·
Culture - Cultural
differences may result in the message being interpreted differently.
Message
The
message is the package of information or meaning that is sent from sender to
receiver. The message can be sent in various forms, such as audio, speech,
text, video or other media. The sender of the messages always wants the
receiver to interpret the message in a certain way. The source’s intention is
therefore translated into a coded message. The receiver should understand the
message with reasonable accuracy. The message is influenced by:
·
Content
- The content of the message from
beginning to end.
·
Elements - Elements are (non)verbal aspects, such as
gestures and signs, that may influence the message.
·
Treatment - Treatment refers to the way in which the
message is sent, the message’s packaging.
·
Structure
- As the word suggests, the
structure of the message refers to the way in which it is structured.
·
Code - The code of the message is the form in
which the message is sent. This may include text, language, video, gestures,
music, etc.
Channel
The
channel is the medium used to send the message. The medium must be able to be
picked up by the sensory system of the receiver and may therefore involve
vision, sound, smell, taste or touch. Humans have the following senses:
- Hearing – hears are used to hear
audio messages
- Seeing – eyes are used to seeing
the visuals and understand the message
- Touching – hanging, shaking
- Smelling – perfume, food
- Tasting – through this channel the
taste of the food is conveyed
Mass communication always involves technical tools, such as phones, the
Internet and television. In these cases, the transmitted information is
assimilated via vision and sound.
Receiver
The
receiver is the person who receives and subsequently decodes the coded message.
In a linear communication process, the receiver is always located at the end.
In order to make communication as effective and smooth as possible, Berlo’s
SMCR Model of Communication assumes the receiver’s thinking pattern must be in
accordance with that of the sender. The same factors therefore influence this
component in Berlo’s SMCR Model of Communication. After all, the receiver
decodes the message him/herself and gives it their own meaning.
29. Stages of design process
Here are the
7 steps most design projects will have to pass through to get from the initial
client briefing to a successful project.
Study the client brief
· Set goals and context from the brief – this intake sheet is the blueprint that leads you to the final design.
· Ask as many questions as you can now, to make sure you start off on the right path.
· Make sure that your questions will yield answers that will enlighten you on the project key points.
Research, research, research
·
Initial
research areas should always include the client's company history and culture,
the local competitor landscape, and any industry-related trends.
·
For
the next step, you need to analyze your project's target audience.
·
You
need to consider the age, gender, income, employment, location, and lifestyle
of the people the client wants to reach.
Brainstorm
· One way to generate ideas is to use structured mind maps with ideas linked to your central concept.
· Others prefer to make lists or write random ideas you get from time to time on scrap pieces of paper or on their phone.
· Make sure you keep a record of all your ideas and concepts which will be helpful in later stages.
Sketch
·
Sketching
your ideas to define their visual elements is a good way to save time.
·
It
is a common practice done by experienced graphic design professionals to give
their work a solid foundation.
·
With
sketches and design mock-ups, you can create a number of different concepts
faster as they do not require too many details.
Concept development
·
Once
you've sketched out your initial thoughts, it's time to develop your favorite
concepts a bit further.
·
It
is a good idea to develop 3-5 different concepts to give your client some
choice.
· Present these concepts to your client, explain the rationale behind each one, and why the design will work.
Revisions
·
After
the client chooses one concept, it is time to revise the design so it meets the
goals and outlines.
·
The
client may want you to mix and match from all concepts you have presented, or
come up with something entirely new.
· From comments and suggestions, you can present another round of designs.
Completion
·
Way
to go! Your client is loving it, apart from some minor tweaks here and there.
·
Get
approval. Send the final files – the project is complete!
·
There
is nothing more rewarding than turning around a completed graphic design gig to
a satisfied client.
30. Functions of language
·
Humans communicate with language
·
Language is used to present our ideas, thoughts, feelings
and opinions to others
·
Language is used in oral and written communication
·
People around the world use a specific language to
communicate
·
It is also used to convey emotions, opinion and ideas
·
Different languages used for communication are English,
Tamil, Telugu, Malayalam, etc
31. Mass culture
· Mass culture is a common culture experienced by large number of people.
· It is widely disseminated by mass media.
· It is the set of ideas and values that develop or arise from a common exposure to the same cultural activities, media, news sources, music and art.
· Mass culture conveys the idea that such culture emerges spontaneously from the masses themselves like popular art.
· Mass culture is broadcast or otherwise distributed to individuals instead of arising from their day-to-day interactions with each other.
· Thus, mass culture generally lacks the unique content of local communities and regional cultures.
· It promotes the role of individuals as consumers.
· Mass culture emerged due to the development of print and broadcast which were strong enough to alter perception, convince people to follow ideas on a large scale.
· The main function of Mass culture is to entertain and distract the people.
· Mass culture raised people’s standard of living and economic development.
· It replaced folklore, which was the cultural mainstream of traditional local societies.
· Examples of mass culture includes films, television programmes, popular books, newspapers, magazines, popular music, leisure goods, household items, clothing, and mechanically-reproduced art.
32. Intra personal communication
· A kind of communication that occurs within us
· It involves thoughts, feelings, and the way we look at ourselves
· It is self centered
· The same person is act as both sender and receiver
· The message is made up of thoughts and feelings
· The channel is the brain, which processes what the person think
· It has internal feedback
Advantages of intrapersonal communication
·
It allows the person to be aware of every aspect of their
own personality.
·
A self-aware state makes one secure and increases
confidence.
·
It equips a person to manage his daily affairs
efficiently using his strengths to the maximum which in turn compensates for
his weaknesses.
·
The qualities of self-motivation and self-management will
help develop deeper concentration and direct his focus towards the task at hand.
·
Self-awareness allows the person to be independent
·
The person is highly adaptable to his surroundings as the
knowledge of his own qualities allows him to confidently and calmly take
decisions and change his approach accordingly in response to situational
stimuli.
Disadvantages of intrapersonal communication
·
Since the person prefers working alone, he is perceived
as shy or anti-social by others.
·
Since there is absence of a feedback, that is, the
conversation is in a one-way flow, it could lead to the development of
misconceptions and faulty assumptions.
·
Wrong assumptions made by an individual could lead to
incorrect decisions.
·
There is a possibility of an individual categorizing and
viewing certain individuals or events with a biased opinion.
·
Over analysis of situations and prolonged thinking about
them will lead to the imagination of unrealistic and unnecessary scenarios, and
in extreme cases, may even lead to self-doubt.
·
One may be incorrectly perceived as being arrogant.
33. Inter personal communication
· Communication between two persons is called interpersonal or dyadic communication
· It is used to communicate our ideas, thoughts and feelings to another person
· It is message sending and receiving by the two persons
· It includes listening, persuading and non-verbal communication
· It can also use charts, graph, animation, music, and sound for communication purpose
Forms or types of interpersonal communication
(a) Face to face communication – Meeting two persons in a formal or informal way to exchange of view, ideas, and thoughts. Participants are speaker and listener. In face to face communication we can observe the facial expression, and the interest of the listener. Both speaker and the listener have eye contact. Communication is very fast and can get immediate feedback
(b) Telephonic conversation – It is interaction between two persons on the telephone. It is the fastest way of communication. We cannot have eye contact and observe facial expression. Since it doesn’t have eye contact the truthfulness of message is not verifiable.
(c) Interview – It is the meeting between interviewer and interviewee with a specific purpose. Generally it is a formal way of dyadic communication. It is to get new information about the person which is not available already.
(d) Instruction – It is directing others to perform a particular job. In this the language should be polite, plain and direct. The speaker should understand the receivers understanding capacity.
Stages of interpersonal communication
(a) Phatic stage – This is the formal stage of communication. It begins with hi, hello, etc. It is the introduction or first meeting between two persons. It can be called as warming up stage.
(b) Personal stage – It is the stage of sharing personal details. We can talk about our feelings, job, family, etc
(c) Intimate stage – This stage is reserved for friends and relatives. Since it is the stage of closeness all things will be shared between them.
Advantages of interpersonal communication
· It is fastest mode of communication
· Possible to convey message clearly
· We can observe facial expression and eye contact
· Possible to get immediate feedback.
· No chance for misunderstanding since the doubts are clarified during conversation
Disadvantages of interpersonal communication
· There is no record or evidence of conversation
· In telephonic conversation we can’t observer facial expression and eye contact
· Technology may be the reason for the barrier to communication in telephonic conversation
34. Group communication
· It is the communication taken place between the group members.
· Three or more members (approximately 15) are present in a group
· Each group has a common goal
· Group members are working together to achieve the goal
· Since it is a common goal, each member in a group depending on each other
· Group members use verbal, non verbal and text messages to generate meanings and establish relationship.
Types
of group communication
(a) Primary group – It is a small social group whose members
share close, personal relationship. Family and friends group are comes under
primary group
(b) Secondary group – It can be small or large in size. It is impersonal. Group in a work place is an example for secondary group.
(c) Learning group – It is an educational approach. It allows students to develop their studies and communication skills
(d) Service group – This group render their service to God and society. Choir, group counseling are examples of service group
(e) Discussion group – It is a face to face interactions in a
group. Group members respond, react and adopt to the communication
Advantages of group communication
· Group members can easily reach the goal
· It is a coordinated work
· The work is decentralized to complete the task easily and effectively
· Each member can contribute many ideas
Disadvantages of group communication
· There is a chance for miscommunication
· Ego problem may arise among the group members
35. Importance of communication
Survival –
Communication is useful for a person to survive because he is depending on
others
Relationship – Communication
is used to build relationship. It is to identify relationship among people to
accomplish different task
Persuasion –
Communication is used to influence others. Advertisement, political meetings
are used to influence public
Power – It is used in
business organization to command power over others
Social need –
Communication used to fulfill one’s desire in the society
Information – It is
exchange of information from one person to another. It can be news, ideas,
entertainment.
Decision making – Communication
is used to take decision on various matters among family / in society
Publicity – Communication is used to announce
message to public. Advertisements are used to announce about the product
36. Nature of communication
·
Communication is related to every human activity
·
Communication involves two or more persons
·
Communication may be one way or two way process
·
The success of communication depends on proper
understanding of sender and receiver
·
Communication in organization flows horizontally or vertically
·
Communication is media/channel based
37. Importance of feedback
·
It
is response to the communicated message
·
It
completes the communication cycle
·
It
maintains communication between sender and receiver
·
It
Promotes understanding
·
It
fulfills the need for recognition
·
It
solicits more information
·
It
acts as a tool of motivation
·
Feedback
can be positive or negative
·
It
can be internal or external
38. Optical illusion / visual illusion
·
An optical
illusion (also called a visual illusion) is an illusion caused by the visual
system and characterized by a visual percept that arguably appears to differ from reality.
·
Optical
Illusions can use color, light and patterns to create images that can be
deceptive or misleading to our brains.
·
The
information gathered by the eye is processed by the brain, creating a
perception that in reality, does not match the true image.
·
Optical
illusions occur because our brain is trying to interpret what we see and make
sense of the world around us.
· Optical illusions simply trick our brains into seeing things which may or may not be real.
· A classical example for a physical distortion would be the apparent bending of a stick half immerged in water
39. Qualities of a good designer
Artistic Ability: A great graphic designer must be
talented and have a variety of artistic skills and ability.
Client Oriented: A great graphic designer is able
to work easily with clients to ensure that designs meet specifications.
Communication: A great graphic designer is able
to effectively communicate with clients and other members of the design team to
ensure they are on track with deadlines and other goals.
Creativity: A great graphic designer is very
creative and can come up with new and exciting ideas for designs.
Knows Audience: A great graphic designer
understands that different audiences respond to different images and can
integrate this understanding into their designs.
Manages Priorities: A great graphic designer is able
to work within boundaries of deadlines and changing priorities and can
effectively manage a workload to meet deadlines and satisfy clients.
Open to Change: A great graphic designer hears all
criticism with an open mind and is willing to change designs based on the needs
or wants of a client or opinions of members of the design team.
Strategy: A great graphic designer
understands how strategy plays a part in marketing and advertising, and is able
to develop strategic ideas and work within the scope of a client's strategic
plan to execute top notch designs.
Teamwork: A great graphic designer works
well as part of a team and recognizes that all team members must work well
together and communicate openly to get a project completed.
Technology: A great graphic designer is well-versed in
desktop publishing software and is able to quickly learn new programs and
incorporate them into his or her work.
40. Significance of non verbal communication
·
Various non-verbal cues of the speaker like physical
movements, facial expression play an important role in expressing the inner
meaning of the messages in face-to-face conversation.
·
Sometimes the appearance of the listeners and receivers
conveys their attitudes, feelings, and thoughts regarding the messages they
have read or heard.
·
Clothing, hairstyle, neatness, jewelry, and cosmetics of
people convey impressions regarding their occupation, age, nationality, social
or economic level, job status, etc.
·
Non-verbal cues also help to determine the relative
status of persons working in an organization. For example, room size, location,
furnishings, decorations, lightings, etc. indicate the position of a person in
the organization.
·
Non-verbal cues can effectively express many true
messages more accurately than those of any other method of communication. For
example; the use of red, yellow and green lights and the use of various signs
in controlling vehicles on the roads.
·
Non- verbal cues such as hands, fingers and eyeballs are
used by the deaf people for communication purpose.
·
Communication with illiterate people through written
media is impossible. In such situations, non-verbal methods like pictures,
colors, graphs, signs, and symbols are used as the media of communication.
·
Non-verbal cues like sign and symbol communicate messages
very quickly than written or oral media. For example; speed breaker, hospital
and school zone, railway gate are easily conveyed through signs and symbols.
·
Sometimes quantitative information on any issue may
require a lengthy written message. But this quantitative information can be
presented easily and precisely through tables, graphs, charts, etc.
41. Types of non verbal communication
Body Language
It is the movement of body or its parts used to communicate information. A firm handshake, given with a warm, dry hand, is a great way to establish trust. A weak, clammy handshake conveys a lack of trustworthiness.
Facial Expressions
It is communication through face. The human face can produce thousands of different expressions such as happy, sadness, anger, angry, etc. Happiness is associated with an upturned mouth and slightly closed eyes; fear with an open mouth and wide-eyed stare. The effect of facial expressions in conversation is instantaneous.
Posture
The position in which someone holds their body when standing or sitting is posture. The position of our body relative to a chair or another person is another powerful silent messenger that conveys interest, aloofness, professionalism—or lack thereof. Head up, back straight (but not rigid) implies an upright character.
Touch (Haptics)
The meaning of a simple touch differs between individuals, genders, and cultures. It involves handshake, kiss, slap, hug, massage, hit, kick, etc. Each touch communicates a unique message like fear, disgust, love, encouragement, gratitude, sympathy, anger, pain, violence, etc.
Space (Proxemics)
It is
also called as proxemics that deals with the use of space in communication. The
subordinates maintain some distance (space) with his superior is the example
for space in communication.
Gestures
Communication takes
place through the movement of part of the body such as hand, leg, head is
called gestures. Arms crossed over the chest, nail biting, head tilted to one
side, hand placed on the cheek are the examples of gestures. However, the
meaning of some gestures can be very different across cultures. While the OK
sign made with the hand, for example, conveys a positive message in
English-speaking countries, it’s consider offensive in countries such as
Germany, Russia, and Brazil. So, it’s important to be careful of how you use
gestures to avoid misinterpretation.
Eye contact
Since the visual sense is dominant for most people, eye contact is an especially important type of nonverbal communication. The way you look at someone can communicate many things, including interest, affection, hostility, or attraction. Eye contact is also important in maintaining the flow of conversation and for gauging the other person’s interest and response.
Paralinguistics
Paralinguistics refers to vocal communication that is separate from actual language. This includes factors such as tone of voice, loudness, inflection, and pitch. Consider the powerful effect that tone of voice can have on the meaning of a sentence. When said in a strong tone of voice, listeners might interpret approval and enthusiasm.
Appearance
Our choice of color, clothing, hairstyles, and other factors affecting appearance are also considered a means of nonverbal communication. Uniforms, for example, can be used to transmit a tremendous amount of information about a person. A soldier will don fatigues, a police officer will wear a uniform, and a doctor will wear a white lab coat. At a mere glance, these outfits tell people what a person does for a living.
Artifacts
Objects and images are also tools
that can be used to communicate nonverbally. On an online forum, for example,
you might select an avatar to represent your identity online and to communicate
information about who you are and the things you like. People often spend a
great deal of time developing a particular image and surrounding themselves
with objects designed to convey information about the things that are important
to them.
42. Advantages and disadvantages of non verbal communication
Advantages of non-verbal communication:
1. Complementary: Non-verbal cues
complement a verbal message by adding to its meaning.
2. Easy presentation: Information can be easily
presented in non-verbal communication through using visual, audio-visual and
silent means of non-verbal communication.
3. Substituting: Non-verbal messages may
substitute for the verbal message especially if it is blocked by noise,
interruption, long-distance, etc. for example; gestures-finger to lips to
indicate need for quiet, facial expressions- a nod instead of a yes.
4. Repeat: Used to repeat the verbal
message (e.g. point in a direction while stating directions.)
5. Help to illiterate people: This type of
communication use gestures, facial expressions, eye contact, proximity,
touching, etc. and without using any spoken or written word. So, it is very
much helpful for illiterate people.
6. Help to handicapped people: Non-verbal cues of
communication greatly help in handicapped people especially to deaf people.
Deaf people exchange messages through the movements of hands, fingers, eyeballs,
etc.
7. Attractive presentation: Non-verbal communication
is based on visual, picture, graph, sign, etc. that can be seen very much
attractive.
8. Reducing wastage of time: The message of non-verbal
communication reached the receiver very fast. For this reason, it reduces the
wastage of valuable time of the communicator.
9. Quick expression of message: Non-verbal cues of communication like sign and symbol can also communicate some messages very quickly than written or oral messages.
Disadvantages or
limitations of non-verbal communication:
1. Vague and imprecise: Non-verbal communication
is quite vague and imprecise. No dictionary can accurately classify them. Their
meaning varies not only by culture and context but by the degree of intention.
2. Continuous: It is possible to stop
talking in verbal communication, but it is generally not
possible to stop nonverbal cues.
3. Multi-channel: while watching someone’s
eyes, you may miss something significant in a hand gesture. Everything is
happening at once and therefore it may be confusing to try to keep up with
everything.
4. Culture-bound: Gestures seen as positive
in one culture may be seen as obscene in another culture.
5. Long conversations are not
possible:
In non-verbal communication, long conversation and necessary explanations are
not possible.
6. Difficult to understand: Difficult to understand
and requires a lot of repetitions in non-verbal communication.
7. Not everybody prefers: Everybody does not prefer
to communicate through non-verbal communication with others. Sometimes it
cannot create an impression upon people or listeners.
8. Lack of formality: Non-verbal communication
does not follow any rules, formality or structure like other communication.
9. Costly: In some cases, non-verbal
communication involves huge costs. For example, neon signs, power point
presentations, cinema, etc are very much costly compared to other forms of
communication.
10. Distortion of information: Since it uses gestures,
facial expressions, eye contact, touch, sign, sound, paralanguage, etc. for
communicating with others, there is a great possibility in distortion of
information.
43. Methods of visual thinking
Brainstorming
It is
the most popular form of visual thinking, and what springs to mind when someone
mentions thinking visually. Brainstorming is a way in which we can separate
ideas into themes and see connections. Whilst also coming up with
new ideas as our eyes are able to scan the idea as a whole.
Presentation Slides
Slides allow us to ensure that our audience understands us coherently, and keeps everyone on the same page better than speech alone. The focus here is not on the presenter, but on how the audience take in a presentation.
Prezi
Prezi
actually packs a different kind of visual compared to other presentations.
Prezi is great when you’re trying to tell an audience about an interesting
process..
Whiteboard
Use a whiteboard to
keep the minutes of a meeting. This will allow your team to keep everyone on
the same track.
Interactive
Interactive
activities allow technology to take a large part in the idea flow
between person and program. For example, by presenting hard situations
to solve between teams.
Post-its
Sticky notes can also function as
a great way for us to organize our thoughts, plan our roadmaps, and see
connections between ideas we haven’t seen before. Sticky notes can be used by
us alone to plan ideas, or can serve as a great team working tool.
Flow charts
Flowcharts
allow us to be clear about processes. They work brilliantly when on boarding a
new team member on a project, as they can be a constant and clear reminder of
the processes which go behind everyday tasks. They can also be used as a good
way to show employees how decisions are made.
Flash Cards
By using flashcards
to come up with ideas in a team, or in company trainings, the physical
movements between sharing the cards and re-organising them can prove useful for
our brains to remember stuff better.
Doodles
Doodle which has
helped us to organize our thoughts in a meaningful way, and a way in which we
can remember the information it contains for much longer. Visual thinking is
all about being able to recall an image of something, or to come up with ideas
because we think about things differently. From habit building, to boosts of
creativity, doodling can really cross the borders between work and play.
Roadmaps
It can
be a
great tool to force you and your team to make difficult decisions. Whether it’s a team
building exercise in university, a wedding plan, or a weekly team meeting,
using a map of some sort can ensure that you are literally on the right track
with your ideas.
44. Colour wheel
COLOR THEORY
Color can be combined to produce another color. Color depends on the wave length of light. A ray of light consists of a band of color or the spectrum. The normal eye has a sensation of color from red to a long wavelength through orange, yellow, green and blue to violet at the short wavelength end.
When light of one color is added to light of another such as by projection on to a white screen, the combination of color is called additive colors. When one or more color is removed from white light such as happens when light passes through filter or reflected from a colored surface. The color that are not absorbed or the color that are reflected produce what is known as subtractive colors.
Additive theory
The additive primary colors of light are red, green, and blue. These colors cannot be produced by mixture of any other colors. The three projectors are set up so that they will project on the same screen overlapping each other, the fundamental of adding colors can be absorbed.
Place a blue light in one projector and project it on a screen, a second projector place a green light and project it on a screen overlapping part if the blue. It will be noticed that where there colors overlapping on the screen neither blue or green results, but a now color bluish green called cyan is projected.
A red slide placed in the third projector and projects it on a screen so that it overlaps the other two. If red overlaps green, a new color yellow is produced, where the red overlaps blue, purplish red called Magenta is produced. Where all these three colors overlap the result is white.
The spectral primary colors are red, green and blue. The spectral or additive secondary colors are cyan, magenta, and yellow. These three colors which were produced by overlapping pairs of the additive primaries are called also the subtractive primary colors; since they complement the additive primary colors they are called the complementary colors of the additive primary.
Red + Blue = Magenta
Blue + Green = Cyan
Red + Green + Blue = White
Subtractive color theory
This theory is based on manmade pigments and dyes used in printing ink. The subtractive theory deals about color combination in printing on white paper. The image subtracts certain colors and transmits other colors. The primary colors of subtractive theory are cyan, magenta and yellow.
· If cyan is placed between the eye and light it will subtract red. The magenta will subtract green and yellow will subtract blue.
·
If cyan and magenta
filters are super-imposed between the white light the cyan subtract red and
magenta subtract green leading only blue to come through.
· If magenta and yellow filter are used the magenta subtracts green and yellow subtracts blue leaving only red to come through.
· If cyan and yellow filters are super-imposed between the white light the cyan subtracts red, yellow subtracts blue leaving the green to come through.
· If all the three filters are super-imposed and placed between the eye and white light, all lightsare absorbed and the result is black.
· By mixing these primary colors such as cyan, magenta, and yellow secondary colors are obtained.
Cyan + Magenta = Blue
Cyan + Yellow = Green
Yellow + Magenta = Red
Cyan + Yellow + Magenta =
Black
45. Research in design process
· Design research was originally constituted as primarily research into the process of design
· The concept has been expanded to include research embedded within the process of design
· Well-conducted research provides information about current users and competitors.
· It also gives insight into the latest design trends, as well as steady and stable UX patterns which should be adhered to.
· Design research is what makes our approach to understanding users methodical and well-structured.
· It is a necessary part of creating a user-oriented design for a product.
· In practice, the research is carried out by interface designers and starts with the introduction of primary solutions for a given problem.
· These solutions are then coordinated and prototyped.
· After that, they are validated on the target audience, they undergo some changes based on the feedback and, finally, the process is repeated to achieve the most successful result.
46. Facial expression
· It is a form of non verbal communication
· Eyes, mouth, eyebrows, and forehead are involved in facial expression
· Smiling is a positive emotion that tells the receiver happy
· Eyebrows are brought together, forehead is wrinkled indicating worry
· Eye contact is an important sign of confidence and respect
· Opening one’s eyes or mouth widely, indicating excitement and shock
· Blinking eyes could signal that we are joking
· Raising our eyebrows communicate that we are surprised
47. Process and concept of ideation
· Ideation is the creative process of generating, developing, and communicating new ideas
· Where an idea is understood as a basic element of thought that can be either visual, concrete, or abstract.
· Ideation comprises all stages of a thought cycle, from innovation, to development, to actualization.
· Ideation can be conducted by individuals, organizations, or crowds.
· It is an essential part of the design process.
· Problem solution is the most simple method of progress, where someone has found a problem and as a result, solves it.
· Derivative idea involves taking something that already exists and changing it.
· A symbiotic method of idea creation is when multiple ideas are combined, using different elements of each to make a whole.
· A revolutionary idea breaks away from traditional thought and creates a brand new perspective.
· Targeted innovation deals with a direct path of discovery. This is often accompanied by intensive research in order to have a distinct and almost expected resolution.
48. Process of decision making and implementation
Group decision making is a type of participatory process in which multiple individuals acting collectively,
analyze problems or situations, consider and evaluate alternative courses of
action, and select from among the alternatives a solution or solutions.
1. Identify the decision to be
made. It
is important for a group to understand clearly what you are trying to decide so
you have a goal on which to focus your discussions.
2. Analyze the issue under
discussion.
Once you have defined your goal (i.e., the decision to be made or the problem
to be overcome), examine the data and resources that you already have, and
identify what additional information you may need.
3. Establish criteria. Identify the criteria or
conditions that would determine whether a chosen solution is successful.
Ideally, a solution will be feasible, move the group forward, and meet the
needs of every group member. You may want to rank the criteria in order of
importance
4. Brainstorm potential
solutions. Using
the resources and information collected above, brainstorm for potential
solutions to the problem or decision identified in step 1. This involves collecting
as many ideas as possible. At this stage, ideas should not be criticized or
evaluated.
5. Evaluate options and select
the best one. Once
you have a list of potential solutions, you are now ready to evaluate them for
the best alternative according to the criteria identified in step 3. Remember
that you may be able to combine ideas to create a solution.
6. Implement the solution. This involves
identifying the resources necessary to implement the decision, as well as the
potential obstacles, then taking action.
7. Monitor and evaluate the
outcome. Based
on the criteria identified in step 3, evaluate whether the decision was
successful. If not, revisit step 4 to evaluate the other options or generate
new ones.
49. Visual communication
·
Visual Communication is the use of
any image that effectively conveys an idea.
·
It can be a drawing, a poster, a video, an advertisement
or any visual material you may find online and across social media platforms.
·
Visual images include photo posts, viral videos, charts,
infographics and any other piece of communication that utilizes signs and
symbols to deliver a message.
·
The Internet is populated with visual content.
·
From advertisements to personal stories, everything is
narrated with the use of visual media.
·
Visual communication is a key component in visual content marketing.
·
Visual content is a powerful tool that has been
recognized to help increase brand awareness and is effective in driving traffic
to a particular brand or product website.
·
Visual creations top the list of strategies that
companies and marketers are planning to implement.
·
Visual communication is the preferred medium for
information delivery because of its expediency and brevity.
50. Importance of visual communication
It saves time
·
It is easier to process a visual signal quickly than to
read a sentence of a paragraph full of text.
·
An image will pass a lot of information within a short a
time because one image can have a thousand words.
·
It is highly beneficial to utilize visuals to effectively
pass a message within a short time.
It is clear
·
Visual communication improves the clarity of information.
·
Customers fall in love with products and services
depending on how they are advertised by using images and graphics.
·
When using images for business advertisements, use simple
and clear graphics that will pass the same message to the targeted audience to
avoid confusion.
It helps in achieving consistency
·
This is mainly achieved by using same colors of the
original product or company to advertise.
·
The use of logos, images and consistent colors boost the
brand image of the business.
·
It is easy for the people to identify a product with the
company.
Gives better retention of information
·
A person will be able to retain visual information for
long.
·
People easily forget what they hear or read easily but
retain images for long. This is because images are stored in long-term memory
·
It is important to aim at retention of information when
passing marketing products
and services
It is simple
· The illiterate can understand visual communication hence makes it an effective communication method to all.
· Its simplicity makes it easy for people to understand the information.
It is flexible
· Images and graphics are flexible and can be understood by different people.
· Verbal communication will be limited to language, but images are more flexible than words.
It is effective
·
Visual
communication is one of the most effective ways of sending information.
·
Images
and graphics have flooded the advertising field because of the effectiveness of
visual communication.
· The mind remembers images faster than words or texts.
It is popular
·
It
is easy to catch the attention of potential customers by using visuals, images,
GIFs in advertising.
·
Social
media platforms like Facebook encourage ads to have fewer words and more
graphics.