PART - A
11. Depth of field – It is the distance between the nearest and farthest object in a scene, that appear acceptably sharp in an image. Depth of field can be deeper depth of field or shallow depth of field.
12. Focal length – The distance between the center of the lens and the film is called focal length of lens. The focal length of lens determines the size of image.
13. Flash – It is a device used to produce artificial light. It is used to take photo during low light situation.
14. Fill light – It is placed opposite to key light. It controls the shadow produced by key light.
15. Key light – It is the main source of light used to illuminate the object. In indoor shoot, the key light is lamp/light, outdoor sun is key light.
16. Focus – The light from the lens that forms a clear and sharp image is called focus. If the object is not clear it is set to be out of focus.
17. Negative – It is a sheet of transparent plastic film in which the lightest areas of the photographed object appear darkest and the darkest areas appear lightest.
18. Pixel – It is the smallest picture element joined together and forms an image. Pixel determines the quality of image.
19. DPI or Resolution – Dots Per Inch. Number of pixels in a square inch area is called DPI. It determines the quality of the image.
20. Enlarger – It is a kind of projector used to produce photographic prints from film. It can be used to take big size printing.
21. Photo captions – It is short sentence printed at the bottom of photograph in newspaper. It gives information about the incident in photo.
22. ISO or ASA – International Organization of Standardization or ASA – It is the sensitivity of film. Depends upon ISO or ASA, the film is set to be fast or slow film.
23. Large format – Image size is 4 x 5 inches or larger is called large format. The advantage of large format is high resolution.
24. Bellows – It is folded expandable part of a camera. It allows the lens to move front and back for focusing.
25. Light meter or exposure meter – It is a device used to measure the amount of light. It is used to determine the proper exposure for a photograph.
26. Reversal film – Film that gives positive image directly when processed is called reversal film. It avoids negative making process.
27. Photoshop – It is a photo editing software used to edit photos. Cropping, color correction, transformations can be done in Photoshop.
28. Tele converter – It is a secondary lens which is mounted between camera and lens. It is used to capture long distance object.
29. Ambient light – It means surrounding light. The light that is already present in a scene before any additional lighting is added.
30. Photographic film – It is a sheet of paper transparent plastic film coated on one side. It is a light sensitive material which capture image on it.
31. Properties (Props) – It is an object used on stage during photography. Props can be movable or portable object. Example – table, chair, etc.
38. Telezoom lens – It is used to zoom in and zoom out the object. When we zooming the object looks big and zoom out, the object looks small than its original size.
39. Ansel Easton Adams – He is an American photographer. His photograph widely used in calendars, posters, books and internet.
40. Pinhole camera – It is a simple camera without a lens, but with tiny aperture. Light from object passes through the aperture, a small hole to project on film.
41. Filter – It is fixed in front of lens. It is used to reduce glare and improve saturation.
42. Photo paper – It is used to print photo. Photo paper has shiny surface and usually A4 in size.
43. Light box – It is to take pictures of small to medium size. A box with light used to take photograph.
44. Snoot – It is a tube shape object that fits over studio light. Snoot is used to control the direction of light.
45. Diffuser – It is a device used to spread out light to give soft light. It is done with the help of any white material.
46. Red eye – The red colors appear in the eyes. It happens when using flash very close to lens in low light.
47. Auto focus – The auto focus mode in camera makes the object clear automatically in any lighting situation. It prevents the object in out of focus.
48. Motion blur – It is used to show the movement of an image in photo. The foreground object is clear and the background is blur.
49. F-stop – It is also called aperture which controls the amount of light entering camera. Different f-numbers are f/1.4, f/2, f/2.8, f/4, etc.
50. Exposure – The amount of light reaching the photographic film is exposure. It is determined by shutter speed and aperture.
51. Indoor light – The light which is used inside studio is indoor light. Three point lighting technique is an indoor light used to take photograph.
52. Sensitivity – Photographic film is light sensitive material. The image is exposed onto film.
53. Dark room – It is a light proof room used to handle photographic film and paper. Film exposing and developing are done here.
54. Developing – It is the process of developing film and photo. While developing the exposed image on the film and photo paper come out.
55. Washing – The developed film and photo paper is washed with water. It is to remove chemicals over film and paper.
56. Fixing – The washed film and photo paper is placed in fixer. It is to avoid over developing.
57. Drying – The developed film and photo paper are hanged for drying. It prevents film and photo from getting damaged.
58. Outdoor light – The light which is available outside the studio is called outdoor studio. The natural light such as sun, moon are outdoor lights.
59. Trimming – Removing unwanted areas in photograph is trimming. The crop tool is used to trim image.
60. Film speed – How fast a film gets exposed to light is film speed. ISO in camera is used to measure the sensitivity of film.
61. Photo feature – Collecting, editing and presenting photo in order to tell a news story is photo feature. This image has meaning of a recent event.
62. Pen camera – The camera which is attached with pen is pen camera. It is used in investigative journalism to find out the truth.
63. Hasselblad – It is a camera manufacturing company. They produce medium format cameras.
64. Casting – It is the process of selecting actor or actresses for photographing or filming. It is done through auditions in front of director, producer, etc.
65. Shutter speed – Shutter is a small curtain device which allows light enter into camera. Different shutter speeds are 1 sec, 1/30 sec, etc.
66. Gorillapod – It is a kind of tripod used to take photograph. It is flexible and portable.
67. Lens flare – It is an effect where light is scattered in a lens system. It can be done in bright light.
68. Mega pixel – Millions of pixels are present in photo is called mega pixel. This mega pixel determines the quality of image.
69. Cool light – The color temperature is measured in Kelvin. The color temperature around 5000K to 6500K is cool light.
70. Warm light – The color temperature is measured in Kelvin. The color temperature around 2700K to 3500K is warm light.
71. Define Photography - Photography means writing with light. It is a Greek word photo means light and graph means drawing.
PART - B & C
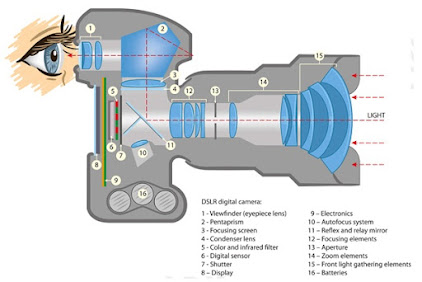
1. Parts and Functions of camera
Lens
The purpose of the camera lens is
to focus and direct the incoming light. The camera lens consists of one or more
precisely shaped pieces of glass or plastic called elements. The light coming
through the elements is "bent" or directed to the image sensor where
the information about the light is captured
Aperture
Aperture is considered to be one of the three pillars of determining the exposure of photographs. The aperture is the opening in camera lens through which light passes through. This part is made up of small, thin blades that shrink or expand depending on how much light want in exposure.
Shutter
The camera shutter is an opaque piece of metal or plastic that controls the amount of light that reaches the camera sensor. The length of which shutter stays open will determine how exposure will look like. It is activated using the shutter release button and adjust it accordingly using camera’s shutter speed setting.
ISO
ISO determines the sensitivity of a digital camera’s sensor to light. The higher the ISO setting, the more sensitive the camera is to light and the more grain that will appear in the image. The lower the ISO setting, the less sensitive the camera is to light and the less grain that will appear.
Viewfinder
The viewfinder is a rectangular-shaped part at the back of camera that used to see and frame the subject. Some viewfinders are fully digital, which shows various details like shutter speed, aperture, and ISO before you take the shot.
Focusing Screen
A camera’s Focusing Screen is the glass surface on which the camera’s mirror projects the image. The focusing screen helps in achieving various focus effects such as sharp and high-contrast shots to blurs.
Digital Sensor
This sensor captures the light coming from the lens to create an image. Modern cameras use charged-coupled device (CCD) as sensor device. The focused light coming through the lens is directed to the digital camera's image sensor. That focused light is "captured" or read by the sensor prior to being stored in the cameras memory card. The image sensor has a grid with millions of microscopic light information gathering elements called "photosites."
Display
The camera display shows the user helpful information about the photos and the camera. Here different camera settings such as exposure, ISO, shutter speed can be adjusted. Most camera displays nowadays show the image before press the shutter release button.
Autofocus System
One of the advantages that digital cameras have over traditional film cameras is their ability to focus on a particular subject quickly and automatically. It sends information to the computer inside the camera and commands the lens to adjust its focusing elements to render a sharp image.
Reflex Mirror
The reflex mirror is found in any SLR or DSLR camera. The reflex mirror is a mirror positioned at a 45-degree angle to reflect light from the lens to the viewfinder, enabling to see what the lens sees.
Zoom Elements
Zoom lenses allow to shift between focal lengths, from wide to telephoto, depending on lens’ focal range, by turning the lens rings.
Batteries
The battery is one of the most important parts of the camera, as most of its components will not work if not powered by one. Having a long-lasting battery lets you shoot more photos.
Memory card
The memory card stores all of the image information, and they range in size and speed capacity. The main types of memory cards available are CF and SD cards, and cameras vary on which type that they require.
Flash
It is a
device used to produce artificial light. It is used to take photo during low
light situation. It can be in-build flash or an external device.
Functions of camera
The
lens, aperture, shutter speed, ISO, and imaging sensor are the primary
components of capturing photographs. Light reflected from an object enters the
camera. The light passes through lens. The lens used to focus the object. The
view finder used to view the object. The aperture determining the amount of
light to the shutter speed allowing light into the camera. ISO is used to
control the sensitivity of the sensor to light, and the sensor’s pixels record
the light information to capture an image. When we click the shutter release
button, the shutter opens and the image is captured onto memory card.
2. Comparison between human eye and camera
|
Human eye |
Camera |
|
Lens – The thickness of the lens can be
altered to control the focus of eye. |
Lens – It forms an image onto film or
memory card |
|
Pupil – Light enters the eye through this
opening |
Aperture – It controls the amount of light
entering into the camera |
|
Iris – It controls the size of pupil |
Diaphragm – It controls size of aperture. |
|
Choroid – It helps to focus light on to
retina. |
Memory card – captured images are stored
here. |
|
Retina – Images are formed here and send
the message to brain |
Black paint – It prevents unwanted light
entering cameras. |
|
Function - The light reflected from an
object controlled by iris and pupil. The light passes through lens and reach
retina forms an image.
|
Function - Light reflected from an object
entering into camera through lens. The aperture and shutter speed settings
are controlling the amount of light. The focusing device used to focus the
object clearly. When we click the shutter release button, the image is formed
on to film or memory card. |
· Wedding photography – photograph taken during wedding function is called wedding photography. It is focused on bride, groom, audience and the formalities of wedding.
· Wildlife photography – photograph is taken in forest. It is focused on capturing reptiles, animals, etc.
· Sports photography – it covers sport event. It is taken during live match. They cover players and their actions, audience, emotions, etc.
· Environmental photography – it covers the environment around us. It is focused on cleanliness, health, etc.
· Fashion photography – it is focused on costumes, models, dressings, styles.
· Architectural photography – taking photos of mosque, church, temple is called architectural photography. It establishes beauty of architectural designs.
· Industrial photography – it is focused on the work done in industry. It covers machines, products, working methods, etc.
· Landscape photography – it covers the elements which are available in land. It includes mountain, trees, land, water bodies, etc.
· Food photography – it is taken during cooking competition, in food festivals, hotels, etc. It is used to capture decorated food items in a nice way.
· People photography – it covers the group of people and their movement, reactions, attitudes, etc. We can cover it in market places, bus stops, railway stations.
· Child photography, news photography, advertising photography, portrait photography, etc are other types of photography.
4. Types of camera
Simple camera
· It is easy to use and for taking photos.
· There is no focusing adjustment in lens and controlling the amount of light.
· The lens forms a tolerably sharp image of subjects.
· No shutter speed or aperture controls are provided.
· Pictures can be taken only on bright environment
Pocket camera
· Easy to use.
· It has automatic exposure control, shutter speeds and aperture setting.
· The film loading operation is easy.
Compact camera
· It has a non-interchangeable lens.
· It has automatic focusing and exposure.
· It has flash unit.
Twin
Lens Reflex Camera (TLR)
· It has two lenses, one above the other.
· The bottom lens is the main lens for photographing; the top lens is for viewing.
· Both lenses are mounted on the front panel of the camera body, which can be moved forward or backward until the image gets sharp.
· Viewing, composing and focusing become easier and more accurate.
· The lenses are not interchangeable.
· The light passing through the viewing lens gets reflected by front mirrors and falls on a ground glass screen.
· The photographer looks into this camera from the top.
The disadvantages of TLR cameras
are, presence of error called ‘Parallax error’. The actual picture is slightly
different from what is seen in the view finder screen. It is difficult to focus
in dull light conditions.
Single Lens Reflex Camera (SLR)
· Generally SLR cameras take 35mm films.
· In SLR camera the viewing lens and the main lens are same.
· Hence parallax error is avoided.
· What you see through the viewfinder, the lens is exactly capture.
· The image through the lens is reflected by a front-surface mirror and is seen through the finder for viewing.
· When the shutter release button is pressed, the shutter opens and closes thereby the film gets exposed.
· The shutter is in the form of horizontally or vertically travelling screen situated just in front of the film surface.
· SLR cameras can take up different lenses like wide angle lens, telephoto lens for different types of photography.
· Varying shutter speeds helpful to take good action pictures.
· Apertures are available to produce good sharp image.
· It is easily and quickly focused, which makes it good candid photography.
The disadvantages
of SLR is heavier and less compact. It is also more complex and chance for
break down. It makes a loud click when a picture is taken.
5. Different aperture settings
· Aperture determines the amount of light entering into the camera.
· Different f-stop numbers are f/2, f/2.8, f/4, f/5.6, f/8, f/11, f/16, f/22.
· If the f-number is small, the opening in the lens is big which allows maximum amount of
ight.
· If the f-number is high, the opening in the lens is small which allows minimum amount of light.
· Small f-number is used during low light and big f-number is used during high light environment.
Depends upon the lighting the f-numbers is set.
6. Different shutter speed
· The shutter speed controls the length of time light is allowed to enter into the camera.
· The shutter—which can open and close in a fraction of a second.
· For example, a shutter speed of 1/500th of a second means that when you take a picture, the shutter will be open and the camera will be exposing for exactly 1/500th of a second.
· The shutter speed range varies from 1 second to 1/8000th of a second.
· Some cameras have shutter speed setting called “bulb,” or B-mode where the shutter will stay open for as long as the shutter is closed.
· Faster shutter speeds used in freeze action and slower shutter speeds used to create motion blur.
The ISO range from 100 to 3200 or higher. ISO100 will require more light and ISO 3200 require less light to make a photo. High ISO produces noisy photograph.
HIGHER NUMBER = HIGHER
SENSITIVITY TO LIGHT
Ø ISO 100–200: used in Bright, sunny environment.
Ø ISO 200–800: used in Indoors or outdoors with less light
(very cloudy, in the shade, twilight hours, and so on).
Ø ISO 800+: Very Low-light situation (darker).
8. Focal length
·
The distance the center of the lens and the
film is called the focal length of the lens.
·
Some lenses have fixed focal length and zoom
lenses have varying focal length.
·
The focal length of a lens determines the
size of image.
·
The longer the focal length the image is
magnified, the shorter the focal length, the image size is small.
9. Types of lenses
Normal Lens
The lens that most closely approximates the views of the unaided human eye is known as a normal focal length lens. For 35 mm camera format which gives a 24x36mm image. It produces brighter and sharper images. A simple lens consists of a single piece of glass, with one or both surfaces curved. Simple lens is a convex lens.
Wide Angle Lens
Lenses with shorter focal length are called wide angle lenses.
a) The object appears smaller and seems to be farther away.
b) The foreground and the background are more emphasized
c) A strong impression of depth is created.
d) It is useful where the area to be covered is wide and
space between the object and the camera is limited. Ex- covering wedding inside
a small hall.
Telephoto
Lens
It has longer focal length.
a) Distant objects are seen nearer and bigger
b) Angle of view is less.
c) Depth of field is less.
We have tele-lens up to F2000mm. These lenses are useful to compress distance, to create beautiful effect with the foreground and background out of focus. Hence focusing must be accurate and tripod is essential.
Zoom lenses
Zoom lenses cover focal lengths from a moderate wide-angle to a moderate telephoto; Zoom lenses are generally larger and heavier. It does not offer as large a maximum aperture, typically f/4. The image quality of zooms is generally slightly less.
Fisheye lenses
· Depth of field is the distance between the nearest and farthest object in a scene that appears acceptable sharp in an image.
· The camera focused on the grass at 7 feet, animal at 10 feet, and the mountain at 30 feet are acceptably sharp in the photograph.
· The depth of field is set to be 7 feet to 30 feet.
· Shorter focal length will give more depth of field.
·
Here no object is in out of focus.
·
Aperture setting, shutter speed, focal length
of the lens are all involved in getting greater depth of field.
11. Rule of Thirds
12. Types of camera flash
Built-In & Pop-Up Flashes – It is constructed within the main camera body. This flash fires the light directly at the subject. They are on-axis with the lens, so it causes harsh contrast and hard shadows.
The Dedicated Flash – It fits into the camera's hot shoe (that slot on the top of the camera body). It is a great piece of gear that communicates with the camera. In combination, the camera and flash use information about lens length, ISO sensitivity, f-stop and shutter speed to determine optimal flash-strength output.
A Ringlight Flash fits on the barrel of the lens by screwing onto the attachment threads. It provides a soft, diffused light source that is ideal for Macro Photography.
A Hammerhead Flash is a flash unit that is separate from the camera and is not attached to the hot shoe; it screws into the camera’s tripod bushing. The flash unit sits to the side of the camera and it off-axis just enough to limit red-eye in the subjects.
The Fill-In Flash isn't a separate flash unit, but rather a technique used when the background is much brighter than the subject, or the lighting is high levels of contrast on the subject.
Bounce Flash is also a technique, not a flash unit. When you bounce the flash off of a surface to illuminate the subject instead of the direct. You need a dedicated flash unit to bounce the flash off the ceiling or a nearby wall.
13. Whit balance modes
· Auto – The Auto setting helps in adjusting the white balance automatically according to the different lighting conditions, but you can try other modes to get better results.
· Tungsten – This mode is used for light under a little bulb like tungsten, and it is often used while shooting indoors. The tungsten setting of the digital camera cools down the color temperature in photos.
· Fluorescent – This mode is used for getting brighter and warmer shots.
· Daylight – This mode is for the normal day light setting, while shooting outdoors. Many cameras do not have the Daylight mode.
· Cloudy – This mode is ideal for while shooting on a cloudy day. This is because it warms up the subject and surroundings and allows you to capture better shots.
· Flash – The flash mode is required when there is inadequate lighting available. This mode helps pick the right White Balance under low light conditions.
· Shade – It generally produces bluer pictures.
14. Photo editing and manipulation software
·
For editing and manipulating photos Adobe
Photoshop software is used.
·
Crop tool is used to remove the unwanted
areas in the photo.
·
We can resize, rotate, skew, distort,
flipping, clock wise and anti clock wise rotation of photos using free
transformation.
·
Cloning stamp tool is used to copying and
pasting the pixel from one place to another place in photo.
·
Adjusting the color by adding red, green,
blue, cyan, magenta, and yellow in photo using color balance option.
·
Different selection tools are used to select
particular portion in a photo for color correction, deletion, and moving the
selected portion.
·
Brightness and contrast option is used to
change dull photo into brighter.
·
Layers are used to keep the different
elements of photos in different layer for easy editing.
·
Various filter effects such as blur,
artistic, strokes, lighting effects can be applied to photograph
·
Save and save as options are used to save
file in different file formats such as JPEG, PNG, TIFF, GIF
·
Image size option is used to change the size
of the file
·
Slicing tool is used to slice the photograph
into different parts to reduce the image size and use it in web design.
15. Factors involved in composition of photograph
The placement or the arrangement of object within the photographic camera frame is called composition
(a) Rule of thirds
· Rule of thirds is mentally dividing the picture area into 3 equal parts vertically and horizontally
· Compose the most important object in photograph at the intersecting point
(b) Depth of field
· It is the distance between the nearest and farthest object in a scene, that appear acceptable sharp in an image.
· The human eye recognizes the object and mentally separates them
(c) Balancing
· Compose the main object as with the rule of thirds to create more interest
· To balance the weight lesser important object is placed at the opposite side
(d) Lines
· The different types of lines such as straight, diagonal, curves, zig zag, radial, etc. can be used to enhance photo composition
(e) Symmetry and patterns
·
We are surrounded by symmetry and patterns,
both natural and man made
·
They can make far very high catching
composition
(f) View point
·
The place where the photographer will shoot
the photo is view point
·
The photo can be taken from eye level, about
or below eye level, front, back or top of the object is called view point
(g) Background
· Choose plain and unobtrusive background to compose the shot so that it does not distract from the object
(h) Framing
· The main object should be framed to get the attention of viewer
· The main object should be isolated from other object
16. Triangular lighting principle (Three point lighting)
Lighting means controlling the light and
shadow
(a) Key light
· It is the main source of light used to illuminate the object
· It shines directly upon the object
· The placement of key light determines the shot
· In indoor shoot the key light is lamp and in outdoor the sun and moon is key light
(b) Fill light
· It is also shines upon the object
· It is placed at the opposite side of key light
· It is placed lower position than key light
· It controls the shadow produced by key light
(c) Back light
· It shines from the back side of object
· It separates the object from background
· It is placed either one side or both side of object
17. Silhouette photography
· The object is seen as a black shape without detail
· Silhouette photo is used to convey drama, emotion and mood of viewers through photos
· High shutter speed and low ISO is needed to take silhouette photo
· Here the object is placed in between the camera and light
· Generally this photo is taken during sun rise or sunset
18. Photo journalism
· Photo journalism that uses images in order to tell a news story
· Photo journalist must be well informed about events happening
· They deliver news that is not only informative, but also entertaining
· The images have meaning in the context of recently published record of events
· The images should be fair and accurate representation of events
· Photo journalist should carry photographic equipment wherever he/she goes
· Photo journalist should know what picture to take, how to take and what pictures to show the public
· Photograph of violence should not publish in the newspaper
· Photo editing using Photoshop should not affect the meaning of photo
19. Elements of photography
(a) Composition
· It is the arrangement of objects in a photograph
· The rule of third involves in proper composition
· This creates balanced and pleasing composition
(b) Texture
· The detailed surface properties of the object present in the photograph
· It can be rough or uneven smooth. Example – stone
(c) Depth
· It is the creation of a sense of three dimensionality in a photograph
· Depth is created using focus framing and angles
· The distance between nearest and farthest object is depth
· The nearest object looks big and farthest object looks small
(d) Line
· Lines are the outlines of object in a photograph
· It guides the eyes of the viewer and gets the attention
· Horizontal lines is used to convey a sense of rest
· Vertical lines used to convey power, strength and growth
(e) Light
· Light and shadow are the most important element of photograph
· Level of height and the angle of light are important while taking photograph
· Different lighting techniques are used to convey mood of the photo
(f) Patterns and shape
· Our mind automatically organize the object we see into patterns and shapes
· It can be pleasing and draw attention to a photograph
· The aspects of patterns and shapes are rhythm, symmetry and trianlge
(g) Vantage point
· It is the position from which the photograph was taken
· Viewing from a low vantage point looking up at an object conveys dominance and power
· Eye level vantage point conveys neutrality
· High level vantage point conveys weakness
20. A picture is worth a 1000 words
· A picture conveys information more effectively than words
· Picture can tell a story effectively
· Graphics can convey ideas more effectively than words
· Drawing conveys stronger message than words
· In order to effectively conveys the health hazards of smoking, cigarette pack contains a picture of diseased lungs instead of using warning message. The photo creates more impact than words. When the cigarette smokers watch the photo, it threatens them not to smoke else you will die. The government of India has instructed to put the photo in big size in cigarette packet
· When we look at the final ceremony of world cup cricket photograph, it tells so many information. When we look at the banner we come to know that it is ICC cricket world cup. Also the banner tells various sponsors of the tournament. The color dress of the players communicate which country they belongs to. The facial expression of the players shows their happiness and enjoyment. They hold the world cup and express their victory through their gestures
· The jallikattu photo tells so many information about the function. It is happening during pongal festival particularly on kanum pongal. It is one of the culture of Tamil people. It is to express the courage of youngsters of Tamilnadu. They grow bulls especially for jallikattu. The owner of the bull offers prize to whoever controls it. Both bulls and participants are injured during jallikattu. The people of Tamilnadu, the neighbouring states and other country people also interested in participating jallikattu
21. Differentiation between film camera and digital camera
|
Film
camera |
Digital camera |
|
It is
not easy to operate |
It is
easy to operate |
|
Immediate
preview is not possible |
LCD
screen is used to see the image immediately |
|
Deletion
of photo is not possible |
If
photo is not good we can delete it |
|
Film
is used to capture photos |
Memory
card is used to store photos |
|
Film
processing and printing is a long process |
Taking
photo and printout is very easy |
|
Maximum
35 photos can be shot in a film roll |
Many
photos can be stored based on the memory card capacity |
|
Film
loading, unloading, processing requires dark room |
No
special requirement is needed |
|
More
risk in handling film roll |
Handling
camera is risk since it is costly |
|
Color
tone is good in printout |
Not
good like film |
|
It is
not depending on pixel |
The
quality of the image is mainly depending on the pixel |
|
Many
operations are manual |
Many
automatic functions are available |
22. Advantages of digital camera
Advantages
· It is easy to operate
· Immediate image review and deletion is possible
· Memory card is used to store many photographs
· Auto focus option is available
· Taking printout is easy process
· Since it is a digital device the color correction and other modification can be done easily with the help of computer
· It is a fastest process of taking and printing photograph
· Nikon and Canon are the main manufacturer of digital camera
Disadvantages of digital camera
· The color tone of the digital camera is low compare to film camera
· Since it has many automatic options the aesthetic composition is missing
23. Photography studio set up or indoor photography
(a) Studio space
·
Medium size studio space is needed to set up a
studio
·
If the space is too small, customer will feel
discomfort
·
The photo shoot place should be separated
from other activities
(b) Ceiling
·
Sufficient ceiling height is must to get
proper bounce light
·
If it is low ceiling, it is difficult to
increase the height of light
(c) Window light
·
The light that comes through the window into
studio room
·
It is soft and even. It does not need for
flash
(d) Ambient light
·
It is extra light that appears in photo
·
It includes window light, room light,
reflections, etc.
(e) Back drop
·
It is background of the image
·
It is clean and simple look
·
It can be plain white, blue, grey colors or
printed graphic designs
·
Photoshop is used to change the back drop of
image
(f) Properties
·
Using props is to add a new element to the
photo
·
It can be clothes, furniture, backgrounds,
etc
(g) Lights
·
It is used to illuminate the object and make
the photo bright
·
In studio umbrella lights, flash lights and
other lights are used
·
It controls the shadow and makes the photo
perfect
(h) Camera
·
It has various types of lenses and focusing
device
·
The flash in the camera is used in darkness
·
Quality camera produces high quality images
(i) Tripod
·
It is used to hold the camera tightly
·
It has three adjustable legs and a head to
hold the camera steadily
(j) Printer
·
Color printer is must to take printout
immediately after photo shoot
·
It satisfy the emergency needs of customers
24. Panorama photography
·
Series of photos are taken and stitch them to
make panorama photo
·
Photo size is big and it can cover 360 degree
angle
·
Tripod is used to maintain the horizontal
level of photograph
·
From the above illustration photo 1,2,3 are
taken separately and joined together to make panorama
·
It is to cover wider landscape area
·
Standard lens is used to avoid distortion
25. Freezing the action
26. Tele-converter
27. Film developing process
· The film is exposed to light
· The developer solution is used to develop the exposed film
· The developed film is washed in water to avoid over developing
· Fixer solution is used to make the image permanent onto film
· After fixing the film it is again washed in water
· Film is dried in a dust free environment
· Once the film is processed it is said to be negative
28. Photographic printing
· The negative film is exposed on to photographic paper which is coated and light sensitive
on one side
· Contact printer or enlarger are used to take printout
· Developer solution is used to develop the exposed photographic paper
· After developing, the photographic paper is washed in water
· The paper is placed in fixer solution to avoid over developing
· The paper is washed in water and dried
Colour
printing
Colour
negative films consist of three emulsion
layers, each sensitive to red, green and blue light. Upon
processing, colour couplers produce cyan, magenta and yellow dyes, representing
the true colours of the subject.
29. Photo essay
· A photo essay is a set of photographs that are made to create series of emotions in the viewers
· A photo essay will often show picture in deep emotional stages
·
It can be photographic works with captions or
full text essays illustrated with photograph
·
It includes an article in a newspaper,
magazine, book and in internet
·
The photo essay is an engaging tool
for teaching students important elements of narrative writing,
media literacy, argumentation, and presentation.
30. Types of filters
(a) UV filter
· It protect the lens from dust moisture and scratches
· High quality UV filters can be permanently mounted on lenses
· It is suitable for all kinds of photography
(b) Polarising filter
· It reduces reflections, enhancing and increasing contrast
· It is circular in shape
· It is used fro all kinds of photography
(c) ND filter (Neutral Density)
· It reduces the amount of light entering the lens.
· Useful for creating motion blur
· It is mainly used to take landscape photographs
(d) GND filter (Graduated Neutral Density)
· It is used in high contrast situation, where the sky is much brighter than foreground
· It is rectangular in shape and used to take landscape photography
(e) Soft GND filter
· It is also used in high contrast situation
· It is rectangular in shape and used with filter holder
· Used to take landscape photography
(f) Reverse GND filter
· It is used to shoot against sun
· It is used to take landscape photography
(g) Colour filter
· It corrects colours
· Some colour filters can subtract colurs, blocking one type of colour and allowing other colours through
· Mainly used in film production
(h) Close up filter
· It allows lens to focus closer on object
· It is used in macro photography – showing smaller object into big size
(i) Special effects filter
· Star filters make bright object look like star
· Softening filters create a dreamy look
· Multi vision filters create multiple copies of an object
31. Special effects filters in photography
Cross star filters
· Star filters, also called cross filters, take a point of light and turn into a star
· One filter may turn the light source into a six point star, others a 4 or 8 point star
· Cross star filters are typically the circular, screw in type
· Cross star filters add a bit of flair to an image, used when there is just one or two light sources
Soft or diffusion filters
· Most of time, photographers are aiming to get that pin-sharp image
· But intentionally rendering an image a bit soft for an artistic effect
· The softening, dreamlike effect they produce is also good for artistic still life images
Centre spot filters
· Centre spot filters are diffusion or soft filters on the edges, but clear in the middle
· The design allows the centre of the frame to remain sharp, while the outer edges of the frame retain the same effect a soft filter has
· Centre spot filters are typically used when the subject is at the center
Fog filters
· As their name suggest, fog filters add fog to an image where there is not one
· Fog filters can be either the square slide-in or the circular screw-in type
· Fog filters are often used to mimic the look of a foggy morning in a landscape, or to enhance the feeling of humidity
Multivision filters
· Multivision filters create cloning effect
· It usually multiplying the subject between 2-6 times
· Linear multivision filters create the duplicates in a straight line, where circular multivision filters make the duplications appear in a circle
Infrared filters
· An infrared or IR filter blocks out all light except for that within the infrared spectrum
· Using the IR filter creates a surreal, dramatic image
· Colours appear much different when reflecting infrared light, skies will appear more dramatic, and skin smoother
· IR filters typically come in the circular, screw-in type
Day for night filters
· Day for night filters take an image shot during the day and darken it while also adding a blue tint, creating the appearance the shot was taken at night
32. Perspectives in photography
It refers to the relationship of imaged objects in a photograph. This includes their relative positions, sizes and the space between the object
(a) Linear perspective
· Our eyes judge the nearest object is big and the farthest object is small in a photograph.
· This is because of the focal length of the lens and the distance between the lens and object
(b) Rectilinear perspective
· Lines that are straight in the subject are reproduced straight in picture
· Panomaric lens produces panoramic perspective
(c) Vanishing point perspective
· In vision lines that are parallel to each other give the sensation of meeting at vanishing points
· When parallel lines are perpendicular to the lens axis.
(d) Height perspective
· Seeing the taller building from the ground is high perspective
· When they look at any temple from bottom to top, it is perspective shows
(e) Dwindling size perspective
· When two people are shown in a picture and one appears taller than other, we assume that one is in reality taller than other
· But actually the taller person is closer and shorter person is farther away from camera
(f) Volume perspective
· When front or side lighting is used the length, depth and shape of shadow provide a perspective of each object
33. Risk involved in wild life photography
· Taking photograph of wild animals is called wild life photography
· Wildlife photographer should be very careful while taking photograph
· While taking photograph maintain some distance from animals
· Reptiles might bite while taking photography
· We won’t get proper food and water in the forest
· There will not be proper shelter facility while taking photograph
· The tele zoom lens is required to take photograph
· We have to walk for long distance for photography
· The whole luggage has to be carried by the photographer only wherever he/she goes
· Heavy rain, fast wind might threat to wildlife photographer
· We need to stay for long days in the forest
34. Visual perception
· Visual perception is the ability to interpret the surrounding environment using light which is reflected by objects
· It is the part of central nervous system which give organisms the ability to process visual detail
·
It detects and interprets information from
visible light
·
There are five senses touch, smell, vision,
taste, hearing which involves reception and transmission of information to
brain
·
The visual sensory input begins in the eye,
where the light is detected by neurons, its proceeds to brain
35. Principles of photography
(a) Balance
· Arranging the elements in an equality from one side to another
· A symmetrical image has perfect balance
· Balance can be achieved by asymmetry balance
(b) Harmony
· It is a consistent, order and pleasing arrangement of object
· This happens by using similar elements in photograph
(c) Rhythm
· It is simply repeating an element (pattern)
· This will cause viewer’s eye to move around to each element
(d) Unity
·
The image could be separated into each part,
but together they become a unified object
·
Unity can be achieved by proper composition
(e) Contrast
·
Contrast is created in an image by using
light and dark
·
It can be applied to overall image
(f) Proportion
·
It is using the size of an object to give it
more or less importance
·
The more important object is composed in big
size than less important object
(g) Variety
·
It is having different object in photography
·
Having some object at the left side and some
other object is variety
(h) Movement
·
It makes the viewer’s eye to move around the
photograph
·
It leads the viewer’s eye all around the
photo and land on focal point
36. Accessories needed for outdoor photography
Taking photo outside studio is called outdoor photography. It can be landscape, wildlife photography
(a) Camera
·
We need to take DSLR camera to take photo
·
The working system of the camera is ensured
before taking it for outdoor shooting
(b) Lens
·
We can take wide angle lens to take
landscape, telephoto lens to cover long distance object, and also
tele-converter and macro lenses for covering small size objects
(c) Tripod
·
Tripod or any other camera mounting device
should be taken
·
Particularly in wildlife and panoramic
photography we must need camera stand
(d) Filters
·
Polarizing filter is used to manage
reflections and GND filter is used to control light.
·
Many other filters are also used to take sky
and creating dramatic effect
(e) Lighting
·
External flash units use to produce during
low light situation and reflectors to control light.
·
Extra battery also should be taken for
outdoor photography
(f) Camera bag
·
Quality camera bag is used to carry camera
and its
·
It safeguard the equipment's from rain, hot
sun, etc.
(g) Miscellaneous
·
Field guide, trucking materials, medicines,
bed sheet, and other necessary materials should be taken for outdoor
photography
(h) Flash
·
External flash and light control equipment is
essential for outdoor photography
37. Usage of mobile phone cameras in daily life activities
· Mobile camera is used to take photograph like DSLR camera
·
It is used in the absence of DSLR camera
·
Mobile camera has flash unit to take photo in
low light situation
·
It is used to take photo of other person as well
as selfie
·
It is easy to carry and use than DSLR
·
High mega pixel mobile camera produce quality
images
·
Mobile camera is used to take motion picture
·
It records visual as well as sound
·
Colour adjustment, cropping, lighting
controls also available in mobile camera
38. Changing trends in photography in India
1. Phoneography
Cameras, smartphones,
and tablets have begun to rival professional cameras in terms of quality and
software. Any individual with a smartphone or a tablet can easily capture an
image, edit it, and post online on various social media websites.
2. Macro Photography
Fascination with science
and improved camera technology now allows people to take extreme close-up shots
of insects, plans, and other never-before-seen images.
3. HDR Photography
High Dynamic Range
photography allows cameras and images to display greater luminosity that is
closer to what the human eye can see. This has become quite popular among
photographers.
4. Retro-Style Photography
From black and white to
sepia, the clarity of modern photography has pushed people back towards classic
photos, and the depth behind them.
5. 360 Panorama
Now that software can
correct for the unsteady hand, panoramas that capture a 360-degree view of a
location are becoming popular Day by day.
6. Point and Shoot Size DSLRs
Professional cameras are
becoming smaller and nimbler, which is attracting not only photographers, but
also traditional consumers.
7. Drones
Drones are also a
popular new photography style, used not only for casual shots, but also at
weddings to capture the beauty of the venue. It is especially popular in the
real estate industry.
8. Selfie
The "Selfie"
has become one of the most well-known trends in photography, but the Selfie
Stick allows people to also take group shots of themselves, making it possible
to capture an entire group without a photographer out of the picture.
39. Types of lighting
1. Flat light
·
When
the light source facing directly at the front of the subject, this is flat
lighting. Flat lighting on a face will mean that the subject is well lit and
unable to see any shadows along their face.
2.
Broad light
·
With
broad light (a type of side lighting), the face of the subject is at an angle
and the most well-lit side of the face is closest to the camera and the shadow
falls on the back side of the face.
·
This
type of light can make a face look fuller so it’s ideal for those with very
narrow faces.
3. Short light
·
Short
light is the opposite of broad light in that the face is at an angle and the
shadow falls on the side of the face closest to the camera.
·
One
thing to keep in mind is that shadows draw out textures and imperfections.
4. Split light
·
Split
lighting is another type of side lighting but it is defined as light that hits the
subject from the side at a 90 degree angle.
·
We
can easily recognize split lighting in an image by half of the subject being
lit and the other half in the shadows.
5. Backlight
·
Backlight
is just that, light that comes from behind the subject.
·
Sources
of backlight can include a window behind the subject.
·
It can be used to create silhouettes, or you
can combine it with certain atmospheric conditions–like fog–to get more
dramatic images
6. Rim light
·
Rim
light falls under the backlight category but deserves a spot of its own.
·
With
rim light, comes from behind only highlight the edges of your subject
·
This
is great to use when you need to separate your subject from the background.
7. Butterfly light
·
The
light is placed above and in front of your subject to create a small shadow
under the nose resembling a butterfly.
·
This
type of light beautifully highlights prominent cheekbones which is why you most
often see it used on women.
8. Loop light
·
The
light is about 45 degrees to the side and slightly above eye level.
·
This
position of the light creates a shadow just under and to the side of one
nostril and the nose.
9. Soft light
·
Soft light is light where shadow edges are soft and open,
and there is less contrast.
·
This type of lighting can be achieved by diffusing the
artificial light.
·
Soft light is used mostly for portraiture, macro, and
nature photography.
10. Hard light
·
Hard light is the opposite of soft light
·
It creates strong shadows and high contrast.
·
It creates more dramatic images.
40. Double and multiple exposure
·
It is more than one exposure in photography
·
It is a kind of superimposition effect
·
We can see two or more images simultaneously
in a photograph
·
Superimposition of 2 images to create single
image is double exposure
·
Superimposition of more than 2 images to
create single image is multiple exposure
·
Camera shutter is opened for exposing many
times
·
Medium light to low light is used to take
double and multiple exposure
41. Visual story telling
·
Telling story with the help of visual (photo)
is visual story telling
·
Single photo or sequences of photos are used
to tell the story
·
In cinema expressions convey story
·
Teacher teaches story using pictures to
children
·
It is one of the effective way to convey
messages even to illiterate people
·
It is easily remember by the receiver for
long time
·
Visuals convey story (message) with the help
of emotions, costumes, properties, etc.
42. Advertising photography
· Taking photo to advertise a product is advertising photography
· The products are photographed in various angles and shots
· Models are photographed beautifully to attract the audience
· Without photograph an advertisement does not look nice
· Photo occupies more space in advertisement than text
· It can be outdoor shoot or indoor shoot
· Photogenic faces are used as advertising models in advertisement
· Big companies use cinema artist and sports players as models
· The model selection should e suitable for the product being advertised
· Photographer, make up man, costume designer and lighting director are all involved in taking advertising photography
· Advertising is not effective without photo
43. Motion blur in photography
·
If the subject or the camera moves during an
exposure, the image gets blur
·
In this the object looks clear and background
blur
·
It gives the feeling of movement
·
Slow shutter speed is used to get motion blur
44. Functions of exposure meter or light meter
· The handheld meter is the necessary norm, to know what lights are doing.
· It is used to measure the amount of light required to take photo
· It is useful to get correct exposure in taking photo
· Some camera has built in light meter
· Incident light meter is used to measure the diffused light
· Reflected light meter is used to measure reflected light
· A light meter can read the ambient light in a scene, or the direct light from a light source and calculate the correct shutter speed and aperture values required to capture an accurate exposure.
· The simplest technique is to hold the light meter out in front of the camera, making sure that the same light falling across the scene also falls on the lumisphere. Then press the meter button. Read the results on the meter and set your camera's shutter and aperture to match
45. Process involved in color photography
·
Color photography is photography that
uses media capable of reproducing colors.
·
In color photography, electronic sensors or
light-sensitive chemicals record color information at the time of exposure.
·
This is usually done by analyzing the spectrum of colors
into three channels of information, one dominated by red, another by green and
the third by blue, in imitation of the way the normal human eye senses color.
·
The recorded information is then used to reproduce the
original colors by mixing various proportions of red, green and blue light
·
Monochrome images which have been "colorized"
by tinting selected areas by hand or mechanically or with the aid of a computer
are "colored photographs", not "color photographs".
·
Their colors are not dependent on the actual colors of
the objects photographed and may be inaccurate.
·
Color photography has been the dominant form of
photography since the 1970s, with monochrome photography mostly relegated to
niche markets such as art photography.
46. Special effects technique in photography
Repeat One Subject in One Photograph
Include Multiple Reflections in One Frame
Distort Your Subject
Use Glass to Magnify
To make a more interesting portrait, ask the person to stand behind a transparent glass like a bottle or a drinking glass. The part of them behind the glass will be magnified, while everything else will look normal.
Shoot Very Long Exposures
Long exposures, when done well, can provide abstract results. For instance, fast-moving subjects (like waterfalls or speeding cars) can be made to look like unrecognisable blurs, whereas slowmoving subjects (like leaves swaying in the wind), can look like wavy patterns. All you need to do is choose the appropriate shutterspeed.
Explore Multiple Light Sources
Toss Your Camera
Break up R, G and B
Another simple and fun technique is the
‘Harris Shutter effect’, where you need to expose one frame thrice—one with the
red filter on, the other with green and the last one with blue. Any still
object in the frame will be rendered in neutral colours, and all moving objects
will have vivid colours (R, G or B). This is why it is also called the rainbow
or the tri-colour effect. It works best when you have moving water, clouds or
even traffic in your frame.
Try Flash Pumping
47. Image stabilizer or vibration reduction mode in taking photography
Optical Image Stabilization helps produce clear, blur-free images by reducing the effects of camera shake when hand-holding a digital camera.
Continuous Image
Stabilization
·
When a digital camera is set to Continuous Image
Stabilization mode, IS is always on. It keeps an image stable when viewing it
on an electronic viewfinder or LCD.
·
Continuous IS is effective for shooting video and is
usually enabled by default when switching to movie mode.
·
Continuous IS is also helpful when hand-holding a camera
to frame a long telephoto shot.
·
Digital cameras with shoot Only IS mode offers the
greatest degree of stabilization. It is activated the moment the shutter button
is pressed. Because Image Stabilization is enabled only when the shutter button
is pressed, Shoot Only mode generally produces slightly sharper photos than
Continuous IS.
Hybrid Image Stabilization –helps prevent
image blur during macro photography, counteracting
angular and shift shake that becomes more pronounced when taking close-ups.
Panning Image Stabilization
·
Moving a camera in the same direction as a moving subject
is called panning.
·
The technique produces images with the subject in sharp
focus and the background blurred.
·
Panning IS mode only makes adjustments for vertical
movement and is activated, automatically on some models, when the camera shakes
up and down.
Digital image stabilization – to minimize
the effects of camera shake, digital IS increases the shutter speed by boosting
the ISO sensitivity. However, when ISO is increased, so does noise in images.
Dual image stabilization – Dual
image stabilization combines optical IS and an increase in ISO.
Vibration Reduction (Nikon) and Image Stabilization (Canon) is the name of a technology that helps stabilize the lens movement associated from hand shake. These stabilizers help eliminate blurry photos resulting from hand shake or if you’re shutter speed is too slow. It counter-balances motion, just like noise cancelling headsets counters noise.
According to Nikon, vibration reduction can
provide a 4 stops slower shutter speed than a lens without vibration reduction
and still yield a tack sharp image. Vibration reduction works well,
allowing to take extremely slow shutter speed shots hand held that are still
tack sharp. Without vibration reduction would certainly require use of a
tripod. Vibration reduction is an absolute must when doing ring shots with our
macro lens
· M mode is called as manual mode
· Photographer should choose correct aperture
· Based on the availability of light the setting is done
· Different manual settings of an object gives different output
· Different shutter speeds have been used to take varieties of photos
· ISO settings also important in different lighting situations
· Manual-enabled modes give the photographer control over the various parameters of an exposure.
48. Emergence of mirror less camera
· As the name suggests, a mirrorless camera is one that doesn't require a mirror
· In a mirrorless camera there is no optical viewfinder. Instead, the imaging sensor is exposed to light at all times
· This gives a digital preview of image either on the rear LCD screen or an electronic viewfinder (EVF)
· Technically, a point-and-shoot is a mirrorless camera
· The term “mirrorless” is generally used to describe digital interchangeable lens camera (ILCs) that either have electronic viewfinders or simply no viewfinder, and that’s how we’ll be using it here
· Mirrorless cameras can be made much smaller than their DSLR counterparts
· Mirrorless cameras have now grown on professionals as they offer additional advantages not found on DSLRs
49. A photographer should have a sound knowledge in software tools – why?
After taking photograph there may be a need of doing some modifications in it. So the photographer should have knowledge of software tools
· The crop tool can be used to create an entirely new composition by removing the unwanted areas in the photo.
· Brightness and contrast adjustments can be a valuable tool in finding and correcting flaws in exposure.
· Curves and levels allow making much more targeted, finely tuned adjustments of colors.
· Each layer contains data. How much of that data is visible is based on each layer’s opacity and blending mode.
· When apply sharpening, it means increasing edge contrast. This means that small/fine features stand out more.
· The clone stamp and healing brush are two of your most important friends when it comes to removing unwanted elements from your image.
· Color balance addresses how the existing colors interact with each other.
50. Is photography science or art
(a) Photography is an art
· Producing visual object to give aesthetic enjoyment is art, so photography is an art
· Proper composition makes a photo beauty
· Colour in photo is another beautiful factor
· Communicating a message through photo is an art
· Different photography such as portrait, landscape, wildlife, etc gives different feelings to its viewers
· Photo in big size give happy feeling than in small size
· Same subject can be photographed in different way by different photographers
· Lighting plays an important role in taking photograph of different moods
· Appropriate camera shots and angles use to take photo aesthetically
· Photographs hang on the walls of people’s homes, businesses and galleries can be seen differently by different people, creating emotional responses in the viewer
(b) Photography is science
· Taking photograph involves calculation, so it is science
· Learning about lens is science
· Aperture, shutter, and ISO which determines good photograph
· Setting, adjusting and controlling of light is an important factors of photograph which is science
· Some principles and rules such as balance, rhythm, unity, rule of thirds have to be followed while taking photo.
· Light is made up of tiny packets of energy called Photons. These Photons have certain wavelengths based on their energy levels which the human eye perceives as different colors
· The eyes themselves use lenses and apertures to focus an image of the scene before them onto the retina
· Use specific cells for color and intensity the light is converted to an electrical signal to the brain to process and create the image we see before us
· Red, Green and Blue colors cover the spectrum of white light and can be combined to make the colors and shades in between
51. Types of lights
Natural
light
·
It a light that comes by nature such as sun
and moon light
·
Natural light mainly used for outdoor
photography
·
We can control light with the help of white
material such as thermacoal, white paper, etc
·
Sun light is used for day photography and
moon light for night photography
·
It produces different contrast of light
Artificial
light
·
It is mainly used for indoor photography
·
It is used when no natural lights are
available
·
It can be light bulbs, fire, etc
·
Light meter is used to measure light
·
We can produce different mood in photo using
artificial light
52. Advantages and disadvantages of natural and artificial lights
Benefits (advantages) of Using Natural Light
· One advantage of natural light is that there is no need for fixing.
· Another advantage is that it is almost everywhere in the world
· Also since it is a natural light it is free since the light does not belong to anyone.
· Natural light is self generated so you don't need a switch to turn it on and off.
· One of the Natural lights comes in many different examples such as sun, moon, fire, and lightning.
· The biggest benefits of using natural lighting is that it is free, abundant, and very easy to find.
· There’s no need to make huge investments in lighting equipment
· Reflectors and diffusers are used to bounce or manipulate the available light.
· It’s generally recommended that beginning photographers start experimenting with natural light before introducing artificial light to help understand how light works.
Cons (disadvantages) of Using Natural Light
· Sunlight varies greatly.
· Depending on location, season, weather, and time of the day, natural lighting can produce differing colors and contrast in images.
· For example, midday sun tends to produce neutral white colors and extremely high contrast, while golden hours of sunrise and sunset have very warm colors and medium contrast.
Benefits (advantages) of Using Artificial Light
· Artificial light is a light source that is available at any time of the day
· Don’t necessarily have to plan photo shoot around the weather, or availability of sunlight.
· Depending on the artificial light source you choose, sunlight or even moonlight can be replicated
· There’s a wide range of artificial lighting gadgets available for photographers
· LED lights that have simple dimming switches.
Cons (disadvantages) of Using Artificial Light
· It takes some time to set artificial lights.
· Unlike the sun, artificial lighting costs money
· Professional grade artificial lighting sources will also need to be held in place with light stands, and possibly even modified with umbrella, beauty dishes, and soft boxes.
· There are also other accessories needed such as batteries or power cables and plugs, and you’ll need a dedicated studio or space to set your lights up.
53. Freezing an object
1.
Shutter speed
·
When the moving subject is shoot, the shutter speed
should be fast.
·
It must be at least 1/500th of a second or higher.
·
Fast shutter speeds limit the amount of light that comes
into image sensors, so the higher shutter speed is, the more likely that your
pictures would be dark.
·
It would not be a problem in outdoors
2.
Increasing the aperture
·
The aperture is the hole where light comes into your
camera into the image sensor.
·
Choose a low f-stop to open up the aperture and allow
more light in.
·
This will help you counter the low light you get from the
fast shutter speed.
3.
Use a flash
·
Flash is used to counter the low light conditions when
using a faster shutter speed.
·
It is extremely easy to correct dark photos by using
flash.
·
Flash must not be more than a few feet away from the
subject to benefit from it.
4.
Use a high ISO
·
Using high ISOs can usually result in a grainy picture
with a lot of digital noise.
·
The secret to getting a sharp focus on a moving subject
is to increase the shutter speed and correct the dark photos by using flash,
increasing the aperture or using a high ISO speed.
54. Photo feature
· Feature story in Journalism refers to any human interest stories / soft news
· Features discuss various topics, from travelogue, how to recipes, services, gadgets, etc.
· It need not necessarily focus on any current or latest issues and portrays the writer’s point of view
· Photo features consists of a series or collection of photo which are interwoven to convey a story without any need for captions to convey through words
· Photo features appears in newspapers, magazines and web contents
· These photo don’t need any words to explain since they speak for themselves
· A feature photography might be described as a news image that supplements the headline stories
· When an important person or significant event has recently been in the headline news, an editor may decide to run a feature article based upon the background to the original story
· A feature photographer might therefore seek to show a particular person at home in their family environment, perhaps talking about their lives and how events led to their appearance in the news headlines
55. Types of film used in photographic process
(a) Roll film
·
Produce
normally 12 shots of square negative per roll
·
Depending
on the frame size of the camera the small roll produces 8 shots or 16 shots
·
The
total film length is same in all cases. It is divided into 12 or 8 or 16 shots
·
Big
size print out can be made easily from the bigger negatives
(b) Cassette film
·
This
is film is available for any length in loose condition form bulk film or in cut
and ready to load condition, packed in cassette.
·
The
film is packed in light tight cassettes which are loaded in the camera
·
After
exposing the complete film, it is wound back into the cassette and taken out of
the camera for developing
(c) Cartridge film
·
These
films are mostly for sub-miniature cameras which use 8mm or 16mm film and have
to be loaded into the camera as such without any need to insert the film lead
into the taking spool.
·
The
cartridge is pushed into the back of the camera and operation started.
·
At
the end the whole cartridge is broken open in the dark room for taking out the
film for developing
(d) Disc type
·
It
is a rotating disc to be fitted into special disc cameras.
·
Each
disc has 15 exposures
·
The
disc is rotated by a minute electronic motor inside the camera for exposure
(e) Cut films
·
Cut
sheet films are for professional use in studio and field cameras
· They are available in bigger sizes
· They are available in packets of 12 sheets and are used in big studies
56. Types of papers and chemicals used for printing process
·
Photographic paper is a paper
coated with a light-sensitive chemical formula, used for
making photographic prints.
·
When photographic paper is exposed to light, it captures
a latent image that is then developed to form a visible
image
·
The light-sensitive layer of the paper is called
the emulsion.
·
The most common chemistry was based on silver
salts (the focus of this page) but other alternatives have also
been used.
·
The print image is traditionally produced by
interposing a photographic negative between the light source and the
paper
·
It is done by direct contact with a large negative
(forming a contact print) or by projecting the shadow of the negative onto
the paper (producing an enlargement).
Photographic papers fall into one of three sub-categories:
·
Papers
used for negative-positive processes.
This includes all current black-and-white papers and chromogenic colour papers.
·
Papers
used for positive-positive processes
in which the "film" is the same as the final image.
·
Papers
used for positive-positive film-to-paper
processes where a positive image is enlarged and copied onto a photographic
paper.
The three basic chemicals are (1) Developer (2) Stop Bath
and (3) Fixer. Mix these
with the appropriate amount of water and
store them in your bottles. Photographic paper is sensitive to light and should
be handled only in a darkroom with the correct safelight.
57. How do you perceive visuals?
·
Visual perception is the ability to perceive our
surroundings through the light that enters our eyes.
·
The visual perception of colors, patterns, and structures
has been of particular interest in relation to graphical user interfaces (GUIs)
because these are perceived exclusively through
vision.
·
An understanding of visual perception therefore enables
designers to create more effective user interfaces.
·
Physiologically, visual perception happens when the eye
focuses light on the retina.
·
Within the retina, there is a layer of photoreceptor
(light-receiving) cells which are designed to change light into a series
of electrochemical signals to
be transmitted to the brain.
·
Visual perception occurs in the brain’s cerebral cortex; the electrochemical
signals get there by traveling through the optic nerve and the thalamus.
·
Different attributes of visual perception are widely used
in GUI design. Many designers apply Gestalt principles (i.e., how humans
structure visual stimuli) to the design of GUIs so as to create interfaces that
are easy for users to perceive and understand.
58. Wedding photography
· Taking photo of wedding function is wedding photography
· Brides and grooms are mainly focused in this photography
· Crowd also been covered in wedding photography
· Every movement of the function is photographed carefully since it happens only once in bride and groom life
· Covering reception and dining hall also part of it
· Simple lighting technique is used here
59. Landscape photography
· Photograph a wide area of any natural environment is landscape photography
· It includes agricultural land, beach, park, etc
· Compose trees, buildings, land, water, cloud properly to give pleasant feeling
· Shoot in snow, rain, mist, etc gives nice output of landscape photograph
· Use filters to get desired result
· Choosing appropriate view point is most important thing in taking landscape photography
· The angle and composition plays vital role in the beauty of landscape photo
60. Sports photography
· Covering sports event is called sports photography
· It is taken during live action of match
· It covers players action, movement, reaction, their techniques, etc
· Taking photo of football, basketball, cricket match are example of sports photography
· Sport photography includes audience coverage and their reactions towards the game
· It can be indoor or outdoor
· The photo taken here is known as freezing shot since the movement is captured as photo
· High shutter speed is used to capture the movement of the player using appropriate lens
61. Industrial photography
· Photograph of machinery and its environment is industrial photography
· It is developed because of new technology
· People get knowledge about machines through industrial photography
· It is used to advertise new machines
· Various parts and functions of machines are photographed
62. LCD monitor
· The screen on the back of compact digital cameras, known as a Liquid Crystal Display (LCD)
· It is used to frame shots, view menus and settings, and to review recorded images when the camera is set to playback mode
· LCDs vary in size and resolution.
· The higher the resolution of a LCD, the better for viewing. Examples of LCD screen resolution are: 115,000 screen dots, 230,400 screen dots 461,000 screen dots, 920,000 screen dots.
· A LCD displays a 100% view of a framed shot, though it can not always be relied upon for complete color accuracy.
· During the last few years, LCDs have not only become larger but have significantly improved in quality, color and resolution.
· Still, even the best LCD can be difficult to view in very bright light
63. Photography magazines in India
Better
Photography is one of best Photography magazines in South Asia. It is the India’s
first magazine that is dedicated specifically to the art and science of
photography. It offers product tests, gives expert advice and provides many
tutorials and techniques. It also conducts photography contests.
Chiiz Magazine is India’s first of its kind publication which is dedicated to descriptive Photography. This magazine covers the unique stories of the photographers across the globe. Every photo with the EXIF details in the magazine comes with an acute perspective which helps the reader to register easily.
Smart Photography is India’s top Imaging Magazine. This magazine focuses on the finest technologies of the continent. With Amateur and professional photographers working around and with the broad readership, it covers the content in the form of news and also provides equipment reviews, technical features, and portfolio of photographers.
Digital Photographer is the top magazine for photo enthusiasts and semi-pro photographers. It is a very helpful magazine for those who want to learn new tricks and skills in the photography from the top professionals. It keeps you updated with new trends and competitions. Shooting skills, editing tricks, professional insight, career advice, and Kit reviews all you will find under one roof.
Asian Photography is the only premier Business to Consumer photography magazine devoted to the photographic segment. It is also one of the oldest magazines which motivate its readers to explore photography in diversifying range. It comes with a unique, comprehensive content by top professionals. The technical aspects of photography are explored well by amateur photographers.
64. Indian photographer
Raghu Rai is a prominent photogrpaher and has worked on several social and political causes through his photography. He worked with green peace during the Bhopal gas leak in 1984 and portrayed the lives of the victims through his photography. In 1972, he was awarded Padmashree award by the Indian government to honor his photography work. He currently lives in Delhi and works as a correspondent for Magnum photos.
Dabboo Ratnani is a popular indian fashion
photographer. He is quite popular for his kingfisher calender shoots. He has
worked in a Hindi movie named 'Heroine'. For the past 19 years, in January, he
launches a new series of celebrity calender, which is looked forward to by the
film industry.
Atul Kasbekar is a top indian fashion photographer and film producer. He became through his Kingfisher Calender photo shoots and is one of the most sough photographers by many Indian celebrities. Carl F Bucherer has nominated Atul Kasbekar as the brand ambassador for its watches.
Dayanita Singh refers to herself as 'bookmaker who works with photography'. Her styles of photography are: Documentary and Portrait. Her portrait photography focuses more on the lives of the elite and middle class. So far she has released 8 books and they are very narrative and each book is a new experience. In April 2018, she was awarded Infinity Award by Museum Bhavan.
Sooni Taraporevala is a famous indian photographer, screenwriter and flim producer. She is best known for her screenwriting of 'Mississippi Masala'. Through her photography she focuses on the lives of ordinary people in mumbai.
Rathika Ramasamy was born in a small town in Theni and is an amazing wildlife photographer. She enjoys taking wildlife photos of birds and animals in jungles and forest. She has travelled extensively to many national and international sanctuaries. In 2005, she was part of the Clean Ganga Campaign and her photography was exhibited at 'India International Center' at New Delhi.
Arjun Mark is popular for his advertisement photography featuring many celebrities. He has successfully completed several advertising photography campaigns and his favourite was with Farah Khan. He keeps reinventing his style of photogrpahy, since he doesnt want to be tagged as a specific photographer. He doesnt like people posing for his pictures, instead asks them to live and feel the theme.
Prabuddha Dasgupta was a popular fine-art photographer. His sense of fashion and fine -art photography were mostly controversial, but his hardwork and passion made him one of the popular photographers.
Gautam Rajadhyaksha was one of the popular fashion photographers in India. His favorite celebrities for fashion photography were Kajol, Salman Khan and Shah Rukh Khan. His death was one of the saddest moments in the film industry, since he was one of the talented fashion photographers in the industry.
Sudhir is an inspiring wild life photographer from Hassan, Karnataka. He conducts photography tours for children and adults.
65. Significance of light controlling system in a camera
The light controlling systems which are available in a camera are aperture and shutter. Write elaborately about aperture and shutter.
66. Types of film sensitivity
a. Chroma means colour. Panchromatic film is sensitive to all colours and is the type you should use in your camera for regular photographic work
b. Orthochromatic film is sensitive to all colours except deep orange and red. Since panchromatic film is sensitive to all colours it should be developed in total darkness. But an orthochromatic film can be developed in red light as it is not sensitive to it. In earlier days all the films available were orthochromatic.
67. Nuances (difference in appearance) in photo editing
BACKGROUND
REMOVAL - After capturing images, there could be
unwanted objects or people in its background. A client may feel it is better to
edit out these portions and enhance the appeal of an image.
COLOR
CORRECTION - To mend color and imperfections related to
lighting, photo editing services are a must. It is important to take out
imperfections that occur during a shoot, due to camera setting, environmental
factors, or lighting.
IMAGE
MASKING - This editing technique is used to remove the
background from furry dolls, pet animals, and even thin fabrics. So it could be
used as part of product photo editing too, depending on the requirement or the
nature of a product.
SHADOW
CREATION - The creation of a drop or natural shadow is an integral
part of product photo editing. Usually, product images look neat and clean with
a white background. However, a shadow backdrop can give a three-dimensional
perception to your photograph.
IMAGE
MANIPULATION - Editing becomes a manipulative art form when
the complete look of a photo is changed to evoke a sense of awe and wonder in
an audience. To get more traffic to their website, online marketers use
manipulated photos created with the help of graphic designers or product photo
editing companies.
IMAGE
RESTORATION - Editing is important for the recovery of
bromide photographs. This is done by image restoration technique. Personal or
family photos, which get decayed or about to be damaged owing to several
reasons, can be digitally restored.
IMAGE
RETOUCHING - Retouching is important for everything from
product photos to wedding, traveling, real estate, and fashion snaps. When it
comes to model’s portrait retouching, there are more details involved. Every little adjustment made to a headshot or
life-size portrait could invite people to comment on it.
68. How digital technology has changed the way photographers work with the camera?
· The advancement in technology has made it easier for people to use a camera and store their photos.
· Camera today are becoming smaller, making it almost effortless to carry around and allowing people to take pictures whenever and wherever they want to
· The way captured photos are stored has become more convenient. Photos are stored digitally and can be shared on computers and other digital devices.
· Today with the help of social networking sites such as facebook it is very common for people to share their photographs with their friends
· Editing and manipulating images is very easy using software like Photoshop
· Having built in options in the camera, such as sepia, black & white, negative effect, etc makes it more convenient to edit photos and wet them to however we want it to look like.
· It has the ability for you to review the shot taken and if you don’t like how it was taken, you can always capture the image over again.
· The storage capacity for digital technology is enormous.
· Digital photography allows you to print them or store them in computer for future use.
· It is possible to add information on the picture such as added text or even the date.
· All film settings are much easier to adjust and set on a digital camera
· It saves time and enables a faster turn-around on investment when shooting for a client
· The cameras used are a bit smaller much easier to carry around. They are handy and not bulky.
· There are digital photo printers and computers that are available almost everywhere.
69. Features on flash light
· Flash light to be used if the insufficient lamp blinks.
· While clicking one must look for the flash ready lamp to lit up
· The built-in flash tube is comparatively small and has a low output only
· Its effective range is only 10 feet
· Unwittingly people use the flash for longer distances and get quit under –exposed shots.
· When the flash session is complete the flash head should be pushed back as otherwise batteries will run out quickly
· The flash can also be used as fill in flash for day light photography
· Interval between flashes is about 7 seconds
70. Features of digital camera
Resolution - This term refers to the sharpness, or detail, of a picture. The higher the number of pixels, the higher the resolutions. Picture size is measured by how many pixels make up an image and is measured by horizontal by vertical resolution, as in 1280 x 960.
Memory - Digital cameras store
pictures as data files rather than on film. The size of your memory determines
the number of pictures you can take before downloading the images to a
computer, at which time you can go back and fill the memory up with new pictures.
Flash Type - A flash, of course, is the extra light needed to shoot
inside or in low-light conditions. Most digital cameras have built-in flash
with a range of 10 to 16 feet.
Burst Mode - known also as Rapid Fire and Continuous Shooting mode. In general, there is a 1-2 second time lag between pressing the shutter button and a picture being taken with a digital camera. Then there is a 2-30 second recovery time before the camera is able to take another photo. With the Burst Mode feature you can take several pictures in a row. This useful for taking shots in motion – sports event.
Optical Zoom - there are 2 types of zoom lenses, digital and
optical. Digital zoom simply enlarges the picture without adding any clarity of
detail. Optical zoom will do what you really want; add detail and sharpness.
Compression - this process shrinks the file size of a photo. Uncompressed
photos are clearer, the files are enormous and require huge amounts of memory.
JPEG format compresses the files, allowing you to store more, save, download,
and email photos at a faster rate. For general use, JPEG is fine.
Power Source - digital cameras are voracious eaters of
batteries. They use either a rechargeable battery pack or traditional
batteries, usually 2 - 4 double A. Some have an AC adapter as well.
Lens -
lens length will determine how much of a scene will fit into a picture. Some
cameras have fixed focus lenses, which are preset to focus at a certain range.
These pictures typically focus between a wide angle lens and normal range. Many
cameras have auto focus.
Focus and Exposure - most cameras have auto focus, but higher end
cameras will include a manual focus capability. Panorama picture taking is
available, as well as various types of light sensitivity.
LCD Screen - this screen will let you see what the photo will look like and,
typically, let you see what you've already taken and erase what you don't need.
Self-Timer - Self-timers have a pre-set delay, usually giving you about 10
seconds to run into the shot. There are also cameras with a remote control
option to work the shutter.
Manual Features - available on high end cameras, these give more
serious photographers more creative control. They include things such as focus,
aperture speed, and shutter speed.
71. Digital photography
· Digital photography is a form of photography that uses cameras containing arrays of electronic photo detectors to capture images focused by a lens.
· So digital photography is merely the digital process by which an image is captured
· Digital photography is the process of using electronic and computing appliances to capture, create, edit and share digital images/photographs.
· It is mainly used as a means to create, publish or use digital photographs on computers and/or the Internet.
· It uses an electronic digital sensor to translate light into electrical signals. In the camera, the signals are stored as tiny bits of data in bitmaps, tiny bits of data that form the image.
· The captured images are digitized and stored as a computer file ready for further digital processing, viewing, electronic publishing, or digital printing.
· Digital photographs are typically created solely by computer-based photoelectric and mechanical techniques, without wet bath chemical processing.
· Since 2010, the digital point-and-shoot and DSLR formats have also seen competition from the mirrorless digital camera format, which typically provides better image quality
· Many mirrorless cameras accept interchangeable lenses and have advanced features through an electronic viewfinder
72. How color and lights are manipulated in photography?
Color
General photography works within the visible light spectrum. We use the Kelvin temperature scale to describe the color of light. For example, a candle’s flame is 1,200K, which is towards the red-orange end of the scale, and a cloudless day is 10,000K, which is at the blue end.
White
balance
The
human brain is good at correcting colors under different light so that we
usually see “correct” colors. Using White Balance, we can index the color
we want to be white or neutral in color, and all other colors in the scene will
use that as a reference and adjust accordingly. Thus images shot in
daylight, with flash, or under tungsten or fluorescent lights can all be
adjusted for “correct” color.
Light
Transmit – Using lights of various kinds we can transmit
light onto our subjects. We control the quantity, direction, and color of
the light source. By changing the relative size of the light source
to the subject, we can also control the hardness/softness of shadows.
Reflect – All objects reflect light to varying degrees. How
that reflected light plays off of objects, or how we might use other
objects, (reflectors) to bounce light
into a scene is one way we shape and control the light.
Diffuse –We can cause the
light emitting from the source to scatter to varying degrees, (diffused), by
shining it through translucent materials.
Block – As light travels in a straight line, anything between the source and the subject blocks the light and creates a shadow.