TELEVISION PRODUCTION
PART - A
1. Camcorder (Camera + Recorder)
·
A
portable camera attached with VTR is called camcorder.
·
This
camera records both audio and video while capturing.
2. EFP
·
It
stands for Electronic Field Production.
·
Television
production outside the studio is EFP.
·
Ex
– covering cricket and football match.
3. ENG
·
It
stands for Electronic News Gathering.
·
·
It
can be live news or after editing.
4.
Lighting
·
The
manipulation of light and shadow is lighting.
·
It
is to provide camera with adequate illumination for acceptable picture.
5. Monitor
·
For
video the television is the monitor to check the visual.
·
For
audio speaker is the monitor to check the sound while editing.
6. Aspect ratio
·
The
width to height proportions of the television screen is called aspect ratio.
·
For
analog television the aspect ratio is 4:3 and HDTV is 16:9.
7. Compression
·
It
is reducing the memory size of file to be stored.
·
While
compressing, if the video file lost the quality, it is lossy compression or
else lossless compression.
8. CCU ( Camera Control Unit)
·
It
is an equipment that contains various video controls including color balance,
brightness, contrast, etc.
·
It
enables the video operator to adjust the camera picture during show.
9. CCD (Charge Coupled Device)
·
It
is called as imaging device present in camera.
·
The
CCD contains horizontal and vertical row of pixels to produce quality image.
10. White balance
·
The
adjustment of color circuit in the camera to produce white color in lighting of
various color temperatures.
·
To
while balance the camera, we need to focus the lens on white material.
11. Focal length
·
·
Short
focal length lens produce wide angle of view.
12. Depth of field
·
The
distance between nearest and farthest object from the camera appear in focus.
·
It
depends on the focal length, f-stop, distance between object and camera.
13. Color temperature
·
Relative
reddishness or bluishness of white light is color temperature.
·
It
is measured in Kelvin (K).
14. Flood light
·
Lighting
instrument that produces large amount of diffused light is called flood light.
·
It
is often used to illuminate outdoor playing field during night match.
15. Soft light
·
Flood
light that produce diffused light is soft light.
·
It
tends to wrap around object.
16. Spot light
·
The
lighting instrument that produces directional, undiffused light is called spot
light.
·
It
is to highlight an important object in a frame.
17. Chromakey (Blue or Green matte)
·
Effect
that uses blue or green color for the background which is replaced by the
background image during keying.
·
It
is used in news reading, weather forecasting programmes.
18. Dynamic microphone
·
A
microphone whose sound pick up device consist of a diaphragm that is attached
to a movable coil.
·
As
the diaphragm vibrates the coil moves within a magnetic field generating
electric current.
19. Ribbon microphone
·
A
microphone whose sound pick up device consist of a ribbon that vibrates with
sound pressure with a magnetic field.
·
Ribbon microphones are the most natural mics that are used to capture the sound of an
instrument, a voice, and even the ambience of a room.
20. Condenser microphone
·
It uses a capacitor to convert acoustical
energy into electrical energy.
·
Condenser microphones are most commonly found in studios.
·
They capture a larger frequency range and the
ability to reproduce the "speed" of an instrument or voice.
21. Lavaliere or lapel or collar microphone
·
A
small microphone that can be clipped onto clothing.
·
It
is used in interview, news reading.
22. Shotgun microphone
·
It
pick up sound from a great distance.
·
It
is used in the sports events such as basketball, tennis, to pick up sound of
audience and players.
23. Surround sound (DTS – Digital Theatre System)
·
Sound
that produces a sound field in front of, to the side of, and behind the
listener by positioning the speaker.
·
Surround sound is a technique for enriching the depth of sound
reproduction by using multiple audio
channels from speakers that surround the listener (surround
channels).
·
Its first application was in movie
theaters.
24. Plot
·
Plot
refers to be sequence of events inside a story.
·
Its
structure varies from one story to another.
·
Plot
has sub-plot also.
25. Character
·
Character
is a person in a novel, play, television serial or film.
·
The
character may be fictional or based on a real life of a person.
26. Voice over
·
The
voice over is read from script and may be spoken by someone.
·
It
is usually pre-recorded and placed over the top of video.
·
Generally
it is used in programmes like documentary
27. Dubbing
·
It
is a post production process done in television production.
·
The
character voices are recorded and positioned over video.
·
Synchronization
of dialogue with lip movement of the character is very important while dubbing
28. Short film
·
A
short film is any motion picture which contains short story.
·
It
has a running time of 40 minutes or less including all credit.
29. Floor management
·
Arranging
and managing properties in the shooting place is called floor management.
·
It
is done by floor manager in production.
30. Set
·
The
environment is created for the purpose of shooting.
·
It
is generally used in dance and fighting sequence.
·
Art
director designs set for shooting
31. Props (properties)
·
It
is known as properties, used on stage by actors during performance.
·
This
is considered to be anything movable or portable on stage.
32. Video format
·
A
file that stores information about digital video is called video format.
·
It
is a combination of both audio and video datas.
·
Ex
– AVI, FLV, MPEG.
33. CG (Character Generator)
·
It
is a device or software that produces static or animated text over video.
·
It
is computer based and can generate graphics as well as text.
34. Presentation
·
It refers to the way in which television stations present
themselves between programs.
·
They often consist of an animated form of the
station's logo, and many have a continuity announcer who speaks over the clip
with information about programs on the station.
35. Script
·
It
is a written format of play or movie.
·
It
is done in pre-production stage which makes the production easy.
36. Acoustics
·
The
quality of room that determine how sound is transmitted in it.
·
It
prevents outside sound enter into audio studio.
·
Audio
recording room needs this treatment for proper recording of audio
37. Cyclorama
·
It
is a large curtain or wall positioned at the back of stage.
·
It
is used to establish the environment of landscape, forest, sky, house.
38. Vision mixer
·
It
is also called as video switcher.
·
It
is used to select a video source among many.
·
Vision
mixer is used in multi camera production
39. Auto iris
·
It
is an adjustable opening which controls the amount of light coming through
lens.
·
Auto
iris allows the lens to maintain one light level for outdoor views.
40. Production manager
·
He
is a key person in production department who reports directly to producer.
·
41. Advertisement
·
It
is a non-personal presentation of idea, goods, and service by an identified
sponsor through mass media.
·
It
can be print, radio, television, outdoor advertisement.
42. Timecode
·
It
is a signal recorded on video that identifies every frame.
·
Hours,
minutes, seconds and frame details of the video are recorded.
43. Title
·
It
is the text information of television programme, name of cast and crew members.
·
It
may consist of live action, animation, music, graphics.
44. Filter
·
It
is fixed in front of the lens to create effects.
·
It
reduces glare, improve saturation and protect the lens.
45. Special effects (SFX)
·
It
is a visual tricks used in television programmes to simulate the imagined
events in a story.
·
Scaling,
rotating, stretching, chromakeying are the example for special effects.
46. Narrative
·
Narrative
either true or fictitious is designed to create interest to the hearer or
reader.
·
A
report of an item of news in a newspaper, magazine, or television and radio is
an example of narrative.
47. Screenplay
·
It
is a written work by screen writers for television programme.
·
The
movement, actions, expressions and dialogue are also narrated in screenplay.
48. Shooting script
·
It
is used during the production of television programme.
·
It
specifies how script should be implemented and circulated.
49. Synopsis
·
It
is a brief retelling of the story designed to generate interest.
·
It
is a scene by scene breakdown, which contains the information of movement,
action, expression, dialogue.
50. EOS (Electro Optical System)
·
Canon
EOS is an auto focus, single lens reflex camera.
·
All
EOS film cameras use 35mm film.
51. Timeline
·
In
non-linear edit system, the editing is done in timeline window.
·
It
consists of video tracks, audio tracks and frame head.
52. Virtual set
·
It
is a digital design used as the background of scene.
·
It
can be created through a variety of software.
Ex – virtual studio.
53. Continuity editing
·
It
is the process in video creation of combining related shots.
·
While
shooting the story, costume, sound continuity are to be maintained.
54. Safe area
·
The
areas of television picture that can be seen on television screens.
·
It
ensures that the most important parts of the picture are seen by many viewers.
55. Visualization
·
It
is a process of converting text or idea into image diagram, animation or video.
·
It
is an effective way to communicate the message.
56. Ad-lib
·
Speak
or perform without any preparation is called Ad-lib.
·
57. Mono sound
·
It
is single channel of sound perceived as coming from one position.
·
In
mono, only one loudspeaker is necessary.
·
Even
if we are using many speakers we perceive sound as coming from one position.
58. Stereo sound
·
It
is achieved by using two or more loud speakers.
·
It
is to create the impression of sound heard from various directions.
·
The
surround sound (DTS) used in theatres is stereo sound.
59. Teleprompter
·
It
is a device used in television news reading.
·
The
news reader reads the text which is scrolling from bottom to top.
60. POV
·
A point of view shot that shows what a character is looking
at.
·
It is usually established by being positioned between a shot
of a character looking at something, and a shot showing the character's
reaction.
61. Linear editing
·
Linear video editing is
a video editing post-production process of selecting, arranging
and modifying images and sound in a predetermined, ordered sequence.
·
The principle of linear editing is copying and pasting. The
content is copied from the source tape and pasted onto record VTR
62. Non linear editing
·
Non-linear editing is a form of offline editing for audio,
video, and image editing.
·
In non-linear editing, edits are specified and modified by
specialized software.
·
Final Cut Pro (FCP), Adobe Premiere Pro, Avid are some of the
software’s used for non linear editing
63. Genre
·
A genre is
a broadly defined classification of content.
·
64. Production
·
The production
process refers to the stages (phases) required to complete a media
product, from the idea to the final master copy.
·
The process can
apply to any type of media production including
film, video, television and
audio recording.
65. Diffusion filter
·
"Diffusion filter"
may also refer to a photographic filter used
for a special effect.
·
When used in front of the camera lens, a diffusion filter softens subjects and
generates a dreamy haze.
66. Audio sweetening
·
Audio sweetening refers
to the enhancement of audio using
a variety of tools and methods including tone control, dynamics control,
time-based effects, laugh tracks and other audience reaction sounds, the
addition of instruments, sound effects,
and more.
·
Used alone or in combination, these adjustments make sounds
bigger, fuller and give them a professional polish.
67. Lower third
·
A lower third is
a combination of text and graphical elements placed in the lower area of the television
screen to give the audience more information.
·
It doesn't necessarily have to occupy the “lower third” of the screen, but that's
where it gets it's name.
68. Safe title area
·
The area where titles (text) is legible on all television
screens
·
The safe area represents approximately 80 percent of the
screen, measured outwards from the center.
69. Steady cam
·
The camera is fitted on the mechanism and attached with cameraman’s
body
·
A Steadicam combines
the stability of a tripod with the fluidity of a dolly and the flexibility of a
hand-held camera.
·
70. Assemble editing
·
Assemble editing is
often a quick and easy way of creating a rough cut of a video presentation for
preview purposes.
·
'Assemble Edit also
refers to any video material added to the end of a tape.
71. Storyboard
·
A sequence of drawings, typically with some directions and
dialogue, representing the shots planned for a film or television production.
·
It's made up of a number of squares with illustrations or
pictures representing each shot, with notes about what's going on in the scene
and what's being said in the script during that shot.
72. EDL
·
An edit decision
list or EDL is used in the post-production process of film editing and video editing.
·
The list contains
an ordered list of
reel and timecode data representing where each video clip can be obtained in
order to conform the final cut.
73. Time line
·
The timeline panel is where the video
editing is done
·
Video clips are
imported into project panel and
placed in the timeline panel in the sequential order for editing
·
During editing many
layers can be created for titles, superimposed images, etc.
74. Softy
·
Soft light sources are used in production to create a broad, even area of light.
·
In the field, videographers often rely on
umbrella reflectors to create a soft
lighting effect.
·
This is simply a light bounced off the inside of a silver or white,
umbrella-like reflector.
75. Digibeta
·
·
In colloquial use, "Betacam" is often used to refer
to a Betacam camcorder, a Betacam tape, a Betacam video recorder or the format
itself.
76. Script
·
A screenplay,
or script, is a written
work by screenwriters for film, television program, or video game.
·
These screenplays can be original works or
adaptations from existing pieces of writing.
·
In them, the movement, actions, expression and
dialogues of the characters are also narrated
77. OB van
·
Outside broadcasting is the term used for video production done outside the studio.
·
It can be useful in shooting unique
locations and are capable of capturing live events
·
“Outside Broadcasting” entails the use of a
mobile vehicle, equipped with the full capabilities of a production control
room, including technical personnel, and driven to a venue such as a
professional soccer stadium, convention centre or live event
78. VHS
·
VHS (short for Video
Home System) is a standard for consumer-level analog video
recording on tape cassettes.
·
VHS was a popular format for early consumer video cameras.
79. Two column script
·
Television script has two columns in which the
left-hand column includes all the visual aspects of the production, including
the content of each shot.
·
The visual column also includes descriptions
of any special effects.
·
The right-hand column contains the audio
portions of the production, including dialogue, sound effects and music.
80. Teaser
·
A teaser is
a way of advertising a film or
television program before a month of release.
·
PART - B & C
1. Television genres (Different
programmes on TV)
· Serial (soap operas) – It is drama which reflects our life. It is broadcasted for 3 to 5 years and some more than 5 years. Through advertisements, the soap operas get sponsorship.
· Cartoon – It is a kid’s entertainment programme. It contains comedy thriller, action, etc. It contains different characters such as dora, Jackie chan, etc.
· Entertainment progrmmes – Old and recent movies are broadcasted. Some channels broadcast only songs and comedy.
· Sports –Live and recorded programmes are shown in television. Some channels broadcast only sports. Ex - Ten sports, Star sports. This covers local, regional, national and international sports events.
· Devotional – Most of the channels broadcast devotional songs in the morning and evening. Example – Sathyam TV, Sankara TV, Om TV, etc.
·
· Interview – It is conducted to know the unknown information about a person. Television channels generally conducts interview with film stars & doctors.
·
Game show – It is a fun programme.
Celebrities and public participate in the game shows. Different levels are
there in game show.
·
News – It give various information’s
happening around the world. Some channels broadcast news for 24 hours. News can
be live or recorded.
·
Cookery show – It shows how to cook various
food items. Chefs and experts are explaining how to prepare food. We can get
tips about healthy food.
2. Parts and Function of a video camera
Parts of a video camera
Lens
· It draws in light and captures the image at which the camera points.
· This telescopic piece can have multiple lenses within it.
· A number of dials on the tube will shift the lens positions by turning them, and this controls how the lenses focus the light they receive to clarify the picture.
·
The viewfinder is directly connected to the lens and is
meant to provide access to the image for the user.
·
This can be a simple eye-sized window, or it may be a
small pixel screen that folds into the camera
· Viewfinders also double as a video screens for playing back the recorded image.
Microphone
·
The lens picks up only the visual images for the camera
·
It includes microphones that record sound in the area.
· The microphone is usually mounted next to the lens and pointing in the same direction so the audio and video are closely in sync.
Recorder
·
The recorder processes the images received by the lens
and the sound from the microphone and records them to memory.
·
On older analog cameras, this would record the image onto
a magnetic tape within a cassette.
· Digital cameras record the image as a computer video file.
Controls
·
The camera's main controls include the Power switch and
the Record button.
·
It will also include playback buttons such as Play, Stop,
Rewind, Fast Forward and Pause.
· The controls also include output ports to connect the camera for playback.
Battery
·
Battery power is essential for camera use.
·
Every camera is equipped with a rechargeable battery.
·
Batteries are designed to work specifically with its
camera model only.
Functions of a video camera
·
The light reflected from the object is
gathered by the lens
·
The light is focus on beam splitter.
·
Beam splitter splits the white light of the
image into red, green and blue pictures.
·
These beams are directed toward their
respective CCDs
·
The light is amplified, processed and
re-converted by view finder into video pictures
3. Charge coupled device (CCD)
·
It is also called as imaging device
·
It is a sensor for recording images in
digital cameras
·
This imaging device consist of a small solid
state device
·
Charge coupled device (CCD)
is an integrated circuit etched onto a silicon surface forming light sensitive
elements called pixels
·
The CCD contains thousands of pixels that are
arranged in vertical and horizontal rows
·
More pixels in CCD produce high quality video
image
·
Each pixel (picture
element) in the image is converted into an electical charge the intensity of
which is related to a color in the color spectrum.
·
4. Different types of video camera
Analogue and
digital camera
·
In the analogue camera, the video signal
remains analog.
·
But in digital camera the RGB video signals
are digitized.
·
Both in analogue and digital cameras the
light is analogue till it reaches the CCD.
·
After leaving from CCD the light source will
become digitized.
Studio camera
·
It is described as high quality cameras.
·
It is so heavy than other cameras.
·
It is fixed in stand called pedestal.
·
It is used for various productions such as
news, interview, and debate.
·
This is also used in outdoor shooting such as
sports, live concert, etc.
·
It does not have recording device.
ENG / EFP
·
These are light weight and portable.
·
It produces high quality picture.
·
VTR (video tape recorder) is used to record
the information.
·
This camera records both audio and video so
it is called camcorder.
Consumer camcorder
(handy cam)
·
It is small in size and easy to operate.
·
It has recording device. This has special
features such as auto focus, auto iris.
·
View finder is used to capture the image
properly.
·
The video and audio qualities are somewhat
good.
5. Camera mounting equipment's
Handheld and
shoulder mounted camera
· It is not an instrument.
· Light weight cameras are held by the camera man on his hand or shoulder.
· The camera man can lift and lower the camera, tilt up or down, walk or run with it.
Monopod
· It is a single pole (stand) onto which we can mount a camera.
· It is to avoid holding the weight of camera by the cameraman.
· It can be set easily and quickly.
Tripod
· It has 3 legs that can be individually adjustable.
· It is used to fix the camera even on irregular surfaces.
· The bottom of the legs is attached with the rubber gums that keep the tripod from slipping.
Studio pedestal
· It is to withhold the heavy weight studio camera.
· It is used to move the camera in all directions.
· It also moves the camera up and down.
Steadicam
· It is fixed with camera man body itself.
· They can run with the camera to captures the running or chasing sequence.
· It is to capture the video without shaking.
Jimmy jib
· It is a triangular crane system which uses an arm supporting a camera at one end and a counterweight at the other.
· The crane can swing from the ground to the cranes maximum reach of 40ft and can swing 360 degrees.
6. Camera movement
The way a camera moves can give meaning to what's happening on screen.
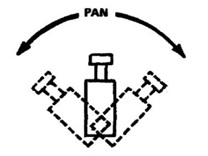
1. Pan
· Turning the camera lens horizontally from left to right or right to left.
· Moving the camera from left to right is called pan right.
·
Moving the camera from right to left is
called pan left.
·
It is used to follow the objects.
2. Tilt
·
Moving the camera lens up or down is called
tilt.
·
Tilt up means that the camera is made to
point up and tilt down means made to point down.
·
Tilt down is used to show the character weak
and tilt up is to show the character strong.
3. Zoom
·
Here the camera is static, only the lens
moves.
·
Zoom in means showing the object in big size,
zoom out means showing it in small size.
· Zoom in used to show emotions of the character
· A zoom shot gives the viewer feeling that the subject or object is coming toward or away to the viewer.
4. Dolly
·
Moving the camera toward or away from the
subject is dolly.
· Move the camera closer to the object is dolly in and away from object is dolly out.
· A dolly shot gives the viewer feeling that they are moving toward or away from the subject.
5. Trucking
·
Moving the camera laterally.
·
The camera moves left to right (or right to left)
·
It maintains the same distance from the subject.
·
We would need to have the camera in the street, moving
parallel with our subject.
6. Pedestal
·
Moving the camera up or down, while keeping
the lens at a constant angle.
· Pedestal up means raise the camera, pedestal down means lowering the cameras.
· The whole time keeping the camera’s lens at a 90° angle to the ground.
7.
Jimmy jib
· It is a triangular crane system which uses an arm supporting a camera at one end and a counterweight at the other.
· The crane can swing from the ground to the cranes maximum reach of 40ft and can swing 360 degrees.
7. Television standard or video standard
NTSC
· National Television System Committee
· It is mostly used in North America and Japan.
· Its aspect ratio is 4:3.
· It scans 525 lines.
· Its frame rate is 29.97 frames per second.
· NTSC follows the interlaced scanning system.
PAL
· Phase Alternating Line used in India.
· It has 625 lines so the image quality is good.
· Its aspect ratio is 4:3.
· It plays at 25 frames per second.
SECAM
· Sequential Color and Memory used in France, Africa.
· It produces 625 lines.
· It is 4:3 aspect ratio.
· It plays at 25 frames per second.
· This gives better resolution.
8. Importance of storyboarding
· Storyboard pictorially represent the shot in a sequential order.
· It is a hand drawn version of movie or advertisement.
· It helps the entire team assess the visual flow of video.
· This helps in understanding the directors vision.
· Helps crew members like the lighting director, camera person, VFX director to understand the scope of work.
· This gives information about camera shot, angle and movement.
· It gives information about dialogue.
9. Importance of script
· Script is the written document of the story
· A script serves as a planning device for the production.
· It tells the complete story, contains all action in the film and all dialogue for each character.
· It involves visualization.
· It helps in smooth flowing of production
· It guides the production people their duties and responsibilities
· This avoids confusion during production.
· Script writer use their own way to write script.
· Structured script, unstructured script, show script and run down script are the types of script
10. Role of floor manager
· He is also called the floor director or stage manager.
· He co-ordinates all the activities on the floor
·
· He arranges place for rehearsal
·
He co-ordinates with the director and art
director for their needs.
·
He arranges food and refreshment for artist
and production people
·
He re-arranges the material after shoot
11. Associate or Assistant director (AD)
· The AD assists the director during production
· AD sit in front of preview monitor to check the performance of artist
· AD checks the mistake and continuity of production
· He is involved in rehearsal
· He is responsible for timing of show
· He notes down all production activities
12. Production Assistant (PA)
· Duplicating and distributing the script to the team
· He arranges properties on the floor
· He arranges cab to pick up and drop the artist
· He supplies food and refreshment
· He takes notes from producer and director and work according to that
· He is also assigned to take notes of production
13. Types of script format
Fully scripted format
· A script that contains complete dialogue and visual information.
· The artist can deliver the words which are in script and not on his own.
· Dramatic show, comedy skit, soap operas, news are some of the example of fully scripted format.
· The overall content, pace, balance and timing can be figured out before the production starts.
Semi
scripted format
· It contains partial dialogue and video information.
· It is used to describe a show for which the dialogue is indicated, but not completely written.
· Eg – In the live music programme the opening and ending dialogue are only scripted. Conversation with the audience is not scripted
Show format
· It lists only the order of particular show segment such as interview, advertisement, etc.
· It is frequently used in studio production.
Run
down script
· An item-by-item sequence of events that will happen within a show is rundown.
· The detailed outline shows what each department should be doing at what time.
· A rundown defines what will be happening onstage, offstage and in other various parts of a live event venue that pertain to a show.
Example : News rundown for 30 minutes
The news rundown will
start at 09:00
Introduction music :
10 seconds
Headlines : 20
seconds
Elaborate news : 10
minutes
Commercial break : 3
minutes
Elaborate news : 10
minutes
Commercial break : 3
minutes
Other news items and recap
news : 3 minutes 30 seconds
14. Types of budget – The estimated cost of the production is
called budget
Above the line and below the line budget
· Above the line budget include expenses for above the line personnel such as writers, directors, art director, actor and actress usually called creative personnel’s.
· Below the line budget includes production crew, equipment, and studio space expenses. It is not related to creative work.
Production
budget
· Preparing the budget based on pre-production, production and post-production.
· Pre-production budget includes the cost estimation of script writing, storyboarding, location searching, casting, audition, etc.
· Production budget includes the cost of hiring the camera and other equipments, transportation, staying, food and refreshment arrangement, properties, etc.
· Post production budget includes cost for audio and video editing, VFX, tiling, adding graphics to the visuals, etc.
15. Stages or Process of television production
Pre-production
·
Pre-production is the first stage of
television production.
·
Scripts are written, story lines are
crafted and a storyboard is developed.
·
Pro
·
Actors will rehearse and the director
will plan his approach.
·
This is more or less a planning
stage, making sure that all the elements are in place for production and
post-production.
· Producers will coordinate different elements of both production and post-production to ensure the most efficient workflow.
Production
·
Production is the actual taping
(shooting) of the TV show or shoot.
·
Cast and crew are assembled, and the
director will coordinate the work to finish shoot as quickly as possible.
·
Production may take place in a studio
or on location.
·
Location shooting is almost always
more work, as production equipment needs to be brought to the location along
with the cast and crew.
· Most TV shows prefer to use established sets since this makes the production process easier.
Post-Production
·
Post-production can occur after
production or simultaneously during production
·
Post-production involves video
editing, titling, sound editing and mixing, dubbing, visual effects and
processing.
·
As soon as raw footage is taken, the
post-production team can begin to process and edit it.
·
Depending on the nature of the show,
post production can be tedious (boring). There may be hours of footage to go
through.
·
If any visual effects or
computer-generated graphics (CGI) are needed, they can slow the process down
significantly.
16. Frame, Shot, Scene and Sequence
Frame
· The smallest unit of visual film structure is a frame.
· A frame is one of the many still images which compose the complete moving picture.
· If you looked at reel of film, you would see that it was a series of images. Each image is a frame of film.
Shot
· The shot is defined as the action captured between camera on and off
· It is made up of frames
· In filmmaking and video production, a shot is a series of frames that runs for an uninterrupted period of time.
· For instance, in a shot kitten playing with a toy mouse. Then you might see a shot of its brother kitten watching from behind a chair. Then a shot of the brother kitten as he pounces on the toy mouse from behind the chair. Then a shot of the first kitten hissing in anger as his brother carries the toy mouse off in his mouth.
Scene
· Scene is defined as the collection of shots
· A scene is defined as action that takes place in the same location or the same time.
· There are exceptions to this, such as if a character has a flashback, or flashforward, or the scene intercuts or crosscuts between two locations with action happening at the same time.
· For example, parts of an action film at the same location, that play at different times can also consist of several scenes. Likewise, there can be parallel action scenes at different locations usually in separate scenes
Sequence
·
· It forms a distinct narrative unit, which is usually connected either by a unity of location or a unity of time.
· For example, the leader of the gang collects together the conspirators, a robbery sequence, an escape sequence, and so on. The sequence is one of a hierarchy of structural units used to describe the structure of films.
17. Types of camera shots
Shot in filmmaking is a series of frames that runs for an uninterrupted period of time.
Extreme Long Shot
·
The extreme wide shot or extreme long shot is
all about showing the world in which the story takes place.
·
In an extreme wide we
will see large landscapes in the frame.
·
Whether it is the desert or outer
space, the audience should get a feel for the time and the place they are about
to spend the next two hours.
·
Though characters can be introduced
in an extreme
wide, they would be very tiny in context to the backdrop
·
An extreme wide shot is often
an establishing
shot.
Long
Shot
·
A wide shot, often referred to as
a long shot
·
The characters can be seen from head
to toe
· This shot is used to show how the character
is small in relation to the vast surroundings.
·
When the term long shot is
emphasized, it can mean that the camera is farther away from the subject,
making them even smaller.
·
A wide shot can also be
a master
shot, which is used to introduce a new location like a dining room
or restaurant.
·
It gives the audience a sense of
geography so when the camera goes in tighter, they can understand who is where.
Medium
Shot
·
The medium shot shows the
character from the waist up.
·
Medium shots are often used in dialog
scenes.
·
It is also known as a cowboy shot.
·
This shot is about revealing
information.
·
You can see more detail than you can
in a wide
shot.
Close-Up Shot
·
A close-up frames the
character’s face.
·
It gives more detail that tells us
how a character feels.
·
A close-up highlights
emotional clues in the eyes.
·
It is more intimate so the audience
can feel what the character is feeling.
Medium
Close-Up Shot
·
Halfway between the close-up and
the medium
shot is the medium close-up
·
It frames the subject from the
shoulders up.
·
This shot might be used to show more
body language, some emotion and facial expressions.
·
Medium close-up can reveal more
information, but it is not as intimate as a close-up.
Extreme
Close-Up Shot
· An extreme close-up frames
even tighter on a face (or subject), highlighting facial features more.
·
It usually frames a particular part
of the face like the eyes or the mouth.
·
It is even more intimate than
the close-up
·
It is used to show more intense
emotion.
Two Shot
Over-the-Shoulder Shot
18. Camera angles and its types
In addition to subject size within a frame, shot types can also indicate where a camera is placed in relation to the subject. Here are some commonly used terms:
Eye Level Angle
High Angle
Low Angle
· The camera lens is facing up (from below the eye level) to capture the video
· This can have the effect of making the subject look powerful, heroic, or dangerous.
· Taking a photograph from a low angle, also know as a ‘worm’s-eye view’, makes subjects appear larger than normal.
Dutch Angle
· It is often used to show a disoriented or uneasy psychological state.
· That is the subject is not entirely right.
· Dutch angles can be artfully utilized to tell us that something is wrong.
· Maybe the subject is in danger, or their state of mind isn’t properly grounded.
Bird eye angle
· The Bird's Eye photos are angled at 40 degrees rather than being straight down.
· Satellite imaging programs and photos have been described as offering a viewer the opportunity to "fly over" and observe the world from this specific angle.
19. Three point lighting
· This is the main light.
· It is usually the strongest and has the most influence on the look of the scene.
· It is placed to one side of the camera/subject so that this side is well lit and the other side has some shadow.
Fill Light
· This is the secondary light and is placed on the opposite side of the key light.
· It is used to fill the shadows created by the key.
· The fill will usually be softer and less bright than the key.
Back Light
· The back light is placed behind the subject.
· Rather than providing direct lighting, its purpose is to provide highlights around the subject's outlines.
· This helps separate the subject from the background and provide a three-dimensional look.
20. Types of lenses
Normal lens
· The dolly speed and the speed of objects moving toward or away from camera also appear normal.
· It has shallow depth of field.
· Focal length of standard lens is 35 mm – 85mm
Wide angle lens
· It has wide field of view used to cover wider area within short distance.
· It makes object relatively close to the camera look large.
· This lens can be moved to left or right to capture video.
· This lens has a greater depth of field.
· Focal length of wide angle lens is 14mm – 35 mm
Telephoto lens
· It covers long distance object.
· It compresses space between the object.
· Gives the illusion of reduced speed of an object moving toward or away from camera.
· It produces shallow depth of field.
· Focal length of telephoto lens is 85mm – 135 mm
Zoom lens
· It is used to make the object bigger or smaller.
· When we zooming in the object comes closer to the viewer and zoom out the object goes away from the viewer.
21. Framing or composition of shot
Screen size – Since the TV screen is small in size, we should take close up or mid shot than long shot.
Field
of view – It refers to how wide or close the object appears relative to the camera
that is how close it will appear to the viewer. It allows for coverage of an
area rather than a single focused point
Aspect
ratio – It is width and height of screen. The aspect ratio of standard TV is
4:3 and for HDTV is 16:9.
Nose
room –The space left in front of a person looking toward the edge of screen is
called nose room. The space in front of person or objet gives the feeling of moving
toward the edge of screen.
Closure
– Mentally filling in spaces often incomplete picture. Our mind fills in
information that we cannot actually see on the screen.
Depth –
It is the creation of third dimension (Z axis). Wide angle lens produce greater
depth of field.
Screen
motion – If two characters are moving in a shot, show only one character which
creates more impact.
22. Roles and responsibilities of a television director
· Director is a person who is responsible for a programme.
· He is like captain of ship
· He selects artists and control them
· He also selects technical person such as camera man, music director, etc.
· He prepares idea or concept for programme.
· He prepares budget for the programme.
· He sits with editor, music director for post production work
· They co-ordinate with the whole team
· Some directors do other functions such as music, editing, etc.
· Director is involved from pre-production to till broadcasting.
23. Importance of dialogue
· Dialogue is oral speech between fictional characters.
· The characters on the screen speak from a script; to inform the audience.
· Dialogue create a realistic flavor, to represent the everyday exchanges people have.
· It helps to identify fictional location and characters.
· Dialogue is to communicate "why?" and "how?" and "what next?" to the viewer.
· Dialogue helps audiences understand the characters' personalities and motivations.
· Their main function is to frighten the viewer, to increase the scene's tension. It is working straight on the viewer's emotions.
· It moves the story forward.
· It makes the audience understand the story.
24. Importance of make-up
· Make up is done with the help of cosmetics
· It is done by make up artist
·
· It plays major role in drama, television, fashion, etc.
· This helps to communicate the personality of character to viewers
· It create various appearance for character such as black eye, uncombed hair, etc
25. Importance of costume
· The clothing information of character is called costume.
· It gives overall appearance of character
· It refers to the style of dress for rich and poor people.
· Costume designer designs costume for character
· Historical, fantasy, dance, are some of the types of costume
· It differentiate one character from another
26. Types or categories or forms of sound
Dialogue
· It is the spoken word of character.
· It is used to convey information’s and move the story forward.
· It also used to convey emotions.
· It is to identify the character.
Music
· It is recorded with the help of musical instruments.
· It is used as background music to convey feelings.
· It is used to compose songs.
· Pitch, tone, tempo are the important elements of music.
Sound effects
· These are added sounds that complement the action of film.
· It carriers symbolic meaning - knocking on door.
· It adds reality to the scene.
27. Types of microphones
Lavaliere microphone – It is called collar mic since it is fixed in collar. It is used in the programme such as interview, news reading.
Hand mic – It is handheld by the performer particularly singing, announcing. It is also used in news gathering
Boom mic – It is used to pick up sound from some distance. It is used in drama to pick up voice of the artist.
Headset mic – It is a simple mic fixed with earphone. It is used in production to communicate information without disturbing shooting.
Wireless mic – It works with the help of transmitter. The performer moves wherever in the hall while using mic.
Desk mic – Mic is fixed on small stand and placed on the desk. It is used in debate, press conference.
Stand mic – The mic is fixed on stand. It is widely used in rock music performance and in political meetings.
Hanging mic – The mic is hanging on the ceiling. It is used in song recording
Hidden mic – It is small size mic which is placed in unseen area. It is used to pick up the sound secretly.
Long distance mic – It is used to pick up sound from long distance. It is used in sports coverage.
28. Microphones based on pick up pattern
Unidirectional mic
· It picks up sound from a single side of mic.· I will not pick up ambient sound.
· If a speaker use unidirectional mic, it records the speaker voice only.
Bidirectional mic
· It pick up sound from the front and back of mic.
· It is used during conversation (interview) to record both the voices.
· It will not pick up sound from side.
Omnidirectional mic
· It picks up sound from all sides of mic.
· If the speaker speaks from the front, back, left or right side of mic, it pick up sound.
· It can be used during group discussion.
29. Functions or importance of editing
Combine
· It is joining various shots into proper sequence.
· During TV serial shooting, various shots are shooting in different places.
· Finally all the shots are combined together in sequences.
Shorten
· Cutting the available material to make the final video tape fit in a given time slot.
·
3 hours of cricket match will be shorten to 2
minutes to show it in news
Correction
· Mistakes are corrected during editing.
· It means deleting unacceptable shot, doing color correction, etc.
Build
· It is the final output of programme.
· Editing, special effects give final shape to programme.
30. Switcher
Preview bus
· Row of buttons used to select the upcoming video.
· It is used to see the preview of each camera.
· Preview bus does not display on the TV or to a recording device.
Program bus
· The row of buttons (C1, C2, C3, …) used to select a video source to display on TV.
· It is also called as direct bus.
· We can change the video source with the help of program bus button.
Mix bus
· Row of buttons used to mix two video sources.
· Fader bar is used to mix the video sources.
· We can apply dissolve and fade effects.
Effects bus
· It is used to apply effects visuals.
· Different wipe effects are applied to visuals.
· Title, image manipulation can be done with the help of effects bus.
31. Continuity editing
Subject identification
· The shot must be gradually changed to avoid confusion.
· If we show extreme long shot the next shot should be long shot, then mid shot, and close up shot.
· Don’t show close up shot immediately after extreme long shot.
Mental map
· It defines on screen and off screen space.
· Our mind automatically fill up the character which is out of screen.
· In an interview, if we show interviewer is on screen, our mind visualize that interviewee is out of the screen.
Vectors
· Graphic vector – The eye angle towards taller building
· Index vector – It shows the direction
· Motion vector – It shows the movement of object in a particular direction
Movement
· It is like following 180 degree rule.
·
Color
· The dress and background color from one shot to another shot must be same.
· If color continuity missing the audience get confusion
Sound
· The music must be appropriately cut to avoid confusion.
· If sound continuity is not good, it disturbs the mood of the scene.
32. Linear editing
· It is tape based editing. The principle is copy and paste
· Source VTR can be single or many
· The video from source VTR connected with switcher for editing and recorded in record VTR
· The audio from source VTR edited in audio mixer and recorded in record VTR.
· Effects device is used to give visual effects to visual
· CD player is used to add extra sounds to visual
· Play, stop, pause, cutting, pasting are done with the help of edit controller
· For example, let’s say an editor has three source tapes; A, B, and C and he decided that he would use tape C first, B second and A third. He would then start by cutting up tape C to the beginning of the clip he wants to use, then as he plays tape C, it would also be simultaneously recording the clip onto a master tape. When the desired clip from tape C is done, the recording is stopped. Then the whole process is repeated with tapes B and A
33. Non-linear editing – It is a system based editing. The
shots are randomly picked up and rearranged. It has 4 steps
Capture – Transferring video sources from tape or memory
card to computer is called capture. Both analogue and digital information’s are
captured into computer. The video file is stored in hard disk.
Compression – Reducing the memory size of video file is
called compression. When we compress some video file format, the quality will
not be lost is called lossless compression technique. When we compress some
video file format and lose some quality of video is called lossy compression
technique.
Storage – Storing video files into computer hard disk.
The file name is properly given and stored in an appropriate location. Proper
storage method helps the video editor to perform his work easily and
effectively.
Juxtaposing
– It is rearranging audio and video files. Premiere, FCP, AVID are used for
editing video files. We can randomly pick up the shot for editing
34. Differentiate between linear and non-linear editing
Linear editing
· It is tape based editing.
· The principle is copy and paste the visual on to tape.
· We play source tape continuously to select the particular shot. We cannot take randomly.
· Editing takes more time
· It is used in television production
· Less number of effects available
Non-linear editing
· Computer is used for editing
· The principle is rearranging video and audio files
· We can select the shots randomly
· Compare to linear it takes less time to complete editing
· Used in television and film production
· More number of effects are available in the software
Cut
· It is the basic type of transition.
· A cut happens when one shot instantly replaces the other.
· It is used to increase the tempo of movie
Fade in and fade out
· When the black screen is gradually replaced by picture, it is called fade in.
· It is used at the beginning of movie.
· When the picture is gradually replaced by black screen is called fade out.
· It indicates that the movie is end.
Dissolve
· It is known as overlapping.
· It happens when one shot is gradually replaced by next.
· One shot disappears as the following shot appears.
Wipe
· It happens when one shot pushes the other shot out of screen.
· Different types of wipes are top, bottom, left, right, etc.
· It is used to give surprise ending of a program
36. Visual effects or visual effects
· The integration of live action footage and CG elements to create realistic imagery is called VFX.
· VFX is to create environments, inanimate objects, animals or creatures which look realistic, but would be dangerous, expensive, impractical, time-consuming or impossible to capture on film.
Some of the VFX techniques are
Computer-Generated Imagery
·
Computer-Generated Imagery (CGI) is the most widely used
technique organized to generate computer graphic images
·
It can be used in print media, films, art, videos,
television programs, and more.
Bullet Time
·
Bullet Time is a visual effect technique that detaches
the space and time of a camera from the visible subject.
·
·
It is technically known as time-slicing, virtual
cinematography, and view morphing.
Virtual
Cinematography
·
Virtual Cinematography includes a variety of subjects
(like real objects), multi-camera setups, etc. to create 3D-objects.
Digital Compositing
·
Digital Compositing involves assembling of multiple
images to create a final image, screen display, or movie.
·
This process is run using digital image manipulation.
Matte Painting
·
Matte Painting is a process to represent a landscape or
distant location.
·
It creates the illusion of an environment that cannot be
seen in the actual filming location.
·
Matte Painting involves manpower and physical effort by
painters and technicians.
Motion Control Photography
·
Motion Control Photography is a VFX technique in motion
photography that enables control and optional repetition of camera movements.
·
This involves filming various elements using the same
camera motion and finally, combining these components into a single image.
Stop Motion Animation
·
Stop Motion Animation is a special effect where still
objects appear to move on their own.
·
This technique can include an object, models, humans,
household appliances, etc.
·
The best example is the traditional flip book that
involves sequential drawings on separate pages.
Prosthetic Makeup
·
Prosthetic Makeup is the VFX technique where cosmetic
effects are applied to characters.
Chroma Key
·
Chroma Key is also known as blue or green screen effects,
where two different videos are combined.
·
This can be mostly seen in movies and in television
programmes such as whether forecasting, news reading, presenting a program, etc
37. Ambient sound
· The sound which is coming from surrounding environment is called ambient sound
· It is also called as background sound
· Ambient sound include wind, water, birds, crowds, market etc
· It provides audio continuity between shots
· It prevents an unnatural silence
· It establishes the mood of the scene
· It establishes the environment
38. BGM – Back Ground Music
· Music that is played at a low volume at the background of dialogue is called BGM
· It is used to support dialogue
· It is used to communicate the feelings of comedy, horror, thrilling, etc.
· It is used as audio continuity between shots.
· BGM creates interest in watching movie along with dialogue
· It establishes the situation of the story
· It also used to introduce and establish the character
39. Chromakey or blue and green matte
40. Need of light or importance of lighting
· To show the object clearly on the screen, light is important.
· It can determine the mood of the scene
· Light determines the quality of the video
· It communicates the story to audience
· Pinpointing light directly on specific objects or people helps persuade the viewers to direct their eyes to the intended spot
· It also add color and texture to a scene
· Proper use of light can change the way of people and objects appear in the scene
· Key light is used to illuminate the objects. It is the main source of light
· Fill light is placed at the opposite side of key light which controls the shadow produced by key light
· Back light is placed between the main object and background.
41. Music director
·
The Music Director coordinates and schedules all
performances for their musical group.
·
They coordinate with the musicians and schedule performances.
·
Music Directors select and plan the specific music that
the group or show will perform.
·
Music Directors work with their musical groups to improve
their skills and prepare for performances.
·
Music Directors conduct live and recorded performances.
·
Well organized and a strong leader, a successful Music
Director is creative.
·
The music director holding auditions, drawing up
rehearsal schedules, selecting music, and updating knowledge in the music
industry
·
He prepares budgets and ensuring staff work within
budgetary constraints
42. Television director
· A television director is in charge of the activities involved in making a television program
· They are generally responsible for creative style of a program, and ensuring the producer's vision is delivered.
· Their duties may include originating program ideas, finding contributors, writing scripts, planning 'shoots', ensuring safety, leading the crew on location, directing presenters, and working with an editor to assemble the final product.
· The work of a television director can vary widely depending on the nature of the program, whether the program content is factual or drama, and whether it is live or recorded.
· In television, Directors work across all genres, including news, sport, documentaries, current affairs, light entertainment, children's programs, situation comedies, soaps or serial dramas, or one-off dramas.
· These programs may be either transmitted live, recorded as live, or prerecorded in any multi camera environment in studios or during outside broadcasts (OBs), or shot on single or multi camera film or tape shoots and edited in post production.
· Directors are responsible for the look and sound of a production and its technical standards
· They collaborate closely with all heads of department, including designers, camera, sound, lighting and choreographers.
· Directors work closely with producers and/or writers, embellishing, refining and ultimately realizing original ideas into finished programs.
· They make careful preparations in order to ensure the success of each shoot.
43. Camera man
As a television cameraman, he/she will need to:
- Assemble, prepare and set up
equipment prior to filming, which may include tripods, monitors, lighting,
cables and headphones
- Offer advice on how best to shoot a
scene and explain the visual impact created by particular shots
- When filming an expensive drama
scene, such as an explosion, shots need to be carefully planned beforehand
- Study scripts
- Find solutions to technical or
other practical problems
- Be prepared to innovate and
experiment with ideas
- Work quickly, especially as timing
is such an important factor
- Take sole responsibility in
situations where only one camera operator is involved in the filming
- Keep up to date with filming
methods and equipment
- Drive crew, actors and equipment to
and from locations.
44. Production personnel’s
Assistant
director Question number
11
Production
manager Question number 55
Floor
manager Question
number 10
Art
director Question
number 46
Camera
man Question
number 43
Music
director Question
number 41
45. Types of telecasting
Terrestrial television
·
It does not involve satellite transmission or cables
·
It uses antennas to receive signals.
·
It requires a Tuner (television) the view content.
Satellite television
·
It is television programming delivered by the means
of communications satellite and received by an outdoor antenna, referred to as
a satellite dish
·
A satellite receiver either in the form of an external
set-top box or a satellite tuner module built into a TV set.
·
Satellite TV tuners are also available as a card or a USB
stick to be attached to a personal computer.
·
Satellite television provides a wide range of
channels and services, that are not serviced by terrestrial or cable providers.
Cable television
·
It is a system of providing television programs to
consumers via cables
·
FM radio programming, high-speed Internet, telephony, and
similar non-television services may also be provided.
DTH Television
· Direct broadcast satellite, (DBS) also known as "Direct-To-Home" refer to the communications satellites themselves that deliver DBS service.
· DBS systems are commonly referred to as "mini-dish" systems.
· DBS uses the upper portion of the Ku band, as well as portions of the Ka band.
WEB TV
· Web TV, TVIP, or TV on the Internet is the transmission of a programming grid through the Internet.
· It can be known "normal" TV channels or channels specifically designed for the Internet.
·
Web
TV is the provision of video and audio over the Internet; and the way to assist
the transmission varies from the monitor of a computer through the use of an
iPod or a mobile phone to the TV set if one have the decoder.
46. Duties of art direction in television production
· Art Directors act as project manager.
· They facilitate the production designer's creative vision for all the locations and sets
· Art Directors are responsible for the art department budget and schedule of work
· Art Directors are responsible for the assistant art director, the draughtsman, the art department assistant(s) and all construction personnel.
· Many Art Directors work on television dramas and commercials, as well as on films.
· Some Art Directors work on a freelance basis.
· Art Directors analyze the script to identify all props or special items that may require longer times.
· Art Directors must also tightly control the budget.
· During pre-production, they are also responsible for commissioning all special effects (such as explosions or car crash sequences), hiring all vehicles (from cars to horse drawn carriages) and organizing the casting of all animals (chosen by the director).
· As the shooting date approaches, Art Directors coordinate closely with the location manager to negotiate when locations can be prepared and dressed.
· During filming, Art Directors continue to oversee the construction, dressing and striking (dismantling) of the remaining sets.
·
After
shooting is completed, Art Directors must ensure that all sets are struck and
locations cleared, and that all outstanding art department bills are paid.
47. Script writing
CREATE A LOGLINE &
DEVELOP YOUR CHARACTERS
·
A great way to start the process is by coming up with a
logline (one line story)
·
One or two sentences that will summarize the story in an interesting
manner.
·
Then develop the story characters.
·
Write their back stories. Refine their personalities.
·
WRITE AN OUTLINE
·
An outline
is a brief synopsis of the entire story.
·
Try to fit it on one to two pages, and be concise.
·
It breaks down the movement of the story, plot point by
plot point.
·
It follows classical format of three act structure: the
first act should introduce your characters and setting and feature an inciting
incident that gets the story underway. The second act is where your characters
encounter obstacles as the story escalates into a crisis. The third act is
where the crisis becomes climax (think victory or defeat), after which the
story slows down and resolves itself.
WRITE A TREATMENT
·
Treatments are effectively a more in-depth version of
outline.
·
Explain upon it and write the whole story scene by scene.
·
Make note of what you want your characters to say.
·
Develop your settings. Have fun with descriptions.
·
The treatment is where you really start building the
world that your story takes place in.
·
A typical feature treatment will clock in at around
thirty pages.
WRITE YOUR SCRIPT
·
Write the script in present tense.
·
Brevity (briefness) is your friend.
·
Remember to show, not tell: you’re writing for the eyes
and the ears.
WRITE YOUR SCRIPT AGAIN (and again, and again)
· Completing the first draft is just the beginning.
· If you think your first draft is perfect, it’s not (sorry).
· Go back, read it through, take stuff out, and add stuff in.
· Get other people to read it and commit yourself to being open to constructive criticism.
48. Story
·
A story can be defined as an account of imaginary or real
events.
·
A story consists of a plot, characters,
chapters, etc.
·
·
This clearly suggests that a story refers to two
different things. In a story, the reader is left along with his imagination on
many points so that he can explore the universe on his own. While you will get
even minute details in a script and no room for imagination is left while
writing this.
·
A story gives the reader a clear account of characters
through even some subplots.
·
Chapters in a story also suggest the same and through
each chapter, the writer slowly builds up his story.
·
A story also carries characters. A story is a journey
where new information about the characters is revealed to the reader and it
develops the story more interesting.
·
It leaves the reader to use his own interpretation to
embrace the story in a more dynamic form.
·
In a script, there are scenes. A script is a written text generally created
for a film, play, TV serial, etc.
·
It provides an elaborated explanation of the incidents
and characters.
·
A script also gives an opportunity to the actor to
comprehend the nature of the character, personality, likes and dislikes.
·
Scriptwriters write their script in the present tense as
well as in the dialogue form.
·
A script comprises multiple scenes and the climate is
nicely mentioned in each scene. For instance, what the actor is going to
perform. What are his/her dialogues and what are his movements?
49. Screenplay
· A screenplay is a written work by screenwriters for a film, television program, or video game.
· In screenplay, the movement, actions, expression and dialogues of the characters are narrated.
· A screenplay written for television is also known as a teleplay.
· One page of screenplay writing equates to roughly one minute of screen time
· The major components are action and dialogue.
· The action is written in the present tense - for example descriptions of settings, character movements, or sound effects.
· Unique to the screenplay is the use of slug lines. A slug line, also called a master scene heading contains the information of : whether the scene is set inside (interior/INT.) or outside (exterior/EXT.), the specific location, and the time of day.
50. Types of television lighting
Key Light
· This is the main light.
· It is usually the strongest and has the most influence on the look of the scene.
· It is placed to one side of the camera/subject so that this side is well lit and the other side has some shadow.
Fill Light
· This is the secondary light and is placed on the opposite side of the key light.
· It is used to fill the shadows created by the key.
· The fill will usually be softer and less bright than the key.
Back Light
· The back light is placed behind the subject.
· Rather than providing direct lighting, its purpose is to provide highlights around the subject's outlines.
· This helps separate the subject from the background and provide a three-dimensional look.
Background light
· A background light is used to illuminate the background area of a set.
· The background light will also provide separation between the subject and the background.
· Background light is placed directly behind the subject and pointed at the background.
Cameo lighting
·
Cameo lighting in film is
a spotlight that highlights a single person and maybe a few props in
a scene.
·
Here light relief figure is set against a darker
background.
·
It is often achieved by using barn-doored
spotlights.
·
It helps focus on the subject and not its environment.
Chiaroscuro lighting
· Chiaroscuro is an Italian term which means light and dark.
· Chiaroscuro technique employed in the visual arts to represent light and shadow as they define three-dimensional objects.
· The lighting adds depth and impact, and the contrast between shadows and highlights creates a mysterious atmosphere.
· Dark colours add richness and drama to a scene.
51. Lighting equipment used in television production
"Quartz" Lamps
·
For many years most of the lights used
in TV production have been tungsten-halogen
lamps (commonly called quartz lamps).
·
Quartz lamps can get very hot, which makes ventilation
important.
·
Special care must be taken when these lamps are changed
(in addition to unplugging the lights and letting them cool down) to make sure
that oil from fingers is not deposited on the outer glass (quartz) envelope of
the lamp.
Fresnels
·
Although Fresnels used to be so bulky and
heavy that they were confined to studios, recent versions are small enough to
be packed away in lighting kits and used on location.
·
It consists of concentric circles that both concentrate
and slightly diffuse the light
· In the studio these lights are typically hung from a grid in the ceiling.
LED Lights
·
They produce more light per watt than incandescent bulbs
·
They can emit light in a range of color temperatures
without the use of color filters.
·
Some LED instruments are designed to focus and
direct light.
·
Being solid state, they are difficult to damage.
Fluorescent and incandescent bulbs are easily broken, if dropped.
Ellipsoidal Spots
· The ellipsoidal spot produces a hard, focused beam of light.
· Some ellipsoidal used to project a wide variety of patterns on a background.
· For example, a colored stained glass pattern behind a person suggests that person is in a church.
Barn doors
·
Adjustable black meal flaps called barn doors can be
attached to some light to mask off unwanted light
·
Barn doors provide a soft cutoff (edge) to the perimeters
of the light
Flags
·
Flags consist of any type of opaque material that can
block and sharply define the edges of the light source.
·
They are often created and shaped, as needed, from double
or triple layers of aluminum foil
·
Flags are either clipped to stands or attached to the
outer edges of barn doors
Filter frames
·
Filter frames are typically a part of the barn door
attachment that slides over the front of lighting instruments.
·
They can hold one or more diffusers to soften the light
·
They hold a colored gel to alter the color of the light
52. Types of linear editing mode
The two types of linear editing: Assemble editing and Insert editing
ASSEMBLE EDITING
·
This type of editing allows assembling the
basic pieces of various video segments.
·
During an assemble edit, all signals (video,
audio, and control track) are recorded.
·
This type of editing is done in chronological
order.
·
When perform assemble edits, the beginning of
the edit is very precise and clean, but the end is very rough and uneven
·
Assemble edits always break existing time
code/control track at the end of an edit
·
Even if the edit master tape has a previous
recording on it, the assemble mode will clear the portion of the tape that is
needed for the new first shot.
·
When you use a tape that has last year's
vacation pictures on it, the assemble
editing every time you shoot a new scene: it will simply erase
what was there before and replace it with the new video and audio.
INSERT EDITING
· The process of using a continuous control track is called insert editing.
· To prepare the edit master tape for insert editing, you need to first record a continuous control track on it.
· The simplest way to do this is to record "black," with the video and audio inputs in the opposition.
· Some editors prefer to record color bars as a continuous color reference.
· The recording of black or color bars happens in real time
53. Lip (video and audio) synchronization
·
The appropriate matching of lip movement in
visual with recorded audio is called lip sync
·
It is coming in dubbing of film
·
The lip sync in animation movie is between
the sound and animated character
·
It is important in television program such as
serial, game show
·
In music video, the movement of artist is
match with audio
·
Dubbing of foreign films needs proper
synchronization
·
- Identify the sound requirements for
a given task or idea and perform the appropriate actions to produce sound.
- To set up and operate the sound
equipment on set.
- Consulting with producers and
directors to determine the sound requirements.
- Selecting, positioning and
adjusting the equipment used for amplification and recording.
- Recording sound onto digital audio
tape or hard disk recorders to make sure the audio is saved and therefore
reducing the chance of it getting lost.
- Synchronization of pre-recorded
audio (Dialogue, sound effects and music) with visual content.
- Re-recording and synchronizing of
audio.
- Mixing and balancing speech, sound
effects and music.
· He is in charge of how the production budget is spent and making sure that everything runs smoothly during filming.
· Meeting the producer and other senior production staff to examine scripts or program ideas
· Drawing up a shooting schedule and estimating cost
· Hiring crews and contractors, and negotiating rates of pay
· Negotiating costs and approving the booking of resources, equipment and suppliers
· Overseeing location bookings and arranging any necessary permissions and risk assessments
· Managing the production schedule and budget
· Managing the production team
· Dealing with any problems
· Making sure that insurance, health and safety rules, copyright laws and union agreements are followed
56. Role of computer graphics (in post production)
· Mechanical effects includes the creation of physical wind, rain, fog, snow, clouds, making a car appear to drive by itself and blowing up a building, etc.
· Optical effects are techniques in which images are created photographically, either "in-camera" using multiple exposure, blue or green mattes, etc.
Digital effects
· It covers the various processes by which imagery is created or manipulated with or from photographic assets.
· Digital Effects often involve the integration of still photography and computer generated imagery(CGI) to create environments which look realistic but would be dangerous, costly, or impossible to capture in camera.
Matte painting
· A matte painting is a painted representation of a landscape, set, or distant location that allows filmmakers to create the illusion of an environment that is not present at the filming location.
· Matte paintings are either filmed on set, where they are framed to look like a physical set piece, or they are combined with live footage in post production
· In the scenes the painting part is static and movements are integrated on it.
Motion capture
· The process of recording the movements of objects and or people.
· It can be used to track the facial movements and expressions of an actor and transfer them to a 3d model.
· The movement of the camera is also recorded, which allows editors to use this data to enhance the environment the motion captured set is imagined in.
Modeling
· 3D modeling is the process of creating a 3D representation of any surface or object
· 3D modeling software produces three-dimensional digital effects.
· It produces a digital object capable of being fully animated, making it an essential process for character animation and special effects
Animation
· Computer animation is the art of creating moving images via the use of computers
· It speeds up the process of creating the many images needed for such a sequence
Compositing
· Compositing is the combining of visual elements from separate sources into single images
· Live-action shooting for compositing is called "chroma key", "blue screen", "green screen".
VFX
· Visual effects are the processes by which imagery is created and/or manipulated outside the context of a live action shot.
· Visual effects make use of graphic design, animation, modeling, etc. using software such as After Effects, Maya, Cinema4D, and NUKE
57. Visual thinking
· Visual thinking is the phenomenon of thinking through visual processing.
· Visual thinking has been described as seeing words as a series of pictures
· Visual thinking is important in any art form. For making film it's a very essential element.
· At the time of reading story, director starts visualizing the script and starts to set the casting accordingly.
· It is also defined as “Communicating visually in forms that can be read or looked upon.
· In cinema a story is most visual when ideas and emotions are expressed through performance and aesthetics as opposed to dialogue.”
· This process is typically utilized for a motion picture, television program, documentary, music video, play, or television advertisement, etc.
· The casting process involves a series of auditions before a casting panel
· Casting panel composed of individuals within a theatrical production such as theatrical producer, and theater director.
· Casting panel can consist of a television producer, or within film production a casting panel could contain a film producer, film director, or choreographer
· In this process performers are presented with prepared audition pieces such as monologues, songs, choreography, scripts and or sides.
· These audition pieces are usually videotaped and then attached with resumes
· The casting panel considers both the individual actor, and the chemistry created with other actors such as boy meets girl, etc.
59.
· The handheld meter is the necessary norm, to know what lights are doing.
· It is used to measure the amount of light required to take photo / video
· It is useful to get correct exposure in taking photo / video
· Some camera has built in light meter
· Incident light meter is used to measure the diffused light
· Reflected light meter is used to measure reflected light
· A light meter can read the ambient light in a scene, or the direct light from a light source and calculate the correct shutter speed and aperture values required to capture an accurate exposure.
· The simplest technique is to hold the light meter out in front of the camera, making sure that the same light falling across the scene also falls on the lumisphere. Then press the meter button. Read the results on the meter and set the camera's shutter and aperture to match
60. Timeline
· It looks, sounds, and feels the way you want it.
There are several components of a video editing timeline
Timeline
·
It’s called a timeline because the various pieces of
video will be lined up horizontally
·
The timeline will have time code markers indicating the
location of each frame.
Tracks
·
Usually stacked vertically, allowing for multiple pieces
of media (both audio and visual) to be added to your video.
·
In most editing programs, visual items on the higher
tracks will appear on top and the audio tracks are at bottom.
Media
·
The media sits on the timeline and can be made up of
video, audio, text, images, etc.
·
Playhead
·
The playhead depicts where in the video you are
previewing.
·
The playhead is to make sure you are editing the correct
part of your video.
Timeline window includes tools for cutting, splitting, zooming in for a close view of your timeline, track locks and more. Usually, a tool tip will appear giving you the name of the tool, so you can easily research what it does and how it works.
Workflow for Editing with a Video Timeline
·
Gather all of the footage that you think you might want
to use in your video.
·
If you have a lot of footage, it is helpful to label
everything.
·
Once you have your footage gathered, add the key footage
to the timeline to start building the order and general flow of the video.
· Once added to the timeline, you should trim each clip, and narrow down the footage to the key pieces.
· Once you have your main footage in place and are giving the message you want, you can start adding secondary footage, including adding b-roll, lower thirds, and other images or text.
· Once you’ve built out your video visually, you can add audio, like music.
·
Re-recording is the process
by which the audio track of a film or video
production is created.
·
As sound elements are mixed and combined
together the process necessitates "re-recording" all of the audio
elements, such as dialogue, music, sound effects
·
This is the final soundtrack that the audience hears when
the finished film is played.
·
Re recording is the recording of dialogues by actors
again in the recording studio.
·
As the original recording contain so much of noise and
disturbance it is of no use.
·
So the artists record their dialogues by following the
original recording inside a recording studio.
·
Then the re-recorded dialogues are made more effective by
adding foley sounds and background music.
·
In monaural sound one
single channel is used.
·
It can be reproduced through several speakers, but all
speakers are still reproducing the same copy of the signal.
·
The sound in each ear is identical (same).
·
It can be recorded with just one mic.
Stereo sound
·
In stereophonic sound more
channels are used.
·
This is used to create directionality, perspective,
space.
·
In a common stereo setup of two channels: left and right,
one channel is sent to the left speaker and the other channel is sent to the
right speaker.
·
To record this stereo sound, two mics(at least) are used.
63. Soft and hard lighting
Hard Light
·
Light that is transmitted directly from a small point source
gives the light a hard, crisp, sharply defined appearance.
·
The
light from a clear, unfrosted light bulb, a focused spotlight, or the noonday
sun in a clear sky, all represent hard light sources.
·
Hard light casts a sharp, clearly defined shadow.
·
When
hard light is used to illuminate a face, imperfections in the skin stand out.
·
Bringing
out the texture in leather, or the engraving on a piece of jewelry, hard
(coherent) light can be an advantage.
·
Several
types of lighting instruments are used in TV to create hard light, including
the beam-spot projector and the ellipsoidal spotlight.
Soft Light
·
Soft (diffused) light tend to hide surface irregularities
and detail.
·
·
At
the same time, diffusers also reduce the intensity of light.
·
Soft light sources are used in production to create a
broad, even area of light.
·
Videographers
use umbrella reflectors to create a soft lighting effect.
·
It
is simply a light bounced off the inside of a silver or white, umbrella-like
reflector.
·
A soft light source placed close to the camera
minimizes surface detail. The effect is commonly referred to as flat
lighting.
· Previsualization is the visualizing of complex scenes in a movie before filming.
· It allows a director, cinematographer or VFX Supervisor to experiment with different staging and art direction options—such as lighting, camera placement and movement, stage direction and editing
· Previsualizations can add music, sound effects and dialogue
· Previsualization is used to describe techniques such as storyboarding, photography, illustrations
· It is also known as previz, previs, pre-rendering, or wireframe windows.
· Previsualization is used to lower budget and time limitations as well as give them greater control over the creative process.
· Previs is the process of creating and planning a final product.
· The previs team works with a director to quickly generate an idea of what cameras, effects, performances, stunts, etc. may be needed for them to film.
· It’s a faster and less expensive, way to remake a movie or sequence, so they have a visual blueprint of the final product.
· It gives the director the ability to make changes before they start to film.
· Now with animation, the process of visualizing a product has moved from storyboards to animatics to previsualization animation.
· Now previs has become mainstream in the film industry.
· It is used to experiment lighting, stage direction, editing and camera movement and placement- without having to incur the cost of actual production.
65. Importance of research in documentary production
·
Documentary filmmaking is a
non-fiction style of filmmaking that seeks to document some aspect of reality.
·
·
Documentary filmmakers often choose
subject matter they are passionate about, and a great documentary can be about
any non-fiction, real-world subject.
·
Documentary
filmmaking requires research to provide the context, footage and other visuals,
narration, and interviews that will appear in the film.
· There are several types of research that documentary filmmakers might undertake, including archival research, academic research, and in-person interviews.
· Documentary filmmaking process requires research into the subject it seeks to document.
· In order to document actual events, histories, people, and cultures, you must find the documents, people, and objects that will tell your story.
· Research is necessary for the raw visual materials that will provide you the context necessary to understand, interpret, and share the subject of your film.
· Research is also important to organize and plan out your documentary.
This
often begins with archival research. Archives have a diverse range of different
research materials, including:
- Still photos, footage, newspapers,
and online articles
- Paintings, etchings, sketches
- Letters, journals, and diaries
- Governmental documents
· It is simple and inexpensive
· For some jobs linear editing is better.
· Learning linear editing skills increases your knowledge base and versatility
· Who learn linear editing first tend to become better all round editors
Disadvantages
· It is not possible to insert or delete scenes from the master tape without re-copying all the subsequent scenes.
· It is not possible to go back to make a change without re-editing everything after the change.
· If you want to replace a current clip with a new one, the two clips must be of the exact same length
· If the new clip is too short, the tail end of the old clip will still appear on the master tape.
· If it is too long then it will roll into the next scene.
67. Advantages and disadvantages of non linear editing
· It allows you access to any frame, scene, or even groups of scenes at any time
· You are able to return to the original take whenever you like
· It offers the flexibility of editing. Easy to change to cuts and undo prevision decisions
· Any number of times the changes can be done
· It is possible to edit both standard definition (SD) and high definition (HD) broadcast quality videos
· Digital video storage and compression is possible
· Loss of video quality is also avoided
· It is easy to learn and do editing
Disadvantages
· It is very costly
· The system set up and software is too costly
68. Aspects ratio and its types
·
Width and height proportion of a television screen
is called aspect ratio.
·
In 4:3 aspect ratio the width of the screen is 4 and
the height is 3.
·
In 16.9 aspect ratio the width of the screen is 16
and height is 9
4:3 standard
·
4:3 (1.3:1) generally read as Four-Three, Four-by-Three for
standard television
·
It has been in use since the invention of moving
picture cameras and many computer monitors used to employ the
same aspect ratio.
·
4:3 was the aspect ratio used for 35 mm
films in the silent era.
·
·
With the adoption of high definition television, the
majority of modern televisions are now produced with 16:9 displays instead.
·
Apple's iPod series of tablets, however,
continue to use 4:3 displays to better suit use as an e-reader.
16:9 standard
·
16:9 (1.7:1) generally named as Sixteen-by-Nine,
Sixteen-Nine is the international standard format of HDTV
·
Many digital video cameras have the capability
to record in 16:9, and 16:9 is the only widescreen aspect ratio natively
supported by the DVD standard.
·
DVD producers can also choose to show even wider ratios
within the 16:9
·
It is now also being used in smartphones, laptops and
many types of media.
69. Montage
· Montage is an editing technique in which a series of short shots are sequenced to condense space, time, and information.
· In French the word "montage" applied to cinema simply denotes editing.
· It is a method by which through two unrelated shots we may create a third and different meaning.
· For example shot A which is a pumpkin, shot B which is a hammer going down. Mixing the two shots together creates the meaning that the pumpkin is destroyed by the hammer
· Montage speed up time whether it a day, a week, a month or a year
· It is used to convey a lot of information at once
· A montage can be a vehicle to reveal the ways a character is changing.
· A montage can renew and strengthen an audience’s interest in a character or a storyline as the film builds to a conclusion.
· A montage that compares and contrasts the daily lives of two characters can establish their statuses, and thus their levels of power, in relation to one another.
· Metric montage, Rhythmic montage, tonal montage, Intellectual montage are some types of montages
70. Types of interview in television
Personal
· This might be a short interview about someone well-known about themselves, or a longer, more curious and intentionally revealing personality profile.
· The interview is intimate (personal) to the viewers.
Emotional
· It is dealing with a subject's inner self, an area into which the media too frequently trespasses uninvited.
Entertainment
· The entertainment factor often plays a part in attracting and keeping an audience.
· The entertainment interview looks at the lighter side of life, the things that make us smile.
Actuality only
· The technique is occasionally used to good effect in documentary.
· The interviewee is asked some questions to answer
· Multiple questions are often required to get a good flow of answers.
Telephone or remote
· Interviews may be carried out the phone or with a subject who is speaking from a remote studio.
· Maintaining proper sound quality is important in this type of interview
Vox
pop
·
Vox pop is
an abbreviation of the Latin vox populi, or 'voice of the people'.
·
The vox is used in broadcasting to
provide a cross-section of public opinion on a given subject.
·
The technique is to get a broad mix of
opinion and different voices.
Grabbed
·
This concerns interviews which people do
not want to give but which reporters are determined to take.
·
Grabbed interviews are obtained by
pushing a camera or microphone under the nose of a subject and firing off
questions.
·
It usually works best on camera, where,
even if the subject says nothing, he can be watched by the audience and his
reactions notes.
Outdoor broadcast
interviews
·
Interview away from the studio in a more natural environment
can be relaxing
·
Multi-guest
interviews
·
It is the kind of interview with multiple interviewees.
·
Film crews are interviewed for the film promotion
71. Online editing
·
It is also called as live editing or instantaneous
editing
·
It is done on the place where the program is happening
·
Online editing is a final cut of the project by editing high
quality footage together.
·
We can add visual effects, lower third titles, and apply
color correction.
·
Online editing focuses on image quality, maintaining
broadcast video specifications, audio levels, and so on.
·
Compared to the offline editing phase, an online edit
session goes very quickly
·
It is generally requires more expensive equipment.
72. Offline editing
·
It is part of the post-production process of filmmaking and television
production
·
Raw footage is copied and edited, without
affecting the camera original film
stock or video tape.
·
Modern offline video
editing is conducted in a non-linear editing (NLE) suite.
·
The digital revolution has made the offline editing workflow process immeasurably quicker
·
Adobe Premiere, Final
Cut Pro, Avid, Sony Vegas,Light works and VideoPad are some of the softwares
used for editing.
·
Typically, all the original footage is digitized into the suite at a low resolution.
·
Timing, storytelling, and fine-tuning your edits should
be complete in the offline editing phase.
·
Offline editing is actually a rough or draft cut of the
project. The main editor and possibly director could get ideas for the final
cut.
·
Another role for an offline editor is to create an edit
decision list (EDL)
·
Offline editors can also make creative descisions; shots,
cuts, dissolves, fades, etc.
73. Video recording formats
Videotape recording process
· For decades it was the dominant recording medium in TV production
· Today it is primarily used for archival storage
· Two inch wide videotape was the first practical video recording medium
· Because it used four video heads to scan a complete video picture on two inch wide tape
Disk based recording
· In 1997 the DVD was introduced
· The initials stand for both digital versatile disk and digital videodisk
· Although DVDs resemble audio CDs they are capable of holding much more information up to 17GB of data
· For a greater storage capacity both sides of the disk can be used
Solid state memory
· Many camcorders – amateur, prosumer, and professional – now record on solid state memory cards, sometimes called flash memory
· The memory can hold up to 90 minutes of video
· This approach provides faster camera-to-computer transfer speeds
· Camera memory cards can be slipped into a computer and quickly accessed by an editing program
· A common transfer approach for cameras with hard disks is with camera-to-computer cable often a FireWire connection
74. Functions of tripod
· A tripod is a portable three-legged frame or stand, used as a platform for supporting the weight and maintaining the stability of camera.
· A tripod provides stability against downward forces and horizontal forces and movements about horizontal axes.
· The positioning of the three legs away from the vertical centre allows the tripod better leverage for resisting lateral forces.
· Tripods are used for both motion and still photography to prevent camera movement and provide stability.
· They are especially necessary when slow-speed exposures are being made, or when telephoto lenses are used.
· They reduce camera shake, and thus are instrumental in achieving maximum sharpness.
· A tripod is also helpful in achieving precise framing of the image.
· Use of a tripod may also allow for a more thoughtful approach to photography.
75. Types of filters
Neutral Density (ND)
· A colour-neutral filter which absorbs light evenly throughout the visible spectrum.
· Used to reduce the amount of light coming through the lens in strong lighting situations
Ultra Violet
· Video cameras are sensitive to both visible light and ultra violet (UV) light.
· UV is invisible to humans but it can create a blue tinge and/or washed-out effect on video, especially outside.
· A UV filter removes UV light while leaving visible light intact (undamaged).
· UV filters are also commonly used as a protective filter for the lens.
Polarizing
· A special type of lens which removes polarized light, reducing the washed-out effect sometimes created by reflected light.
· This results in more saturated, vibrant colours.
· Polarized filters are usually mounted with a rotational adjustment to align the polarization.
Diffusion
· Effectively blurs the image for a slightly soft look.
· A mild diffusion filter can be used to soften faces (remove wrinkles etc), a stronger filter can be used to create a dream-sequence effect.
Sepia
· Creates a sepia-tone effect, commonly used to depict historical images or flashbacks.
· The word “sepia” refers to the name of the rich brown pigment that was widely used by photographers back in the early days of photography.
· Sepia effect gives your images a warm brownish tone.
· Sepia filter improves the general look and feel of your image.
Fog
· Creates a fog effect.
· Fog filters have different density values.
· In general, the higher the value, the thicker the fog.
Color conversion/correction
· Adjusts the colour temperature of the light.
· Appropriate color conversion filters are used to compensate for the effects of lighting
Star effect
· Makes single points of light stretch out in various star patterns.
· This effect is created by numerous fine etches in the filter
· It can be used to give a dramatic, sophisticated or glamorous look to the image.
76. Formats of television program
Format refers to the general shape of the show, rather than the show's genre. For instance, a Sitcom is in a particular genre. It might be any length from a half-hour up to a miniseries. That's the format.
·
The programme may be introduced by a host, then the programme
cuts directly to the people involved.
·
For example, child labourers working in a fireworks’
factory.
Animation
·
Here a series of still drawings or individual shots are
combined to give the illusion of movement.
·
25 separate pictures can make one picture showing full
animation per second.
·
Making animation is time consuming and expensive also as
each frame of the film has to be shot separately.
Demonstration
·
·
These could be studio or on the field demonstrations.
Documentary
·
Documentaries feature any subject of interest or give
detailed information on real situations, people, news.
·
For example, documentary on puppetry, environment,
political situations, regional handicrafts and so on.
·
Television documentary takes the form of a direct
presentation of the substance of a problem or an experience or a situation”.
Graphics
·
Graphics means pictures.
·
The camera moves across the series of painted pictures,
which are created on a particular topic.
·
They are divided in to several sections or ‘episodes’ to
make the message explanatory.
·
These pictures are drawn horizontally with soft edges to
fit the TV screen so that the picture fades out to the edges of the paper,
rather than stopping abruptly.
Drama
·
Dramas have been very effective in involving the viewers
in television programme since they represent the life realistically.
·
A drama is a play which presents a true-to-life story in
a dramatized form with actors playing the parts of the story’s characters.
·
The story develops through what the characters do and
say.
·
Dramas on television have provided a cheaper substitute
for theatre plays which are beyond the reach of the middle class man.
Interview
·
This is face-to-face conversation between a host and the
interviewee or an invitee.
·
It could be an interview of renowned person, or
outstanding personality, literary person, group and so on.
Panel Show
·
·
Mostly this format is used for discussion of current
events or affairs where the audience is interested in learning various opinions
on an issue.
77. Importance of sound
·
Background music, dialogue and special
effects are the forms of sound
·
It communicates information happening in
various situations to the audience.
·
It creates feelings such as sadness,
happiness, anger etc
·
It is used to communicate the mood of scene.
·
Dialogue is used to reveal the character,
communicating information etc
·
Background music is used to communicate the
feelings, create tension and thrilling moment
·
·
It establishes the environment where the
action is taken place. Train sound indicates that the action is taken place in
railway station.
·
Doubtful contents of a movie
can be pushed into the “right” direction by music
·
Music can also work very
well to establish a certain time or period. Music that sounds very baroque will
put us back into the 18th century
·
Anything that gives the
feeling of not being real can be greatly enhanced by the music.
·
Music that sounds like
something that is not expected in a certain scene will create a feeling of
“something is not right”.
·
Music can help the audience
to understand or develop character.
·
Dubbing is the post production process in
filmmaking
·
It is recording and replacing voices on a
motion picture to original shooting
·
It refers to the substitution of voices of
the actors
·
It is practiced in musicals when the actor is
not able to sing
·
It is done in other language films
·
It is to improve audio quality. The audio
recorded in shooting is not having the projection quality.
·
Films, videos and video game are dubbed into
local language of foreign market.
79. Digital video formats
1. MP4
·
MPEG-4 or MP4 is one of the earliest digital video file
formats
·
Most digital platforms and devices support MP4.
·
An MP4 format can store audio files, video files, still
images, and text.
·
MP4 provides high quality video while maintaining
relatively small file sizes.
2. MOV
·
MOV is a popular video file format designed by Apple.
·
It was designed to support the QuickTime player.
·
MOV files contain videos, audio, subtitles, timecodes and
other media types.
·
It is compatible across different versions of
QuickTimePlayer, both for Mac and Windows.
·
Since it is a very high-quality video format, MOV files
take significantly more memory space on a computer.
3. WMV
·
The WMV video format was designed by Microsoft and is
widely used in Windows media players.
·
WMV format provides small file sizes with better
compression than MP4.
·
That is why it’s popular for online video streaming.
·
It is not compatible with Apple devices
4. FLV
·
FLV is a file format used by Adobe Flash Player.
·
It is a video formats supported by all video platforms
and browsers.
·
It is a good choice for online video streaming platforms
like YouTube.
·
They have a relatively small file size which makes them
easy to download.
·
It’s not compatible with many mobile devices like
iPhones.
5. AVI
·
The AVI file format was introduced by Microsoft.
·
The AVI video format uses less compression than other
video formats such as MPEG or MOV.
·
This results in very large file sizes, approximately 2-3
GB per minute of video.
·
This makes the files lossless.
6. AVCHD (Advanced Video Coding High Definition)
·
AVCHD is a format used for HD video playback and digital
recording.
·
This video format was designed by Panasonic and Sony for
professional high definition video recording.
·
Latest version of AVCHD 2.0 supports three dimensional
video.
7. WebM
·
The video codecs of WebM require very little computer
power to compress and unzip the files.
·
The aim of this design is to enable online video
streaming on almost any device, such as tablets, desktop, smartphones or
devices like smart TV.
8. MKV
·
MKV file format incorporates audio, video and subtitles
in a single file.
·
MKV format was developed to be future proof, meaning that
the video files will always stay updated.
·
MKV containers support almost any video and audio format
80. Analogue video formats
· It is the standard that connects most consumer video
equipment, including VCRs, camcorders, security cameras and video CD players.
· As its name suggests, Composite video has the luminance
(black and white), chrominance (colour) and sync pulses combined in one signal.
·
When developed, Composite video was designed to work with
both colour and black-and-white TV signals.
·
Composite video doesn’t project a very sharp picture.
·
It can cause picture defects like dot crawl and colour
smear.
Y/C video (also often called S-Video)
·
It was introduced to overcome some of the
shortfalls associated with Composite video.
·
Colour (C) and luminance (Y) information are
transmitted separately to produce a sharper picture image on the display
device.
·
Most video equipment with an S-Video connector also has a
Composite video connector.
·
It separates the signal to an even greater extent than
S-Video,
·
It produces quality picture.
·
Component video separates colour information into two
colour difference signals: B-Y (Blue minus luminance, also called Cb or Pb) and
R-Y (Red minus luminance, also called Cr or Pr).
·
These along with Y (luminance) result in a total of three
signals.
·
We can find Component video on the latest DVD players and
TV receivers, displaying the very high quality images permitted by DVDs to
their best advantage.
81. Features of digital video camera
·
Inputs for external microphones and outputs
for headphones
·
Large, clear LCD viewfinder that lets you see
what you're doing
·
Charge-coupled device (CCD) or CMOS
sensor—get the biggest image sensors that you can afford
·
Zoom lens
·
Manual white balance, focus, and exposure
controls
·
Option to output video at lower resolution
·
Standard outputs,
including FireWire (i.LINK on Sony), USB, HDMI components
·
Compatibility with standard
accessories, LANC input, tripod screw
·
Internal hard drive space and card slots for
flash memory
·
Rechargeable battery with at least two hours
of shooting time
· Fiction (imaginary story) generally is a narrative form, consisting of people, events, or places that are imagery.
· It is not based strictly on history or fact.
· It is opposite to documentary.
· Novel and short stories are examples of fiction
· Fiction covers storytelling in any format including writings, audio recordings, live theatrical performances, animation movies, etc.
· Characters and events within a fictional work may even be set in their own context entirely separate from the known universe.
Non fiction
·
Nonfiction is
any document or content that represents truth and accuracy
regarding information, events, or people.
·
Nonfiction content may be presented
either objectively or subjectively, and may sometimes take the
form of a story.
·
·
Common literary examples of nonfiction
include opinion pieces; essays on art or
literature; biographies; journalism; and historical, and scientific
writings.
·
Journals, photographs, textbooks, and travel
books are also considered nonfictional.
·
Including information that the author knows to be untrue
within any of these works is usually regarded as dishonest.
·
Some fiction may include nonfictional elements.
83. Tele film
· A television film is a feature-length motion picture that is produced and originally distributed to a television network
· Such a production has also been called a TV movie, TV film, television movie, telefilm, etc
· The term "made-for-TV movie" was coined in the United States as an incentive for movie audiences to stay home and watch
· These features originally filled a 90-minute programming time slot including commercials
· Many early television movies featured major stars, and some were accorded higher budgets than standard television series of the same length.
· In 1996, 264 made-for-TV movies were made by American television networks (CBS, NBC, Fox, ABC, and UPN).
84. Feature film
·
A feature
film is a film with a running time of approximately 2 hours.
·
The notion of how long a feature film should be has
varied according to time and place.
·
According to the Academy of Motion Picture Arts and
Sciences, the American Film Institute and the British Film
Institute, a feature film runs for more than 40 minutes
·
While the Screen Actors Guild asserts that a
feature's running time is 75 minutes or longer.
· Most feature films are between 75 and 210 minutes long.
· The term feature film came into use to refer to the main film presented in a cinema and the one which was promoted or advertised.
· It is longer than the duration of short film
85. Equipment required to set up a television studio
A typical studio floor has the following characteristics and
installations:
·
Decoration and/or sets
·
Professional video camera mounted
on pedestals
·
Microphones and fold back speakers
·
Stage lighting rigs and the
associated control equipment
·
Several video monitors for visual
feedback from the PCR
·
A small public address system for
communication
·
A glass window between the PCR and studio
floor for direct visual contact is often desired, but not always possible
PCR –
Production Control Room
·
Here the composition of the outgoing program takes place.
·
The production control room is also called a studio
control room or a "gallery"
·
The vast majority of devices in a PCR are interfaces for
rack-mounted equipment that is located in the Central Apparatus
Room (CAR)
·
The central apparatus room (CAR) houses
equipment that is too noisy or runs too hot to be located in
the production control room (PCR).
·
It also makes sure that coax cable, SDI
cable, Fibre optic cable or other wire lengths and installation
requirements keep within manageable lengths.
This can include the actual circuitry and connections between:
·
Character generator (CG)
·
Camera control units (CCU)
·
Digital video effects (DVE)
·
Video routers
·
Video servers
·
Vision mixer (video switcher)
·
VTRs
·
Patch panels
·
Master control is the technical hub of a broadcast
operation.
·
Master control activities such as switching from camera
to camera are coordinated.
·
·
If the program is broadcast live, the signal goes from
the PCR to MCR and then out to the transmitter.
A television studio usually has other rooms with no technical
requirements
·
One or
more make-up and changing rooms
·
A reception area for crew, talent, and
visitors, commonly called the green room
·
An audience handling area
· A television production uses
more than one camera for shooting is called multi camera production
·
Several cameras are used on
the set and simultaneously record or broadcast a scene.
·
Multiple shots are obtained in a
single take without having to start and stop the action.
·
Apart from saving editing time, scenes may be shot far
more quickly.
·
It avoids re-lighting and the set-up of alternative
camera angles for the scene to be shot again from the different angle.
·
It also reduces the complexity of tracking continuity
issues.
·
Drawbacks include a less optimized lighting setup which
needs to provide a compromise for all camera angles and less flexibility in
putting the necessary equipment on scene.
·
A multiple-camera setup will require all cameras to be synchronous to
assist with editing and to avoid cameras running at different scan rates
·
The multiple-camera method gives the director less
control over each shot but is faster and less expensive than
a single-camera setup.
·
In television, multiple-camera is commonly used
for light entertainment, sports events, news, soap
operas, talk shows, game shows, and some sitcoms.
·
From the below drawing camera 1covers a close up of one
person, camera 3 frame the close up of other person and camera 2 frame the wide
shot of both the persons. Usually it is used in the television interview.
·
Switcher is the device used in multi camera setup to
connect various camera and mic inputs and to do live editing.
·
Pro Tools is
a digital audio workstation developed and released by Avid
Technology for Microsoft Windows and mac OS
·
Audio editing software is software
which allows editing and generating of audio data.
·
Used for music creation and production, sound for
picture and, more generally, sound recording, editing
and mastering processes.
·
Pro Tools can run as standalone software or
operate using a range of external analog-to-digital converters
·
It is used to provide real-time effects such
as reverb, equalization and compression
·
Pro Tools can perform the functions of a multi track
tape recorder
·
Audio, MIDI and video tracks are graphically
represented in a timeline.
·
Audio effects, virtual instruments microphone
preamps or guitar amplifiers—can be added, adjusted and processed in
real-time in a virtual mixer.
·
Pro Tools supports mixed bit depths (16-bit, 24-bit,
and 32-bit) and audio formats
·
It also imports and exports the lossy formats mp3, aac, m4a and
imports audio from video files (mov).
·
·
It features time code, tempo maps, elastic audio
and automation; supports mixing in surround sound, Dolby
Atmos and VR sound.
88. Explain any one of the video editing software
· Premiere Pro is the successor to Adobe Premiere, and was launched in 2003.
·
Premiere Pro supports high resolution video editing
·
Audio sample-level editing and 5.1 surround sound mixing
are available.
·
It supports 3D editing with the ability to view 3D
material using 2D monitors.
·
Premiere Pro can be used for all common video editing
tasks necessary for producing broadcast-quality, high-definition video.
·
It can be used to import video, audio and graphics which
can be exported to the medium and format necessary for distribution.
·
When creating videos using Premiere Pro, various video
and still images can be edited together.
· Titles can be added to videos, and filters can be applied along with other effects.
· Premiere Pro is the industry-leading video editing software for film, TV and the web.
· Edit footage in any format, from 8K to virtual reality.
·
Premiere Pro works seamlessly with other apps and
services, including Photoshop, After Effects, Adobe Audition and Adobe Stock.
·
Available on iOS, Mac, Android and Windows.
89. Live Vs Recorded television program
Live program
·
Live television is
a television production broadcast in real-time, as events happen, in
the present.
·
It may refer to streaming television over the
internet.
·
Shows broadcast live include newscasts, morning
shows, awards shows, sports programs, reality programs and, occasionally,
episodes of scripted television series.
·
To prevent unforeseen issues, live television programs
may be delayed, which allows censors to edit the program.
·
It is a live moment and there are no second takes.
·
Mistakes cannot be hidden in live program
·
On a live broadcast you will have multiple cameras setup
to capture from different angles.
·
The program is shot, edit in the edit room (offline
editing) and then broadcast in television
·
With a pre-recorded program you have the opportunity to
do multiple takes.
·
On movies, for example, scenes are shot multiple times
and cameras are moved to capture the scene from different perspectives.
·
Mistakes can be rectified by retaking the same shot
·
Evan after shoot the mistakes can be rectified such as
color correction, continuity, lightings, etc using computer software.
·
Appropriate sound, sound levels and mixing can be done
effectively in recorded program
·
Sufficient time is available to present quality program