MEDIA CULTURE AND SOCIETY
PART - A
1. Media
·
The term media, refers to the communication channels through which we
disseminate news, music, movies, education, promotional messages and other
data.
·
It includes physical and online newspapers and
magazines, television, radio, billboards, telephone, the Internet, fax and
billboards.
2. Culture
·
It
is an idea and social behavior of a particular people or society
·
Culture
is dynamic (changing) and transmitted from one generation to another
3. Society
·
Society is defined as a group of people living as a community
or an organized group of people for a common purpose.
·
Society is important,
because society is
culture; it is civilization; it is what sets us apart from animals.
·
Society is what defines the way we live every day.
4. Mass media
·
Mass media means technology that is intended to reach a mass audience.
·
It is the primary means of communication used to reach the
vast majority of the general public.
·
The most common platforms for mass media are newspapers,
magazines, radio, television, and the Internet.
·
It
is an approach to understand why and how people actively seek out specific m
·
It
focuses on what do people do with media? Rather than what does media do to
people?
·
It
was founded by Sigmund Freud
·
People
could be cured by making conscious their unconscious thoughts and motivation
·
The study of signs and symbols and their use or
interpretation.
·
Semiotics is the study of signs and their meaning in society. A
sign is anything that can convey meaning.
· Modes of dress and style, the type of bag you have, or even where you live can also be considered signs, in that they convey meaning.
8. Social construction of reality
·
People
and groups interacting in a social system create mental representation of each
other’s action.
·
In
the process, meaning is created in society
9. Audience as readers
·
It is actual people who read your text,
paragraph by paragraph, sentence by sentence, word by word.
·
An audience is
the group of people who will be attracted to your writing.
· Writers need to learn to anticipate the needs of their readers as well as the interests of their audiences.
10. Popular culture
·
Popular culture is generally
recognized by members of a society as a set of the practices, beliefs, and
objects
·
Culture based on the tastes
of ordinary people rather than an educated elite.
·
The most common pop-culture categories are: entertainment (such as film, music,
television and video games), sports, news, politics, fashion, technology, and
slang.
11. Sub culture
·
A
culture within a large culture is called sub-culture
·
A
sub-cul
·
Ex
– Fandom - Fans of movies, a celebrity, or any
shared interest
12. Active audience
·
Media
audiences do not just receive information passively but are actively involved
·
Media
announces voting is our right. People who watched and go for voting during
election are called active audience.
13. Passive audience
·
Media
audiences just receive the message, but don’t react to it.
·
Media
announces voting is our rights. People who watched and do not go for voting are
called passive audience.
14. Brand personality
·
Brand personality is a set of human characteristics that are attributed
to a brand name.
·
A brand
personality is something to which the consumer can relate; an
effective brand increases
its brand equity
(impartiality) by having a consistent set of traits (characteristics)
·
Hero
worship is a very great admiration of someone and a belief that they are special or perfect.
·
It is excessive admiration for someone regarded as a hero.
·
16. Power of mass media
·
Media influence has become so powerful today that they can
easily influence people positively and/or negatively.
· They determine the fate of politicians and political causes, they influence governments and their electorates
17. Indexical
·
Relating to or denoting a
word or expression whose meaning is dependent on the context in which it is
used.
·
Signs where
the signifier is caused by the signified
· Smoke, for example, is an indexical sign of fire; a pointing finger is an indexical sign of whatever it is pointing at; 90 degrees on a thermometer is an indexical sign that it is hot out.
18. Inter textuality
·
It
is the shaping of a text meaning by another text
·
Intertextual figures include: reference, quotation, plagiarism
(copying), translation, and imitation.
·
Deconstruction is an
approach to understanding the relationship between text and meaning
· Deconstruction is defined as a way of analyzing literature that assumes that text cannot have a fixed meaning. An example of deconstruction is reading a novel twice, 20 years apart, and seeing how it has a different meaning each time
20. Contiguity
·
Contiguity is the principle that ideas, memories, and experiences
are linked when one is frequently experienced with the other.
·
For example, if you constantly see a knife and a fork together they
become linked
·
If
a viewer of television news decode the message in which it has been encoded
·
·
The expression of one's meaning by using
language that normally signifies the opposite, typically for humorous effect.
·
When a customer says "Good job," to a
waiter who has dropped his tray.
·
The outcome can be tragic or humorous, but it
is always unexpected.
·
An isomorphism is
a similarity of the processes or structure of one organization to those of
another.
·
It is an idea of contemporary national
societies that is constructed and propagated through global cultural
·
The
content of any medium is always another medium
·
Internet
news, cinema are the content of print
medium
·
Communication
takes place through computer networks is called cyberspace.
· It is the uses of internet, networking and digital communication
26. Bourgeoisie
·
It
means the economic ruling class who controls the working class
·
In
such society the ownership allows them to employ and exploit the way earning
working class
27. Id
·
The id is the most basic part of the personality.
·
It also represents our most animalistic urges
(support), like the desire for food and sex.
·
The id seeks instant gratification for our wants and needs.
·
If these needs or wants are not met, a person
can become tense, anxious, or angry
28. Ego
·
Ego is your conscious mind, the part of your identity that
you consider your "self."
·
·
Your ego is what prevents you from hearing critical but necessary
feedback from others.
29. Super ego
·
Superego is the component of personality that we have acquired from our parents and
society.
·
The superego works to suppress the urges (support) of the id and
tries to make the ego behave morally, rather than realistically
30. Light viewer
·
Lighter
television viewers watch television less than 2 hours a day
·
They
could be younger, employed and more likely to have children at home
31. Medium viewer
·
Medium
viewers watch television 2-4 hours a day
·
They
are likely college students and have a high income
32. Heavy viewer
·
Heavy viewers watch television more than four
hours a day
·
They rely on television more to cultivate their
perceptions of the real world.
33. Denotation
·
It
is the direct meaning of text, drawing, symbol, etc
·
Rose
– It is a flower
· Heart – Parts of body
34. Connotation
·
It
is the indirect meaning of text, drawing, symbol, etc
·
Rose
– Symbol of love
·
Heart
– Symbol of love
·
Hypodermic needle
theory suggests that media messages are injected
directly into the brains of passive audiences.
·
If
any information gets introduced or is deliberately introduced through network
of communication channels over a period of time, the information will reach to
all parts of society
36. Sub genre
·
A
sub division of a genre of film, music, art, television, etc.
·
Horror
films can be taken as horror or comedy is the example of sub genre
37. Media convergence
·
Media convergence brings technologies such as a computing, and
communication, together, which is very important in businesses today
·
Media convergence is the technological merging of different media channels – for example, magazines, radio programs, TV
shows, and movies, now are available on the Internet through laptops, iPads,
and smartphones
38. Traditional media
·
Any
form of mass communication available
before the advent of digital media is called traditional media
·
This
includes television, radio, book, newspaper, etc.
39. Symbol
·
Symbols take the form of words, sounds,
gestures, ideas, or visual images and are used to convey other ideas and
beliefs.
·
For
example, a red octagon may be a symbol
for "STOP". On a map, a blue line might represent a
river.
40. Saussure
·
He
was a Swiss linguistic and semiotician
·
His
ideas laid a foundation for many developments in both linguistics and semiology
41. Noise
·
Anything
which disturbs the communication is called noise
·
Sound,
signal problem in radio, television, improper printing in newspaper or magazine
are called channel noise.
42. Audience positioning
·
Audience positioning refers to the techniques used by the creator of a text
to try to get the audience to
understand the ideology of the text.
·
For example, a car maker may position itself as a luxury status symbol. Whereas a battery
maker may position its
batteries as the most reliable and long-lasting
·
Cultural studies is that investigates the
ways in which culture create and transforms individual experiences, everyday
life, social relations and power.
·
It helps us to understand ourselves
and those around us
·
It
is the process of dividing people into sub-groups based upon defined criterion
such as product usage, age, sex, income group, etc
·
It
is used in the field of advertising to attract the audience
·
Converting
our idea or thoughts into symbol, such as text, audio, video, etc.
·
In
a communication process the sender encodes the message.
·
Ex
– A person encodes his friend’s birthday wishes in the form of text, visual
(greeting card), voice message, etc.
·
Converting
symbols such as text, audio, video, etc. into meaningful message is called
decoding.
·
In
a communication process the receiver decodes information
·
Ex
– A person understand his birthday wishes message from the received text,
visuals, voice message, etc.
·
A
text is any media product whether it is a television program, a book, poster,
song, films, etc.
·
It
discusses about how one text is differs from other types of text
·
Consciousness
shared by individuals within a society is called social consciousness
·
The “we feeling” or the “sense of us” may be
experienced in members of various cultures and social groups
·
Semiology is a research method involving the analysis of language
and signs.
·
Semiology operates on the belief that no sign has a definite
meaning, and that different signs can be assigned to different meanings as
needed
·
A stereotype is
a fixed, over generalized belief about a particular group or class of people.
· For example, a “hells angel” biker dresses in leather.
51. Perceived realism
·
Audience
are thought to perceive media content as realistic
·
It
is informed by attributes of the content, style, genre, etc
·
An opinion
leader is a well-known individual or organization that has the
ability to influence public opinion on
the subject matter for which the
· Opinion leaders can be politicians, business leaders, community leaders, journalists, educators, celebrities, and sports stars
53. Icons
·
These are the literal signs and codes: a cop (police
officer) means a cop.
·
They are meant to appear like the thing itself.
·
When we see a cop, we also associate this with our
cultural ideas of “justice” or “the law”.
54. Reinforcement effect
·
People
seek out and remember information from their pre-existing attitudes and beliefs
·
People
do not like to be wrong when their beliefs are challenged
·
It
is one of the properties of language
·
It
is used in human communication to describe thing that are not visually present
·
Capitalism
(private enterprise) has distorted the human relations that are not controlled
by the participants themselves
·
Examples of
personal events are a death in the family, a job change, divorce, or leaving
home for the first time.
·
New
media are forms of media that are related to computers
·
Websites,
mobile apps, virtual world, multimedia, computer games and animation are the
example for new media.
·
A
group or class of persons considered to be superior to others because of their
intelligence, social status, etc. are called elite class
·
They
are small group of powerful people that control wealth, political power in
society.
·
H
·
He
was appreciated for his contribution towards semiotics
·
Play Theory of Mass Communication is a theory that holds the first function of media is to provide
entertainment.
·
Play theory is mainly emphasized on how we use
media for our satisfaction and also how media bring changes in our lives
according to its contents.
·
Persons
who are all accessing the visual media are called media viewer
·
They
can be television viewer, Internet viewer, Movie viewer.
·
A
style or category of art, music, film ,television, etc.is called genre.
·
Action,
thriller, love, comedy are some of the example of film genre. Serials, news,
sports are some of the genres of television
·
The
act of spreading something especially information
·
That
is the spreading of sports, news, foreign news, political information’s to
public
·
·
The purpose of being information and media literate is to engage in a digital society; one needs
to be able to understand, inquire, create, communicate and think critically.
·
Uses and gratifications theory (UGT theory) is an approach to
understanding why and how people actively seek out specific media to satisfy specific needs.
·
It explains how people use the media for their
own need and get satisfied when their needs are fulfilled.
·
He
was an eminent American communication theorist
·
He
originated the diffusion of innovation theory
·
Diffusion of
innovations is a theory that seeks to explain how,
why, and at what rate new ideas and technology spread.
·
Information
theory studies the transmission, processing, extraction and utilization of
information
·
It
is a set of messages which is received by receiver inspite of noisy channel
68. Narcotic dysfunction
·
Narcotizing
dysfunction is a theory that as mass media inundates
people on a particular issue, they become unconcerned to it.
·
Narcotizing
dysfunction refers to the situations where media provide so
much information that people
become numb (unfeeling).
·
It's a concern because people become desensitized to the information
when they see it on the media.
·
The origin of postmodern communication is linked to the development
of communication theory.
· As communication theory studies the technical process of information and the process of human communication, postmodern communications are the newly created tools and marketplaces that allow these communications to happen.
70. Commutation effect
·
Communication effects are basically mental associations or responses,
connected to the brand, that are left in the buyer's head through advertising.
·
They are subject to modification through
experience with the product, word of mouth, and other marketing factors, as
well as through further advertising.
·
Moral conventionalism may be described as a theory of moral conduct,
according to which the criteria for right and wrong (or good and bad) conduct
are based on general agreement or social convention
· Moral codes are relative to a particular culture or society.
72. Discourse
·
It
means written and spoken communication
·
It
is a conversation within the context of communication
·
Semiosphere is the sphere of semiosis
·
The domain of all signs that represent and define a culture.
·
A simulacrum is a
representation or imitation of a person or thing.
·
The word was used to
describe a representation, such as a statue or a painting, especially of a god.
·
Something that replaces
reality with its representation.
·
A paradigm
is a standard, perspective, or set of ideas.
·
A paradigm
is a way of looking at something.
·
When you change paradigms, you're changing how you think about something.
·
A system of beliefs, ideas, values, and habits
that is a way of thinking about the real world.
·
Leadership or dominance, especially by one
state or social group over others.
·
An example of hegemony is the student
government leadership in a school.
·
The emotional release that characters or the
audience experience during the catharsis can
lead to a sense of forgiveness and renewal.
·
Most tragic works of literature end with catharsis.
·
Playing piano is a catharsis for a tired, busy mother after a long day of work.
·
The definiti
·
An example of a metonymy is referring to the King
as "the Crown."
·
Mediation in Marxist theory
refers to the reconciliation (reunion) of two opposing forces within a given
society by a mediating object.
·
Mediation of media is constant and it is
basically the process of altering the media before it gets sent out to the public.
·
The
media which reaches mass number of audiences is called mass media
·
Radio,
television, newspaper are the example of mass media
·
In Marxist theory, the capitalist
stage of production consists of two main classes: (1) the bourgeoisie, the capitalists who own the means of
production, and (2) the much larger working class who must sell their own labour power
·
Marxian class theory asserts
that an individual's position within a class hierarchy is determined by their
role in the production process
·
The ability of an individual to discover their
own meaning in a media text.
·
A set of skills that allows one to rationally
assess their experiences for truthfulness and value.
·
83. Metaphor
·
Merge
to incompatible images or concept to create symbolism
·
It
is used in advertising to enhance the perceived value of product
PART - B & C
1. Characteristics of mass media
· The media which reaches mass number of audiences
· It transmit information to large audience at the same time
· It is one way communication. The receiver cannot interact with the sender
· Audience has many choices in selecting the media
· Radio, TV, Newspaper spreads the news very speedy
· It attract the audiences by providing entertainment programs
· It influences the society by providing different kinds of programs
2. Types of mass media
(i)
Newspaper
· It is a kind of mass media which carry many information’s such as sports, politics, business, etc.
· Many newspapers are daily either comes in the morning or evening
· It gives elaborated news information to the readers
· Newspapers come in English or in regional languages
(ii)
Magazine
· It is another kind of mass media. It may be weekly, bi-monthly, monthly, etc
· This includes article, interview, jokes, etc.
· It can be classified into general magazine, specialized magazine, and special magazine
(iii)
Radio
- It is an audio medium
- This gives correct information about sports, music, news, drama, etc
- It also gives education and health information’s
- This medium is more entertaining and informative
(iv)
Television
· It is an audio visual medium
· This gives many news items and entertainment programs
· It is an effective medium to advertise the products
· It influences and creates impact on society
(v)
Cinema
· It is also an audio visual medium like television
· It is showed on big screen in theatre
· It carries social, political information
· Limited number people sit and watch cinema in theatres
(vi)
Internet
· It is also called new media
· This connects people through e-mail, facebook, etc
· It is used to share information and interpret the messages
3. Reason for studying media
· We get more information through media
· Media is the main source of modern culture and entertainment
· It helps how to communicate with each other
· This helps us to learn latest technology
· It tells about environment such as trees, rivers, mountains, etc
· Media brings us political messages all the time
· It provide various information’s about product through advertisement
· It is to understand the culture and values of society
· Media require us to learn and use critical thinking skills
4. The power of media
· It provides us with information of any kind
· It creates social awareness effectively. For example polio drop campaign, don’t burn tyres during Boghi Pongal.
· It changes the lifestyle of an individual or group by reading or listening to experts
· The attitude and behavior of the people could be changed by media
· Media has the power of making social change. Example - creating job opportunities
· It is possible by the media to influence the audience
· It organize people for National integration – Example – they organize people to help the affected people during flood, earthquake, etc
· It brings out the truth of any crime incident
· It creates more impact on society
5. Role of mass communication in social change
Social change is a general term which refers to change in the nature, the social institution, the social behavior of society, community of people that affects a group of individuals that have shared characteristics.
(i)
Creating awareness
·
Media has contributed a lot in increasing the
general knowledge, current issues, etc
·
Discussions, current affairs, documentaries,
etc are used to enhance the awareness among people
(ii)
Development of country
· Media has assisted in development efforts of country
·
Swatch Bharat has reached people for the
development of (clean) country
(iii)
Development of public opinion - Media
discussion, talk shows, are used to get
the opinion of different group of people on issues
(iv) Education – Both print and electronic media are providing educational programs such as distance education, quiz program, etc to develop the knowledge
(v) Supports democracy – Media supports democracy by providing live coverage of parliamentary proceedings and activities of politician
(vi) Support to public issues – Media provides view point of public on public issues and give voice to public
(vii) Employment opportunities – Media tells about various job opportunities available around us.
(viii) Organizing people – Media organizes people for social
causes during floods, earthquake, etc.
6. Four theories of mass media or Normative theories of mass
media or press theories
(i)
Authoritarian theory
· It describes that all forms of communication are under the control of authorities
· Authoritarians control the media to protect and prevent the people from National threats
· The authorities provides license to the media and make censorship
· If any media violate the Government policies, their license is cancelled
· The censorship protect the authorities from various issues
(ii)
Libertarian theory
· It is opposite to the authoritarian theory
· It means the media is free from any authority, control or censorship
· This theory sees people are more enough to find and judge good ideas from bad
· It gives more values for individuals to express their thoughts in media
· It ignores need for reasonable control of media
(iii)
Social responsibility theory
· This theory lies between both authoritarian and libertarian theories because it gives total media freedom in one hand but externally controls in other hand
· The press ownership is private
· It does not simply give the information, but also investigating
· It allows free press without any censorship
(iv)
Soviet media theory
· It is also known as the communist media theory
· The government controls the total media and communication to serve people
· It says the state has absolute power to control any media for the benefit of people
· They put young to the private ownership of press and the government press is providing information, education, entertainment, etc.
7. Knowledge gap theory
· Systematic differences in knowledge between better informed and less informed segments of population
· This model focuses on the role played by news media in cities and towns
· News media systematically inform higher socio economic groups better than the media that inform others.
· The people who are less well informed will not be able to act as responsible citizens
· To fill up knowledge gap, increased news coverage and passing information to all categories of people is necessary
8. Diffusion of innovation theory
· This theory explains how innovations are introduced and adopted by various communities
· Innovations will pass through a series of stages before it is adopted
· The people will become aware of it
· The innovations will be adopted by a small group of people
· Opinion leaders learn from the early adopters and try the innovations themselves
· If opinion leaders find the innovation useful they encourage their friends
· Now most of the people will adopt the innovation
· This theory sees the communication process from the point of view of elite
· It assigns very limited role to mass media, since the information’s are adopted and informed by opinion leader
· Media are used to draw attention to innovations and as a basis for group discussion
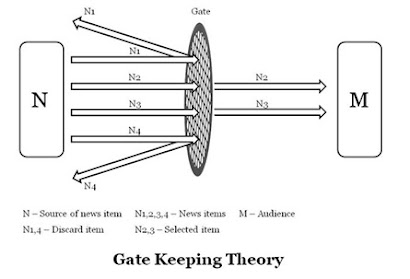
9. Gate keeping
·
Gate keeping is the process through which
information is filtered for dissemination, weather for radio, TV, newspaper,
etc
·
The reporter and editor decides which news
has to reach the audience
·
This process determines not only which
information is selected but also what the content and the nature of message
will be
·
In the above diagram N is the source of news
item and M is the audience
·
N1, N2, N3, N4 are news information’s among
which N1and N4 are rejected not to be published and N2 and N3 are selected news
items for publication or broadcasting
10. Rhetoric of image
·
Rhetoric of
Image analyzes image
or illustration and in what ways do meanings are associated with
particular images.
·
It includes examines images, observes the messages it
entails, and how these messages are extracted from these images.
·
The signification of the image is
intentional in advertising.
·
Advertising images convey a message.
·
In an detergent powder advertisement,
the clothe looks yellow which means it is dirty, then it looks white which is
because of the detergent powder.
· The message conveyed by the image should have denotative (direct) meaning
· Decoding the Image - When looking at the overall sign of the advert, the reader understands from its composition and its placement in a magazine that it is an advertisement.
Linguistic Messages: The Text or Captions the copy, or the title in an advertisement. The
text in TV and Radio is the spoken word in the advertisement
Iconic Non-coded Messages:
The Literal Image or Denoted Message When
the viewer looks at the advertisement, the visible items represent what they
are signifying in reality.
·
This direct
message is providing a non-coded message, and the “realism” of the image makes
it appear to be a “natural” scene.
·
That means
there is no code to decode
·
In a photo
of a tomato represents a tomato is the example for non-coded message.
·
We need no other knowledge than what is
involved in our perception.
Coded Iconic Messages:
The Symbolic or Connoted Message is coded iconic message
·
When we analyze the image we cannot get direct meaning.
·
The viewer derives the message from the visual
suggestions
·
Example - What signifies a man return from the market? In
order to ‘read’ the sign (meaning), we have to understand what the shopping bag
represents and the culture around ‘local shopping’.
11. Uses and gratification theory
· Uses and gratifications theory (UGT) is an approach to understanding why and how people actively seek out specific media to satisfy specific needs.
· UGT is an audience-centered approach to understanding mass communication
· Differing from other media effect theories that question "what does media do to people?", UGT focuses on "what do people do with media?"
· It suggests that media is a highly available product and the audiences are the consumers of the same product.
Categories
of Uses and Gratification
Human needs and gratification can be divided
into five broad categories. They are:
Affective needs
§ Affective needs talk about emotional fulfillment and pleasure people get by watching soap operas, series on television and movies.
§ People relate to the character and feel the emotions the characters show.
§ If they cry, the audience cries and if they laugh, audience laughs along with them.
Cognitive needs
§ People use media to get information and fulfill their mental and intellectual needs.
§ People watch news mostly to gratify this need.
§ Other examples can be quiz programs, teaching programs, arts and crafts programs for children, documentaries, etc.
Social integrative needs
§ The need of each person to socialize with people like family and friends is social integrative need.
§ People use media to socialize and interact through social networking sites like Facebook, My Space, Twitter, etc.
§ Media also helps by providing people with topics and ideas to talk/discuss with their friends and near ones, increasing their social interaction skills.
Personal integrative needs
§ Personal integrative needs are the needs for self-esteem and respect.
§ People need reassurance to establish their status, credibility, strength, power, etc. which is done with the use of media.
§ They use media to watch advertisements and know which products are in fashion and shop accordingly to change their lifestyle and fit in with other people.
Tension free needs
§ People listen to songs and watch t.v when they are in stress to relieve their stress or when they are bored at times.
§ People might have various tensions in life which they do not want to face, so take help of media to escape from it.
Examples of Uses and Gratification Theory
·
In situations like watching movies and listening to the
music of your own choice, this theory is applicable.
·
People choose from their own choices and moods.
·
Some people might watch news for information, some for
entertainment, and some for self-reassurance. Some watch according to their
moods. There are various needs which get fulfilled by the media.
12. Functions of mass media
(i)
Information
§ It collects, process, spread news, pictures, opinion to the public
§ It gives local, regional, national and international news information
§ This develops the knowledge of public
(ii)
Education
§ Media provide education in different subject to people either directly or indirectly
§ Distance education program, quiz program, are example of direct education
§ Drama, documentary, short film, interview are some of the indirect method of education
§ It is an effective tool to create awareness on education
(iii) Entertainment
§ Newspaper, magazine, radio and television offer stories, films, serials to entertain the audience
§ It makes audience leisure time more enjoyable
§ This reduces tension and make the audience relax
(iv)
Persuasion
§ It involves making influence on other’s mind
§ It influences votes, changing attitude and behavior
§ Advertisement is the best example of persuasion
(v)
Surveillance (watch dog)
§ A function of mass communications is to tell you about what's happening around the world and deliver that information to you.
§ Surveillance refers to coverage of a wide range of important topics that impact society.
(vi)
Interpretation
§
The mass media do not supply just facts and data. They
also provide information on the ultimate meaning and significance of events.
§
Articles that analyze the causes of an event or that
discuss the implications of government policy are also examples of the
interpretation function. Why is the price of gasoline going up.
(vii)
Linkage
·
The mass media are able to join different elements of
society that are not directly connected.
·
For example, mass advertising attempts to link the needs
of buyers with the products of sellers.
·
Legislators may try to keep in touch with constituents’
feelings by reading their hometown papers.
·
Voters, in turn, learn about the doings of their elected
officials through newspapers, TV, radio, and websites.
·
Another type of linkage occurs when geographically
separated groups that share a common interest are linked by the media.
(viii) Socialization
·
The transmission of values is an important function of
the mass media.
·
Socialization refers to the ways an
individual comes to adopt the behavior and values of a group.
·
The mass media portray our society, and by watching, listening,
and reading, we learn how people are supposed to act and what values are
important.
·
Cell phones link parents with children. Sports talk radio
joins people with a common interest in athletics.
13. Popular culture (Pop culture)
·
Culture based on the tastes of ordinary
people rather than educated elite is called popular culture.
·
It is the entirety of attitudes, ideas, images,
perspectives and other phenomena within the mainstream of a given
culture
·
This collection of ideas permeates the everyday
lives of the society.
·
The most common pop culture categories are: entertainment
movies, music, television, games, memes, sports, news, politics,
fashion/clothes, technology, and slang.
·
Popular culture has a way of influencing an individual's
attitudes towards certain topics.
14. Elite culture
· High culture refers to the set of cultural products, mainly in the arts
· It is the culture of elite such as the upper class or intelligentsia, and is contrasted with the low culture of the less well-educated.
· Elite culture can be defined as those “high” cultural forms and institutions particularly high class, the commercial bourgeoisie, educated bureaucrats and political power brokers.
· These elite groups dominated cultural styles as opera, symphony orchestras, dance companies, the decorative arts, fine art, museums and galleries.
· Now the power and significance of elite culture has relaxed and become omnivorous.
· New styles such as film production companies and many entertainment media that blur elite cultural forms.
15. Pluralistic concept of mass media
Pluralistic
concept includes a number of aspects have been interpreted and measured from
different perspectives.
Internal pluralism
·
It
reflects how social and political diversity are reflected in media content.
·
That
is, the representation of different cultural groups, political opinion and
viewpoint in the media.
·
Internal
pluralism plays an important role in news and public coverage
·
Governments
stimulate internal pluralism by facilitating public service broadcasting,
financial support such as loans, reduced tax rates, etc.
·
Internal
pluralism focuses on media content
External pluralism
·
It
covers the number of owners, media companies, independent editorial boards,
channels, titles or programs.
·
This
type of pluralism is also known as the ‘plurality’ of suppliers.
·
It
doesn’t concentrate on media content
·
From
the perspective of the competition between these media content suppliers is
considered to be essential in order to ensure a free choice of media content
and the availability of a wide variety of opinions and ideas.
16. McLuhan’s media theory- Medium is the message
· The medium is the message is the form of embeds itself in any message, it would transmit
· It does not include the content it carriers
· A medium affects the society in which it plays a role by the characteristics of the medium itself.
· The content of any medium is always another medium. Speech is the content of writing, writing is the content of print.
· A bulb does not have content, but it is a medium that has effect
· Likewise the message of a crime may be less about the individual news story itself and more about the change in public attitude towards crime
· The pleasure we find in new media is deceiving (cheating)
· McLuhan described change in how people have viewed the world and how those views have been affected and altered by the adoption of new media
· Each medium produces a different message or effect
17. Psychoanalysis
Sigmund Freud explains the different state of mind in psychoanalysis
Id
· It is the only component of personality that is present from birth
· It is the source of our needs, wants and desires
· Id act according to the pleasure principle
· It seeks immediate gratification of any impulse
· According to Freud, the Id is unconscious by definitions
· The mind of new born child is the example of Id
Ego
· The ego acts according to the reality principle
· It seeks to please Id’s drive in realistic ways that will benefit in long term
· It is the bridge between Id and reality
· Ego enables the individual to delay gratifying immediate needs and function effectively in the real world
· Ego is the organized part of personality structure that includes defensive, intellectual functions
· Generally the ego functions are conscious
Super ego
· It reflects the cultural rules, mainly taught by parents applying their guidance and influence
· Child super - ego is constructed on the model of its parents and super – ego.
· Super-ego aims for perfection
· It control our sense of right or wrong
18. Media text
· A text is any media product we wish to examine, weather it is a TV program, book, radio, etc
· Generally media text produces denotative meaning
· The central concept of model is a construct of reality
· Every representation of the world is an attempt to describe the reality
· Media has been deconstructed into text, audience and production
o Text – It is any media product
o Audience – Anyone who receives media text
o Production – Everything that goes into the making of a
media text – the technology, ownership, economic, etc.
·
Each individual of a text will draw meanings
that reflects individuals gender, age, background, etc
·
Meaning of a text is determined in a
challengeable relationship between reader and the text.
19. Media imperialism
· Smaller countries are losing their identity due to the dominance of media from larger nations
· It can be equated to small shops closing down due to larger super stores moving in
· So smaller media companies are being forced out
· The culture of those larger nations along with its interest displays that of the home country.
· The dominance has led to important events getting little attention and biased information and inaccuracy within the news story
20. Hero worship culture
· Hero worship is a feeling of extreme admiration for someone, imagining that they have qualities that are better than anyone else
· People arrange cutouts for their hero or heroine
· They pour milk on their cutout
· They pray for their hero for the success of the movie
· Fans wanted to watch their films on the day of release
· They spend more money to watch film in first show
· People built temple for their favorite stars
· People do good thing to the society on behalf of the hero by issuing notebooks to the poor students, organizing medical camp, etc.
· They dress, speak, do hair style like their favorite hero.
· They support their heroes film even though it is not good
· The Tamil superstar Rajinikanth alone reportedly has a hundred thousand clubs with a total of million-plus members.
· When the Tamil superstar M.G. Ramachandran (MGR) died, as many as 31 people reportedly committed suicide.
· Kannada star Rajkumar death from natural causes brought Bangalore to a complete standstill and several people died.
· Often we can see clash with the fans of two hero’s generally placing cutout in front of the theatre.
21. Concept of selecting media
(i)
Popularity of selecting media
· While selecting media the popularity among people is important
·
For TV
media, Sun TV, Vijay TV, ZEE TV, etc and for newspaper The Hindu, Indian
Express, etc are the examples of popular media
(ii)
The range of media
· This means how long the media reach the audience
·
Some
media reach local, some reach regional level, some national and international
(iii)
Budget
· The amount of money can be spent is an important factor in selecting media
·
Famous
media charge more which cannot be spent by all
(iv)
content
· Some content suitable for print & some for radio and television
·
Launching
a new product should be advertised in television to reach high
22. Hegemony
· Hegemony the dominance of one group over another
· It refers to the moral and political leadership of a social group
· It is not gained by force, but by a culture. For example, USA is a powerful country which tries to dominate other Asian and African nations
· Power, dominance and leadership are three main features of hegemony
· Cultural hegemony is the philosophic and sociological concept that a culturally diverse society can be ruled or dominated by one of its social class.
· Staying away from the dominant power is the solution to overcome hegemony.
23. Mass culture
· Mass culture is a common culture experienced by large number of people.
· It is widely disseminated by mass media.
· It is the set of ideas and values that develop or arise from a common exposure to the same cultural activities, media, news sources, music and art.
· Mass culture conveys the idea that such culture emerges spontaneously from the masses themselves like popular art.
· It promotes the role of individuals as consumers.
· Mass culture emerged due to the development of print and broadcast which were strong enough to alter perception, convince people to follow ideas on a large scale.
· The main function of Mass culture is to entertain and distract the people.
· Mass culture raised people’s standard of living and economic development.
· It replaced folklore, which was the cultural mainstream of traditional local societies.
· Examples of mass culture includes films, television programs, popular books, newspapers, magazines, popular music, leisure goods, household items, clothing, and mechanically-reproduced art.
24. High culture
· The term high culture identifies the culture of an upper class or of a status class
· The term high culture is used to describe a subculture shared by the elite in a society
· It contains the works of art, literature, scholarship and philosophy that establish a shared frame of reference among educated people
· The consumption patterns, mannerisms, beliefs, amusements, leisure activities, and tastes and preferences society's elite.
· High culture includes the cultural objects of aesthetic value, which a society collectively respect as excellent art
· Pop music, romantic Hollywood comedies and soap operas are some of the examples of high culture
25. Catharsis effect
· Catharsis refers to an emotional release for the characters in a film
· Catharsis is a concept in psychoanalytic theory wherein the emotions associated with traumatic events come to the surface. The word has its origin in a Greek term for cleansing or purging.
· Catharsis is associated with the elimination of negative emotions, affect, or behaviors associated with unacknowledged trauma
· Playing the piano is a catharsis for a tired, busy mother after a long day of work.
· Crying is a great catharsis for releasing pain and anger
· Emotional catharsis is an important factor in a person's well-being.
· Laughter can be a catharsis for expressing joy and amusement
26. Agenda setting theory
·
Agenda setting is
the idea that what the public thinks about is set by the media.
·
Agenda setting
means the ability of the mass media to bring issues to the
attention of the public and, related, of politicians.
· If the media gives more attention to an issue, the public perceives it as important.
· Agenda-setting is the creation of public awareness and concern of salient issues by the news media.
· The agenda-setting by media is driven by the media's bias on things such as politics, economy and culture, etc
· For example, a media stressing on what type of work each gender should do, completely neglecting the idea of gender equality, creates similar mindset in the people.
27. Popular discrimination
The unjust treatment of different categories of people, especially on the grounds of race, age, or sex is called discrimination.
Types of discrimination
Age
·
Age discrimination is discrimination and
stereotyping based on the grounds of someone's age.
·
It is a set of beliefs, norms, and values
which used to justify discrimination based on a person's age. Example - old people, adolescents and children.
Caste
· Discrimination based on caste.
· It is the sub division of community such as BC, MBC, OC
Disability
· It is crimination against people with disabilities.
· Disability discrimination, which treats non-disabled individuals as the standard of ‘normal living’, results in public and private places and services, education, and social work that are built to serve 'standard' people, thereby excluding those with various disabilities.
Employment
· Denying someone employment, or disallowing one from applying for a job, is often recognized as employment discrimination
· It is because of various characteristics such as age, disability, ethnicity, gender, height, political affiliation, religion, skin color, and weight.
Language
·
Diversity
of language is protected and respected by most nations.
·
People
are sometimes subjected to different treatment because their preferred language
is associated with a particular group, class or category.
Nationality
·
Discrimination on the basis of nationality is usually
included in employment laws
·
It is sometimes referred to as bound together with
racial discrimination although
it can be separate.
Region
·
Regional
discrimination is discrimination based on the region in which a person lives or
was born.
Gender
· Gender discrimination refers to beliefs and attitudes in relation to the gender of a person.
· Gender inequality in India refers to health, education, economic and political inequalities between men and women in India.
28. Narcotization of dysfunction
·
Narcotizing dysfunction is a theory that as mass
media inundates (overwhelm) people on a particular issue they become
apathetic (uninterested) to it.
·
It
is suggested that the vast supply of communications Americans receive may
elicit (bring out) only a superficial concern with the problems of society,
while importance of real action is neglected.
·
Thus,
it is termed "dysfunctional" as it assumed it is not in the best
interests of the people
·
Because
the individual is assail (set about) with information about a huge range of
issues and problems and they are able to discuss these issues, they believe
they are helping to resolve these issues.
·
However,
being informed and concerned is not a replacement for action.
·
Even
though there are increasing numbers of political messages, information, and
advertisements available through traditional media and online
media, political participation continues to decline.
· People pay close attention to the media, but there is an overexposure of messages that can get confusing and contradictory so people do not get involved in the political process
· Because of narcotizing dysfunction the audience withdraws from real issues and becomes passive.
· In this phase instead of the media telling people what to think, it tells the audience what to think about (sets the agenda).
·
It is a word for the 'way of
life' of groups of people.
·
Different
groups may have different cultures.
·
A
culture is passed on to the next generation by learning
· Culture is seen in people's writing, religion, music, clothes, cooking and in what they do.
· It is an integrated pattern of human knowledge, belief, and behavior.
· The outlook, attitudes, values, morals, goals, and customs shared by a society.
·
Cultures
are what make countries unique. Each country has different cultural
activities and cultural rituals (habits).
·
Culture
includes material goods, the things the people use and produce.
·
Culture
is also the beliefs and values of the people and the ways they think about and
understand the world and their own lives.
30. Active and passive audience
Active audience
· An active audience is one that actively engages with the text.
· They do not simply accept every media message.
· They question what they see and develop their own interpretation of a media product based on their life experiences, education, family and cultural influences.
· Theories such as uses & gratification and postmodernist theory assume that audiences are active
· Media insists people “Voting is your right”. People receive message and go for voting is an example for active audience.
Passive audience
· It was thought that this did not require the active use of the brain.
· The audience accepts and believes all messages in any media text that they receive.
· A passive audience does not actively engage with a media text.
· A passive audience is one that does not question the message that the media is sending and simply accepts the message in the way the media outlet intended.
· Theories such as magic bullet/hypodermic needle and agenda setting function assume audience are passive
31. Mass media audience
· Media audience we mean the recipients of Mass Media messages.
· There is the audience of newspaper, television, radio, theatre, film and non-broadcast media.
· Audience of the above media are heterogeneously scattered. They are a mixture of age, sex, profession, education and social class etc and are strangers to one another.
· If there is no audience to purchase movie tickets and recording, subscribe to newspapers and magazines and attend to radio and TV programmes, no mass medium could stay in business.
· The messages of TV newspapers and film etc,. are determined according to the nature and behavior of the target audience.
Various categories of media audiences
· The elite audience comprises of highly educated people and their number in the society is small (reading English newspaper).
· The mass audience represents the dominant majority in a society. They are relatively average people (reading regional newspaper, watching entertainment program in TV).
· The specialized audience refers to the special interest groups in the society (watching political debate and discussion, sports, news).
· The interactive audience consists of those who have control over the communication process in a society. They may be newspapers journalists or radio or TV broadcasters
32. Portrayal of women in cinema
· It is true that the number of movies that have meaningful roles for women is increasing.
· Mother India is the first Indian cinema in which female actor was in the lead role.
· Roughly up to the 1980s, lead actresses have significant roles. Movies at that time used to have wonderful stories which totally reflected the society. But at the same time, filmmakers used to add ‘vamp’ characters in the movies to provide sexually explicit entertainment.
· This culture has not changed even now. Producers are adding item songs to gain commercial success.
· Since 1980 the role of lead actress started reducing to just an add-on to the hero-centric film.
· In recent times, many lead actresses are doing strong roles. As more and more women are joining in the film industry as directors, producers, actresses etc., the situation of female characters portrayal is improving.
· Most of the mainstream movies are male-centric. Lead actresses are treated as glam dolls in those movies.
· In many movies of present times, female characters are needlessly sexualized. Along with that, adding vulgar lyrics and dances in the name of item songs is very derogatory towards women.
· Lead actors are always shown as saviors. Women are shown as either helpless victims or cunning villains. In general, hero is the one who solves everyone’s including heroine’s problems.
· Movies depict actresses as unrealistically beautiful. This causes a lot of trauma and insecurity issues.
· Stalking (irritating) and eve-teasing are depicted as love in Indian movies. In many mainstream movies, female characters fall in love with these abusers.
· Heroines were portrayed as submissive, prefer to be homemaker, not career oriented and tolerate the force of abusive husband silently.
· Now the female characters in movies are more realistic and are many actresses are not doing such kind of meaningless roles.
33. Gender stereotype in cinema
·
In
films higher level roles are designated to males in terms of occupations in
films. Lower level roles are designated to females.
·
Gender
disparities do exist in Bollywood, that is rare to find plots focused on women.
·
Representation
of female point of view is so less in the Indian film industry. This had been
used as a prevention against women blossoming into individuals.
·
Indian
Film Industry reflects the power dynamics of the Indian society whether
regarding gender, religion or caste.
·
Females
have been suppressed at the very bottom of the social hierarchy and thus, less
representation of their point of view.
·
Female
point of view is less in Indian films because of the male gaze. Everything is
seen from the male point of view.
·
The
year 2018 has been a banner year for women. In the first half of 2018, out of
10 hit films, seven were women-oriented and Padmaavat was the
highest grossing among them.
·
In
the last 10 years, the 2017 study detected only 289 female-centric movies.
·
The
change may be slow. But the potential of films from this genre is increasing
with time.
·
"In
recent years, directors, producers, artists and professionals created
gender-equal cinema.
·
One
factor that has helped this category of films gain momentum is changing taste
of audiences.
·
It
is mandatory to make the right environment to educate more audience to view female
oriented films.
34. Portrayal of children in media
· "Children are under-represented in the news media
· Children are predominantly represented as victims
· Children are portrayed most often in negative terms and in limited roles.
· The media should make an effort to represent children in more positive roles.
· One in two stories featuring children related to negative topics such as crime, violence, abuse or disasters.
· Girls were more likely to appear in stories about child abuse, while boys appeared mostly in sports-related stories.
· This reinforces the stereotypical portrayal in the media of women as victims and men as empowered”
· The use of children's serious comments to make adults laugh
· The use of 'cute' children to add charm appeal
· The use of photos and descriptions of children in miserable situations to evoke emotion
· When the children know more about the subject children being made to perform like circus animals
35. Role of social networking site in cultural change
·
Social media has been a major part of our daily lives.
·
It totally affected our culture in positive and negative ways.
·
Social media increased the connections between people and created
an environment in which you can share your opinions, pictures and lots of
stuff.
·
Social media improved creativity and social awareness for our
society by interacting with other people and sharing new ideas and opinions.
·
It is also important for any business because at some point, you
need to use social media in your business.
·
It is easier to learn about breaking news on social media because
it has unlimited access and flexibility.
·
On the other hand, social media has influenced our culture in
negative ways.
·
People can share whatever they want to on social media and some of
them might be inappropriate pictures.
·
People has become more conservative about each other’s point of
view.
·
People started to argue about each other’s perspective related to
political view, religion, social rights and culture.
·
Social media had negative effect on youth. It reduced physical
activities.
·
People prefer to sit all day in front of computers and chat.
·
Kids might be affected and manipulated by some sites in which
there is inappropriate information.
·
The ugly part of social media is that there is tons of unnecessary
information shared by people and also bullying and harassment on social media
has been increased.
·
People can make brutal and negative comments about anything and
anyone.
·
Social media has good, bad and ugly impacts on our culture.
36. Role of blog in bringing cultural change
· With the widespread use of the Internet, a new form of culture has emerged: the blog.
· A blog contains information of any topic.
· Multiple people can participate in a blog, either as creator or reader
· Blogs are also increasingly important in political organizing in grassroots movements.
· The use of blog is a good example of how technological innovation can create new forms of culture.
· The blogging communities connect people who might not ever meet face to face.
Types of blogs
· Food blogs - It attracts a lot of readers who are interested in recipes, ingredients, healthy eating, fine dining, and other food related stories.
· Music blogs - Music lovers enjoy songs from different languages, cultures and norms.
· Fitness blogs has been a hot trend since they cover important topics like health and general fitness.
· Sports blogging may also include bloggers who are writing paid content for teams, athletes, and other organizations.
· Finance blog gives us help and advice to manage our finances efficiently.
· Political blogs have perhaps the most passionate audience of all. They cover news on politics, analysis of political news.
· Business blogs are the professional blogs related to the corporate agencies, industries and others.
37. Television stereotype
· Stereotype is a fixed or conventional image of a person or group of people.
· It conforms to a pattern of dress and behavior that is easily recognized and understood
· Positive or negative judgment is made about the person or group being stereotyped
· Stereotypes are less real, more perfect, and more predictable
· Commercial television has improved in its portrayal of females, many of the women depicted as someone’s wife or girl friend.
· TV children are generally cast in gender related roles – the girls playing with dolls while boys play at sports.
· The characterization of mother-in-law, police officer, the elderly tends toward the stereotypical.
· Culture and class stereotype are also prevalent in television
· Traditionally blacks were portrayed as servant or criminals.
· Stereotyping can lead children to form false impression of various social groups
· Minorities are portrayed stereotypically and almost never as powerful or rich as the white majority.
38. Recent films spoil our culture
· Indian movies have had great influence on the viewers from the very beginning, especially the youth who have always followed the actors and actresses of their generation.
· Almost every movie loving youth has tried to follow his or her favorite actor or actress in way of talking, style, dressing and actions, even the hair cut also
· Till the eighties, the movies were reformative and were based on social and domestic problems.
· But now violence, crime, vulgarity, obscenity and rapes dominated the movie which is the main cause of rising crime and violence against women as today’s youth is deeply polluted by such movies
· People, especially youngsters, try to follow whatever is shown in modern movies.
· Modern Indian films are trying to mimic West (western movies) without taking ill effects in consideration. Such movies have affected our culture and heritage, including social fabric.
· Cinema has influenced the youth to believe that going to pubs, drinking, smoking is cool and those who do not do all these things do not know how to enjoy life.
· Many movies which spread wrong messages in the society. Our cultural, social and moral values are shown out dated and being obedient or sincere to parents and others is shown as out of fashion and stupidity
· In order to make more and more money easily today’s film producers do not bother about quality and the ill effects of the movies
· Despite knowing the fact that movies have badly affected the youth and the society, the film producers give us violence, crime, exploitation and violence against women
· Social values have been lost in the glamour of movies and the youth has become intolerant and violet.
· Masala movies have spoiled our society and the thinking of the youth
· The extra-ordinary publicity given to actors and actresses gives a notion that they are the most important for our society and we should follow them
39. How media influences our culture
· Newspaper, magazine, radio, television and internet are greatly affects our lives because media has the power to influence our thoughts.
· Communities and individuals are bombarded (attacked) constantly with messages from a multitude of sources including TV, billboards, and magazines, etc.
· These messages promote not only products, but moods, attitudes, and a sense of what is and is not important.
· Mass media makes possible the concept of celebrity. Only in recent times have actors, singers, and other social elites become celebrities.
· Children can develop their skills and intellect by watching these programs because audio and visual media makes it quite easy to understand
· Media can manipulate, influence, and persuade the society, along with even controlling the world at times in both positive and negative ways; mentally, physically and emotionally.
· Controversial stories are reported and printed with no reliance (trust) of it being fact or not. The public is “meant” to believe everything they’re told and not question it.
· Newspapers and magazines have websites, articles can be posted and received quicker than printed articles, and are updated more regularly.
· The media can influence the way people are viewed, which means people’s careers can change within a flash.
· The media can also manipulate people in the spotlight to lead their life a particular way.
· Social media increased the connections between people and created an environment in which you can share your opinions, pictures and lots of stuff.
· Social media improved creativity and social awareness for our society by interacting with other people and sharing new ideas and opinions
· Social media had negative effect on youth. It reduced physical activities.
· Kids might be affected and manipulated by some sites in which there is inappropriate information and inappropriate pictures
40. Importance of culture
· Culture is the characteristic of group of people defined by everything such as language, religion, lifestyle etc.
· Different people in different societies have different culture but they also have some similarities.
· The culture varies in different things such as clothes, foods, religion and many others.
· Culture is the identity of a group of people living in specific place
· People on the occasion of wedding, and other celebrations they follow strictly their culture.
· Culture is the identity of the nation, without culture the society is impossible to do anything.
· Culture is the basic root of any community which gives them the ways of life.
· The culture provides solution to the critical problem that is faced by the community.
· Culture teach us to think for the whole nation not individually, it provide the concept of family, nation etc.
· Culture enhances our quality of life and increases overall well-being for both individuals and communities
41. Impact of movie on youth
Positive impact
· Progressive thoughts like gender equality, organ donation spread easily through movies. For example, ‘Dangal’ movie inspired many to encourage their daughters in sports.
· Most of the Indians preferred engineering or medicine as the career choice. Careers of lead characters in movies impacts young people greatly.
· Many movies are coming with wonderful story lines and is influencing youth to focus on life goals rather than just concentrating on love phase.
· Several Indian movies on current issues are thought provoking and are highlighting the mistakes people are doing.
· Movies are a great source of entertainment. People can relive from stress and pressure at work or studies by watching movies.
· Through movies, cultures are depicted wonderfully. Hence, movies increases cultural sensitivity.
Negative impact
· Eve-teasing and irritation in movie is impacting youth negatively and is turning them into harassers.
· Most of the filmmakers ignore their responsibility towards society and add commercial elements to make their movies success which spreads negative elements like violence, stalking etc.
· Irony is that on one hand they preach gender sensitivity, on the other hand they make songs that are demeaning to women.
· In Indian movies, male lead drinks alcohol and smokes too. This influences teenagers, who have strong emotions.
· Movies always depict luxury lifestyle and rarely shows middle class lives. This leads to increase in consumeristic society, and the worst impact will be on youth.
· Some filmmakers impose their personal opinions on society through movies which depict certain communities or religions in a negative light.
· Movies encourage people to take revenge. In many films, lead characters kill antagonists by themselves. This is a threat to our society and legal administration.
42. Commodities of culture
·
Cultural
commodification referred as "eating the other".
· It means that cultural expressions can be sold to the dominant culture.
· Pop culture, advertisements, mainstream, and capital are all aspects of commodification
· The act of taking something's original form and commercializing it, turning it into an object of trade and capital.
· Commodification plays a large role in how society views subcultures.
· Friendship, knowledge, women, etc. are understood only in terms of their monetary value.
· Commodification of culture is positive when use cultural commodities to challenge and reshape outsiders' views.
· Major negative effects listed are that it reduces authenticity of cultures; destroys local identity and cultural values; turns a local phenomenon into a global one, and all of these result in cultural conflicts
·
Any
messages of social change are not marketed for their messages but used as a
mechanism to acquire a piece of the "primitive".
43. Media & politics
·
Tamil people
have always held two things close to their hearts – films and politics.
·
Tamil
Nadu’s first chief minister, CN Annadurai, along with Karunanidhi, were the
first scriptwriters who pushed forth the agenda of Dravidian ideologies.
·
Sivaji
Ganesan and SSR kept the message of Dravidian movement rolling in their films
·
A
growing independent popularity, Annadurai's death and Karunanidhi's open push
for his first son MK Muthu formed Anna Dravida Munnetra Kazhagam (ADMK), which
was later renamed to All India Anna Dravida Munnetra Kazhagam (AIADMK).
·
His
popularity and astute political alliances helped MGR topple the DMK during the
next assembly elections in 1977, paving the way for Tamil politics
·
MGR's
demise, thrust the light upon another film star J.Jayalalitha
·
In
1989 assembly elections 41-year-old Jayalalithaa entered the Tamil Nadu
Legislative Assembly to become the leader of the opposition.
·
Both
the AIADMK and DMK having production houses in the Tamil film industry.
·
Top
actors, both male and female, would have to select sides and regularly take
part in photos.
·
The
DMK even had actor Napoleon, selected as the Minister of State for Social
Justice and Empowerment in Prime Minister Manmohan Singh's cabinet.
·
While
Kamal Haasan and Rajinikanth's political foray have taken over headlines, actor
Vijayakanth had created similar ripples back in 2005.
·
Vijayakanth
launched Desiya Murpokku Dravida Kazhagam (DMDK), a regional political party
with center-left ideologies.
·
On
the other hand, after stints with both AIADMK and DMK for more than a decade,
actor R Sarath Kumar launched his own political party – All India Samathuva
Makkal Katchi in 2007.
44. Male Gaze in media
· In
feminist theory, the male gaze is
the act of depicting women and the world, in film from masculine perspective.
· It presents and represents women as sexual objects for the pleasure of the male viewer.
· The component of the “male gaze” concept is the interaction of the audience with the onscreen male audience.
· The
male gaze has three perspectives: (i) that of the man behind the camera, (ii)
that of the male characters within the film's cinematic representations; and
(iii) that of the spectator gazing at the image.
· Both
the aesthetic pleasures and the sexual pleasures derived from looking at
someone or something
· It
is the male behavior of voyeurism
· It
is the asymmetry of social and political power between men and women
· In
film, the visual perspective of the male gaze is the sight-line of the camera
as the spectator's perspective — whose sight upon the curves of a woman's body.
· Such
visualizations establish the roles of dominant-male and dominated-female, by
representing the female as a passive object
· Movies
feature the male gaze as more important than the female gaze, based upon the
inequality between men and women.
· Cinema presents and represents women as objects of desire, and she is in the film to visually support the protagonist
· The “male gaze” isn’t necessarily a bad thing. Sometimes the male is showed that he is confused by the female character.
· The “male gaze” become a problem when it is used to excess.
45. Bourgeois heroes
·
It is relating to,
or characteristic of the social middle class
·
The
bourgeoisie are the owners of the means of production and constitute the ruling
class.
·
To
be a bourgeois, hero
is to adopt the idea that these are good.
·
The
bourgeois hero belongs to the middle class and conforms to middle class
standards and conventions, he values work, respects authority
and works for the individual good.
·
Superman
often puts capitalist society back together but clearly suffers from alienation
·
Heros
offer models of identity to imitate, though mostly they “peddle” capitalist
ideology in disguise.
·
As
in Freud’s analysis of characters and their symbolic representation, a Marxist
approach to characters in dramas and other story forms sees them as symptoms.
46. Social construction of reality by media
· The term social construction of reality refers to the theory that the way we present ourselves to other people is shaped partly by our interactions with others, as well as by our life experiences.
· The notion of the social construction of reality is not to say that things in our social world are not real.
· We have built them from our imagination
· There are so many socially constructed concepts that are in our everyday life such as the type of food we eat in our breakfast, lunch, dinner, and the appropriate clothes a boy or a girl should wear.
· It is our socialization process that we learn what to consider real, important, valuable and necessary
· An example of a social construct is money or the concept of currency, as people in society have agreed to give it importance/value.
· Our perceptions of reality are colored by our beliefs and backgrounds.
· What is real depends on what is socially acceptable.
· The meanings we put into the realities also vary in every individual, community, society, and culture.
· Social reality is therefore said to be socially constructed.
· Violence that is depicted in the media can be the root and even intensifies the actual violence in societies.
· The rise of interactivity in new media communications may even modify our world beliefs, human behavior and responses today and in the years to come.
47. Audiences are treated as commodities
· In the case of media advertisement the audience is sold
as a commodity.
· Because audience power is produced, sold, purchased and
consumed, it commands a price and is a commodity.
· Audience members contribute their unpaid work time
(leisure time) and in exchange they receive the program material and the
explicit advertisements’
· Audiences would work, although unpaid; the consumption of
the mass media would be work because it would result in a commodity, hence it
would produce that commodity.
· Also the audience’s work would include ‘learning to buy
goods and to spend their income accordingly’.
· With the rise of user-generated content and free access
social networking platforms like MySpace or Facebook and other free access
platforms that yield profit by online advertisement.
· The users who ‘google’ data, upload or watch videos on
YouTube, upload or browse personal images on Flickr, or accumulate friends with
whom they exchange content or communicate online on social networking platforms
like MySpace or Facebook, constitute an audience commodity that is sold to
advertisers.
·
The difference between the audience commodity on
traditional mass media and on the Internet is that in the internet users are
also content producers: there is user-generated content, the users engage in
permanent creative activity, communication, community building and content
production.
48. Cultivation theory
· It is one of the core theories of media effects.
· Cultivation theory suggests that exposure to media, over time, "cultivates" viewers' perceptions of reality.
· Cultivation theory examines the long-term effects of television.
· George Gerbner’s original focus was on the influence of television violence on viewers.
· "The primary proposition of cultivation theory states that the more time people spend 'living' in the television world, the more likely they are to believe social reality aligns with reality portrayed on television."
· The images and ideological messages transmitted through popular television media heavily influence perceptions of the real world.
· Television is, therefore, considered to contribute independently to the way people perceive social reality.
· The theory argues that the media generally presents an image of the world that does not reflect reality.
· Television images are an exaggeration or fantasy of what actually exists.
· There is a disproportionate number of handsome gentlemen, beautiful women, crime, wealth and violence. As a result, people end up perceiving the real world in a distorted manner and viewing actuality through a ‘television perspective.’
· From George Gerbner’s results he placed television viewers into three categories; "light viewers" (less than 2 hours a day), "medium viewers" (2–4 hours a day) and "heavy viewers" (more than 4 hours a day).
· He found that heavy viewers held beliefs and opinions similar to those portrayed on television rather than ones based in real-world circumstances
· Heavy viewers experience shyness, loneliness, and depression much more than light and medium viewers.
· According to him heavy consumption of violence-related television content leads the viewer to believe the world is more dangerous than it actually is, called “mean world syndrome”.
49. Sociological theory of mass communication
1. Social learning theory
· People learn from one another, via observation, imitation, and modeling.
· It includes attention, memory, and motivation
· People learn through observing others behavior, attitudes, and outcomes of those behaviors.
· From observing others, one forms an idea of how new behaviors are performed and these ideas serve as a guide for action.
2. Catharsis
· It is an emotional release
· The theory states that expressing one's aggression and anger should reduce the feeling of aggression.
· The large amount of violence in the mass media is justified by the concept of catharsis.
· Aristotle told that viewing tragic plays gave people emotional release from negative feelings such as pity, fear, and anger.
· People feel bad when hero and heroine are disturbed by villain. When the villain is arrested by police or killed by hero people come out of the bad feeling and get relaxed.
3. Agenda setting theory – Refer question number 26
4. Uses and gratification theory – Refer question number 11
5. Cultivation theory – Refer question number 48
6. Spiral of silence
· The spiral of silence theory is a theory which stipulates that individuals have a fear of isolation.
· The social group or the society might isolate, neglect, or exclude members due to the members' opinions.
· This fear of isolation consequently leads to remaining silent instead of voicing opinions.
· Media is an important factor that relates to both the dominant idea and people's perception of the dominant idea.
· The assessment of one's social environment may not always correlate with reality
· The spiral of silence theory suggests that "people who have believed that they hold a minority viewpoint on a public issue will remain in the background where their communication will be restrained; those who believe that they hold a majority viewpoint will be more encouraged to speak.
50. Power of media
·
When we are attracted to advertisements, we may begin to
imagine or visualize using it.
·
The media can give us information to tell us what a
product, service or message is.
·
Media can easily influence people positively and/or
negatively.
·
We also live in a society that depends on the media as a
source of entertainment and information. Indeed, the media images affect both
individuals and society which includes women, men, teenagers and younger
children.
·
It provides an easy means of communication where people
are able to contact friends and family from another side of the world.
·
At the same time, media like television, radio and the
Internet enhance our knowledge by providing access to information from all over
the world.
·
We can also receive different types of news or daily
events through media, almost instantly, for example, through the Internet.
·
Images when seen on TV, newspapers or the Internet by
individuals and “society” in general, can influence viewers to either support
or not support those who are in power. (Jallikkattu protest)
·
It can also be such a powerful educational tool for the
younger generation helping to put them on the right path.
·
First and foremost, they taught us to communicate with
the deaf. It brings out the talents of the people. Television provides a good
influence in education by helping to teach right values.
·
Newspapers not only give information or the latest news.
They also help in the positive linkage between government and the people.
·
Advertisements can be created to convince people to buy
or give support for certain products.
51. Semiotics in advertising
· Semiotics is frequently used in advertising to signify an advertiser's message through the use of signs or symbols.
· In some cases, the sign can be an exact representation of the thing being signified, while in other cases, it may be a symbol associated with it.
Images - One of the most frequent symbols used in advertising is the visual image of the product being sold. For example, a picture of skull and crossbones next to a pack of cigarettes could be used to advertise the harmful nature of cigarette smoking.
Text - One word will convey a message with the same effectiveness as an entire picture. For example, boost is the secret of our energy tells that it gives more energy for the players.
Sound - Symbols do not have to be visual in nature. They can be audible, as well. The jingle is used to attract the target audience and an easy symbol to recall. Example- Airtel music
Process - semiotics employs the use of repeated symbols that come to signify the product. Advertisers do this, not only through repetition, but also through the combining of symbols, bringing words, images and music together into one meaningful and coherent composition.
52. Effects of new media on society
· Internet makes everyone a publisher and a librarian, in that anyone can both produce and retrieve more amount of information.
· The gate-keeping and agenda-setting functions of the traditional media establishments are bypassed in favor of search engines.
· Any person with Internet access can gain information about any issue, event, or place, without the restrictions of time, expense, geography, and politics that used to limit such information gathering.
· By chatting with strangers in chat rooms and reading internationals newspapers online, we believe that we are learning about foreign cultures and perspectives directly from the sources.
· The old media model was: there is one source of truth. The new media model is: there are multiple sources of truth, and we will sort it out.
· The mass media audience is no longer a captive; today's media consumer is unique, demanding, and engaged.
· There is a loss of personal one-on-one interaction
· Mobile phone users can access their emails and videoconference through mobile phone.
· Internet is an important tool to develop the business and transactions
53. Digital media effects
• Media consumers are no longer simply an “audience,” but are now “users” – heralding a new era of active consumption
• Communication and media impact are now multi-directional; two-way sender-receiver models are too linear and orderly to represent these interactions
• While some scholars have found high levels of Internet usage correlate with higher levels of loneliness, anxiety and depression, there may also be social benefits for shy or shut-in individuals who go online
• Media fragmentation (the development of many highly-specialized media outlets) makes targeting audiences easier, but may also make mass communication more challenging
• The increased number of media choices may expose children to adult material before they are prepared for it
54. Effects of new media on society
· Internet makes everyone a publisher and a librarian, in that anyone can both produce and retrieve more amount of information.
· The gate-keeping and agenda-setting functions of the traditional media establishments are bypassed in favor of search engines.
· Any person with Internet access can gain information about any issue, event, or place, without the restrictions of time, expense, geography, and politics that used to limit such information gathering.
· By chatting with strangers in chat rooms and reading internationals newspapers online, we believe that we are learning about foreign cultures and perspectives directly from the sources.
· The old media model was: there is one source of truth. The new media model is: there are multiple sources of truth, and we will sort it out.
· The mass media audience is no longer a captive; today's media consumer is unique, demanding, and engaged.
· There is a loss of personal one-on-one interaction
· Mobile phone users can access their emails and videoconference through mobile phone.
· Internet is an important tool to develop the business and transactions
55. Media effects
Priming
• Media messages may stimulate recall of stored ideas, knowledge, opinions, or experience associated in some way with the message content.
• For example, a news story about the French presidential election might trigger thoughts about the French economy, memories of a trip to Paris during college.
Agenda-Setting
• The media may not affect what people think, but may affect what they think about
• Control of the flow of information is often referred to as “gatekeeping,”
Framing
• Frames are the particular treatment or “spin” an individual or organization gives to a message.
• While agenda-setting is choosing which stories to tell, framing is choosing how to tell them.
•
Frames may “promote a particular problem
definition, causal interpretation, moral evaluation, and/or treatment recommendation”.
Cultivation
• Over time, heavy viewers of television may come to believe that the real world is similar to the television world – heavy exposure to the media cultivates this belief
• For example, based on the proportion among television characters, a heavy user of television might estimate that more than one in ten males hold jobs in law enforcement, when in reality only 1 in 100 do.
Mainstreaming
• Heavy television viewers may lose the attitudes, beliefs or customs of their cultures in favor of those they see repetitively on television.
Disinhibitory effect
• Media’s ability to desensitize people to socially unacceptable behavior, making it either acceptable or desirable.
• The disinhibitory effect may enable people to rationalize or justify actions that conflict with their internal code of conduct or morality.
Mean World Syndrome
• Media consumers may become so overwhelmed by negative portrayals of crime and violence that they may begin—either cynically or despondently—to believe the real world is a mean and harsh place.
56. Explain The linguistic message, A coded iconic message and A non coded iconic message
The Linguistic message
•
The Linguistic message is shown in every image of
communication presented in our culture.
•
Linguistic means the study of natural language and the
meaning.
•
It could be the title, caption, comic books, newspapers,
article, etc.
•
Anything that is familiar or an iconic font can have a
linguistic message.
•
You need cultural knowledge to decode the text to get
that message.
Example:
•
For example DISNEY, if you downloaded that font and type
any text with it anyone who knows that font will still know that font is THE
DISNEY font. That could be the linguistic message you were trying to relay.
The Non Coded Iconic Message
•
The non coded iconic message is the literal visual
message.
•
It could be the difference in using a photograph of the
actual subject to show the message instead of using illustrations, or text to
make a symbolic message.
•
It is used however to support the symbolic message.
•
It is completely spelled out for the audience with no
questioned on what the advertisement is about.
•
Non coded iconic messages tending to be simple and a
little boring.
• Example: Guitar - everyone knows what it is, all you need is to see it and it will make you think of playing it.
• Non-coded iconic messages are important for designers because they allow a medium that can be detached from loaded connotations.
Coded iconic message
• The coded iconic message is the symbolic part of the message
• It brings with it its own meaning and connotation within our social construction.
• Coded iconic messages are extremely useful in design because they allow a great deal of information to be conveyed in a simple, succinct and visually pleasing way.
57. Media analysis
• Make a list of all the different media outlets in your community and the surrounding area.
• Make a second list of statewide media.
• Develop a set of search terms. In this case, you will likely want to include some of the following: education, learning, Act 77, school reform, etc.
• Using Google, Google News, and or the media outlet’s search or archive function, collect a “slice” of media coverage over a set time frame, in this case, the last six months.
• Once you’ve drawn the sample, read and categorize the stories. In traditional media, opinion, news and feature stories are the three primary categories you’ll encounter. Facebook and other social media are also becoming important sources for media analyses.
• You may get some irrelevant articles such as calendar items and obituaries. Be sure to eliminate those to come up with a list of stories that have substance.
• Analyze what you have in front of you. Which outlet or source does the piece come from? Where is it placed, e.g., on a front or home page, in the back pages, at the beginning or end of a newscast? .
• Write a short summary of what you have learned from this exercise. Now you have scanned the media landscape, what are your thoughts about the opportunities you have to introduce our well-framed public story into the public conversation?
58. Marxist approach to media
• Traditional Marxists argue that those who own the media also control it
• They note that the media is owned by members of the bourgeoisie : very wealthy business owners
• They argue that these bourgeois owners instruct editors and journalists to put across particular messages to the audience
• These messages spread the dominant ideology which seeks to justify the power and privilege of the bourgeoisie
• Trough this the media is able to contribute towards creating a false class consciousness
• He argued that the editors and journalists in newspapers and other media organizations depend on the owners for their jobs
• There certainly are examples of owners directly interfering with the content of the media
• Politicians clearly believe media entrepreneurs to have a great deal of control over media content because they try to get on the right side of them
59. Our movies follow cultural adoption
·
From
the times of first movie ‘Raja Harishchandra’ Indian cinema has undergone a paradigm
shift.
·
During
1970s, 80s the villains in movies were mostly zamindars and
industrialists who exploited small farmers and laborer's. This led to
glorification of poverty on screen where poor often fought for their rights and
won.
·
A
large number of Indian families migrated to other nations due to western
movies.
·
Youth
forms the major audience of cinema. The influence of cinema on their lifestyle,
the music they listen to, their dressing sense, eating habits is evident.
·
The
rural population and the elder population remain unaware of most of the
developments in the world of cinema.
·
The
shaping of popular culture, involves an influence of society such as its
language, literature, music, art, beliefs etc.
·
All
over India people dance to Bollywood beats in marriages and parties.
·
Some
people doing Bhangra in South India and numerous people
singing ‘Why
this kolaveri di?’ in North India which shows Indian cinema
reflects what is happening in society and influences the popular culture.
· Today, children and youth greatly admire the display of outfits and style of the actors in the movies.
· Even the modern outfits of actors and actresses enter into our daily life quickly. It shows that Indian cinema impacts Indian culture in different proportions in different regions.
· Movies based on orthodox and regional anti-social activities like child marriage, exploitation, class conflicts, etc have been eye-openers to those who practice.
60. According to Barthes myths were the dominant discourses of contemporary culture
• According to Barthes, myth doesn't seek to show or to hide the truth when creating an ideology
• It seeks to deviate from the reality. The major function of myth is to naturalize a concept, a belief.
•
According to Barthes, myth is based on humans’ history,
and myth cannot naturally occur.
•
There are always some communicative intentions in myth.
•
Created by people, myth can easily be changed or
destroyed.
•
Also, myth depends on the context where it exists.
•
By changing the context, one can change the effects of
myth.
•
At the same time, myth itself participates in the
creation of an ideology.
•
Myth “abolishes the complexity of human acts, it gives
them the simplicity of essences.
•
The power of myth is in its impressive character. It
seeks to surprise the audience.
61. Target Audience
A target audience is the intended audience or readership of a publication, advertisement, or other message.
In marketing and advertising, it is a particular group
of consumers within the predetermined target market, identified
as the targets or recipients for a particular advertisement or message.
Determining target audience
Demographic information
•
Demographic information involves statistical aspects of
consumers such as gender, ethnicity, income, qualification and marital status.
•
Demographic information is important to the business
because it gives a basic background of the customers the business is intending
to aim its marketing campaign at.
•
This helps them to judge on a basic level how to
communicate effectively with who they have identified as the target audience.
Psychographic information
•
It is consumer behavior, style of living and self-concept
to determine how different market segment groups make decisions about a
philosophy, person or product.
•
This information can be utilized by the business to gain
a deeper understanding of the consumer groups they intend to target.
•
Things like financials, interests, hobbies, and lifestyle
will all be filtered by the business to create a target audience.
Behavioural information
•
Consumer behavior is the purchase decision process
•
Behavioral trends could include online purchasing instead
of in-store purchasing
• Audience interests, hobbies and past purchase activity provide a platform on which the business can base their marketing campaign.
Geographic information
•
Geographic information is essentially where the customer
is located
•
This is because customers located in different geographic
areas are going to encounter different things that influence their purchase
decisions.
•
These can be any number of things, including resources,
cultures, and climates
62. Role of cinema in social change (with reference to Tamil films)
· Yes, each film has a social messages which try to make some changes in the society
· Kanaa - The story of a girl whose one wish in life is to make her father smile. It is for this reason that she chooses to play her father's favourite sport - cricket - and win.
· Mersal film exposed the corruption in the medical industry. It said that the medical camp is the biggest scam in our society.
· Theri film tries to stress on the importance of raising our children well and making them responsible citizens of the country. And safety of women.
· Ramana - The film is about a man named Ramana who decides to abolish corruption completely with the help of his ex-students who are working in various government offices
· Vetri Kodi Kattu – this film expressed the poverty of farmers and stressed people should work for our country, not go to foreign countries.
· Anniyan is about how procrastination is plunging our society into an irredeemable abyss
· If Gentleman, Indian and Mudhalvan were about a society widespread with corruption
· Velaikkaran fights against food adulteration committed by high-class companies.
· Sarkar showed the practice of illegal voting present in our country.
· Bigil is the film made to give importance to women empowerment and equality as themes,
· Enthiran 2.0 – how mobile phone technology ruin the environment
63. How to interpret media text?
Rhetorical
•
This model is concerned primarily with communication as
a speech
•
Rhetoric has expanded its area of focus to include
mass communication that attempts to persuade, such as political communication
and advertising.
•
A rhetorical approach to communication might look at who
was speaking to whom, in what context, and to what end or purpose.
Semiotic
•
This model sees communication primarily as an exchange
of signs within a meaning-making system.
•
Signifier and signifies are two
important elements of sign
Phenomenological
•
This model is primarily concerned with communication as
an experience.
•
A phenomenological approach would see communication as
both a representation and a reinforcement of what the communicators see to be
self-evident.
•
A phenomenological approach can take on both
interpersonal and mass communications
Cybernetic
•
This model views communication as a flow of information.
•
This is not just the pragmatic A sends a message to B
type of flow, but also tries to take into account factors which influence and
constraint the flow of information
Psychological
•
This model is concerned with the impact of communication
acts on the individual, particularly their sense of self in society.
•
This model sees communication as representing certain
individual choices made in order to maximize benefit to the individual or
group.
Sociocultural
•
This model sees communication as a way of replicating and
reinforcing the social order.
•
This approach assumes that people in societies have
models of how that society should operate; communication acts to build,
reinforce, and propagate these models.
Critical
•
This model views communication as a set of assumptions
that are open to challenge and negotiation
•
Approaches such as Marxist critique are
representative of this model.
64. Effects of media on individual / society
• Media technologies are becoming an important aspect of today’s society.
• Each and every day, people interact with media of many different forms.
• Media is commonly defined as being a channel of communication such as Radio, newspapers, and television.
• Since many people use media very frequently, we assume that it has affects on people.
• Media effects are changes in knowledge, attitude, or behavior
• Information can be spread after a few clicks of a button, whether it is true, false, speculation or gossip.
• This can affect relationships in various ways, be it between celebrities and ordinary people or between celebrities themselves and their loved ones.
• The media can manipulate, influence, and persuade society, along with even controlling the world at times in both positive and negative ways; mentally, physically and emotionally.
• Controversial stories are reported and printed with no reliance of it being fact or not.
• The public is “meant” to believe everything they’re told and not question it.
• Additionally, as newspapers and magazines have websites, articles can be posted and received quicker than printed articles, and are updated more regularly.
• Today, the media is everywhere, and can easily get to places if needs be in ‘BREAKING NEWS’ scenarios.
• The media can influence the way people are viewed, which means people’s careers can change within a flash.
• The media can also manipulate people in the spotlight to lead their life a particular way
65. Impact of film on society / individual
·
Cinema
can be a very powerful tool. Many leaders have used the power of film to help
achieve their goals. Both Hitler and Stalin used film as propaganda and they
did so very successfully.
·
Cinema
can easily change people’s opinions and their outlooks on life. Good films
almost always impact the viewer
·
There
are also numerous ways in which movies affect society and the modern world we
live in: some of them negative, some of them positive.
·
Films
affect society is by expanding our knowledge of history and culture. An example
of this is the Academy Award winner for best picture “Gladiator”. This film
shows life of gladiators, the political situation of Rome at the time, and the
overall state at which the world was.
·
Another
huge way that movies affect society is through advertisement of different
products in movies. Because when so many people watch the movie, surely some of
them will want to buy the can of Coca-Cola.
·
People
try to mimic things they’ve seen in cinema constantly and in numerous ways. For
example, violence in films is very influential to many young viewers. People
subconsciously try to be like some character they see in a film they very much
like
·
Another
way in which movies affect our modern world is that they help the economy grow
and prosper. For every big blockbuster, action figures are created and
distributed. Fans buy them for aesthetic and collectable value.
·
Films
can also both improve and ruin the health of individuals. Being scared while
watching a horror movie increases heart rate and blood pressure.
·
Films
affect society through giving individual people the opportunity to fantasize
and inspiring them about who they want to be.
·
Currently, movies are the most powerful form of art. Even
though it’s called ‘the seventh art’, cinema is surely the most influential art
form.
·
Movies can affect society in both positive and negative ways.
They can help the economy grow, inspire individuals, and expand our basic
knowledge of the world around us.
·
Movies can also create violence and bad habits, can make
people greedier, and can send a bad message to the public.
·
Individuals must be careful about what they take from movies,
since even the smallest thing can push them to do something bad or to become
someone different. It’s fairly clear that movies affect society very much. Not
only that, they shape the modern world we live in and help individuals develop.
66. Theories of media audience
•
Active audience theory argues
that media audiences do not just receive information passively but
are actively involved
•
Decoding of a media message may therefore be influenced
by such things as family background, beliefs, values, culture, interests,
education and experiences.
•
Encoding/Decoding model and the Uses and
gratifications theory states that audiences are actively involved in
determining what media they engage with and how, in order to gratify specific
needs or desires.
•
The Mass media article refers to a Culturalist
theory, however there is little evidence of its use in relation to (mass)
media.
•
An active audience does not mean that media effect or
influence is not possible.