MEDIA ORGANIZATION
PART - A
1. Media organization
· A person or company engaged in disseminating information to the general public through newspaper, magazine, radio, television, etc.
· The Hindu, Vijay TV, AIR, are the examples of media organization.
· Organization is a company comprising multiple people that has collective goal.
· It has a management structure that determines relationship between the members.
· Communication channels through which news, entertainment, education are disseminated.
· It includes newspaper, radio, television, internet.
· It is the combination of education and entertainment.
· Video games, television programs are intended to be both educational and entertainment.
· It is a tool provided to judge which programs are viewed the most.
· For calculation purpose, a device (TAM) is attached to the television set.
· It is the specialized branch of media research
· It is one of the two television audience measurement analysis firms of India.
· Besides measuring television viewership, TAM also monitors advertising expenditure.
· It is a combination of advertisement and editorial content.
· A newspaper or magazine advertisement giving information about product in the style of editorial article.
· It is a non - profit circulation auditing organization.
· It certifies and audits the circulations of newspaper and magazines in India.
· It is the combination of information and entertainment.
· Quiz, news is providing information and entertainment.
10. Budgeting
· It is the process of creating a plan to spend money
· It determines to choose the media for advertising
11. Creativity
· The use of imagination or idea to create something new.
· It is the process involved in creating advertisement, TV programs
12. I & B (Information and Broadcasting)
· It is a branch of government of India which formulates and administrate the rules and regulations and laws relating to information, broadcasting, the press and films in India.
· The ministry of I & B is administrating Prasar Bharati and CBFC.
13. RNI (Registrar of Newspapers for India)
· It is for the registration of the publication such as newspapers and magazines in India.
· It regulates and monitors printing and publication of newspaper and magazine.
14. Oligopoly
· A market or industry is dominated by a small number of sellers.
· It reduces competition and lead to higher prices. Cars in India is dominated by Maruti, Tata, Hyundai, Ford, etc.
15. Space selling
· Selling the space for advertising in newspaper and magazine.
· The cost for advertising is based on the space it occupies.
16. Time selling
· Selling time for advertising in radio and television
· The cost for advertising is based on the duration. That is seconds or minutes.
17. Slot
· The time a television or radio program is broadcasted is slot.
· The programs which are broadcasted between 8 pm and 10.30 pm is called prime time slot.
18. Organizational culture
· It is system of shared values and beliefs which governs how people behave in organization.
· It dictates employees how to dress, act and perform their job.
19. Public broadcasting
· It is broadcasting programs for public service.
· Community radio such as Anna FM, MOP FM, are example for public broadcasting.
20. Editorial
· It is an article written by the senior editorial staff of a newspaper and magazine.
· Editorial board evaluates which issues are important for their readership to know the newspaper opinion.
21. Satellite television
· The programs are broadcasted in television with the help of satellite is called satellite television.
· Dish, set-top boxes are used to receive signal then decodes for viewing on television.
22. Production house / company
· The media company which creates program for radio, television, film called production house.
· AVM, Radan, Global villagers are example for production house.
23. SWOT - A study undertaken by an organization to identify its internal strengths and weaknesses, as well as external opportunities and threats.
S – Strength
W
– Weakness
O
– Opportunities
T
– Threats
24. Crisis management
· It is a process by which an organization deals with an unexpected event that threatens to harm the organization.
· The problems are solved in a short duration of time with permanent remedy.
25. Market research
· It provides studies or surveys on a specific advertising medium including radio, television, and print.
· It is to generate information such as audience awareness, audience attitude, etc.
26. Sponsorship
· Financial support given by a person or an organization is sponsorship
· Sponsor for TV program (Airtel Super Singer), college event (Culturals) are examples for sponsorship
27. Production team
· It is a group of technical staff who produce television show.
· It includes assistant director, floor manager, production manager, etc.
28. Paid news
· A company pay to the media to publish their company news in newspaper and magazine.
· Paid news financially benefits the individual journalists and specific media organizations such as newspapers, magazines and television channels.
29. Market segmentation
· It is dividing the market into groups based on age, gender, income level, etc.
· It is about identifying the specific needs and wants of customer group
30. Leisure
· It is time when a person is not working – free time.
· Free time is used for enjoyment using radio, television, etc.
31. Pre-production
· It is the first stage of production. The other stages are production and post-production.
· Pre-production works includes story discussion, script writing, budgeting, etc.
32. Audience
· People who watch television, listening to radio and reading newspaper and magazine are audience.
· Audiences are divided into active and passive audience.
33. Monopoly
· A single seller, selling a unique product is monopoly.
· In a monopoly market the seller faces no competition.
34. Strategic management
· It is the formulation and implementation of the major goals in an organization.
· It provides overall direction, specifying organizations objectives, policies and plans to achieve goals.
35. Project work plan
· Work plan shows the entire task involved in a project.
· It tells who is responsible for each task and when it is completed.
36. Audio visual industry
· Media which produces audio video content for broadcasting is called audio visual industry.
· Television, gaming industry, film industry are examples for audio visual industry.
37. Media industry
· It consists of film, print, radio, and television which are used to inform, educate and entertain the audience.
· It includes movies, television and radio shows, news, newspaper and magazine.
38. Cheque book journalism
· The practice of playing large amount of money to publish a person story in newspaper.
· Obituary in newspaper is the example for cheque book journalism
39. Advocacy Journalism
· It is a genre of journalism that intentionally and transparently adopts a non objective view point, usually for social or political purpose.
· It is intended to be factual but supports a specific point of view on an issue.
40. Organizational behavior
· It is the study of both group and individual performance and activity within an organization
· It examines human behavior in a work environment, performance, communication, leadership, etc.
41. Below the line cost
· It is the method of budget for non-creative personnel in television production and film making
· It includes light man, crane operator, production assistant, etc.
42. Production chain
· Moving the product from supplier to customer is called production chain
· The programs, news are prepared and shown to public by the medias.
43. Media convergence
· It is the interlinking of computing and other information technologies.
· Internet is the example for media convergence, since it contains text, picture, audio, and video elements.
44. Stakeholders
· The employer, employee, government, buyer, seller are the stakeholders of an organization.
· It can be affected by the organizations actions, objectives and policies.
45. Project manager
· A person who is professional in the field of project management is project manager.
· He has the responsibility of planning and execution of project.
46. Community media
· It is a form of media that is created and controlled by a community
· It helps person to know about his surroundings.
47. Promotion department
· It is a department in an organization used to promote its product.
· It includes new film release, new serials in TV, new edition in newspaper, etc.
48. Media meshing
· It is the process of using one of the media to enhance the experience of another medium
· Example – website is used to enhance newspaper articles and television programs.
49. Niche market
· It is the subset of market on which a specific product is focused
· It tells about product features, price, and product quality to attract the audience.
50. Audience rating
· It is the process to judge which program a viewed by most.
· For calculation purpose a device (TAM) is attached to television set
51. In house production
· Media programs are prepared within the organization is called in-house production.
· It requires equipment, qualified staff and other resources.
52. Media management
· Media management is an area of business administration that deals with organizing and supervising teams of media professionals, various mass communication channels and technologies, media and entertainment productions
· There are four functions of management: planning, organizing, leading, and controlling.
53. PPC (Production Project Cycle)
· The production process refers to the stages required to complete a media product, from the idea to the final master copy.
· Pre-production: Planning, scripting & storyboarding, etc. Production: The actual shooting/recording. Post-production: Everything between production and creating the final master copy
54. Public interest
· The public interest is not just what the readers, listeners or viewers want either as consumers or people who want to be entertained.
· It is about issues which affect everyone, even if many of them are not aware of it or even if they don’t appear to care.
· Public interest journalism could be considered the antithesis of media’s darker side, which includes fake news, propaganda, censorship and voyeurism.
· The outcomes of public interest reporting can expose corruption, launch royal commissions, remove improper politicians from office, and jail wrongdoers.
· Put simply, the public interest is about what matters to everyone in society. It is about the common good, the general welfare and the security and well-being of everyone in the community we serve.
55. Media identifier
· A social media identifier is any name used by the individual on social media platforms including, but not limited to, Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram.
56. DAVP
· The Directorate of Advertising and Visual Publicity is the nodal agency of the Government of India for advertising by various Ministries and organizations of Government of India
· The Directorate includes 4 Campaign wings, an advertising wing for print, Audio-Visual (AV) wing, New Media & Personal Media wing, exhibition wing, mass mailing wing, outdoor publicity wing, research wing, distribution wing and language wing in addition to an audio visual publicity cell.
57. Communication
· Communication is simply the act of transferring information from one place, person or group to another.
· Every communication involves one sender, a message and a recipient. These include our emotions, the cultural situation, the medium used to communicate, and even our location.
58. Development
· Media development involves capacity building for institutions or individuals related to freedom of expression, pluralism and diversity of media, as well as transparency of media ownership.
· Media development plays a role in democracy and effective democratic discourse through supporting free and independent media.
59. Evaluation
· Media evaluation is the analysis of media content, rating its exposure, utilizing various established criteria, frequently including tonal value and the existence of key messages.
· It is considered by businesses to be one of the most accelerating vehicles of mass communications research.
60. Agencies
· Media agencies advise companies on how and where to advertise, and on how to present a positive picture of themselves to the public.
· Primary services include advertising, public relations and other forms of media management.
· A media agency ensures that a marketing message appeals to consumers, appears in the right place, at the right time and that the advertiser pays the best possible price.
61. Cross media management
· The term “Cross-Media” is often explained as something that includes the distribution of content (e.g. music, text, pictures, video etc.) amongst different media.
· One frequently used combination is television, newspapers/magazines mobile devices and Internet.
62. Workable competition
· Workable Competition is a situation where high degree of monopolistic power exists but there is enough competition which protects consumers from being abused due to the existing monopoly.
· Hence this is a workable alternative to the theory of perfect competition.
63. Above the line cost
· It is the method of budget for creative personnel in television production and film making
· It includes director, art director, actor and actress, etc.
64. Commodification of media content
· Commodification is the process of transforming things valued for their use into marketable products.
· A good example is the process of turning a story into a film or novel.
65. Mass culture
· Mass culture is the set of ideas and values that develop from a common exposure to the same media, news sources, music, and art.
· Mass culture is broadcast or otherwise distributed to individuals instead of arising from their day-to-day interactions with each other.
66. Ombudsman
· An ombudsman or public advocate is an official who is charged with representing the interests of the public by investigating and addressing complaints of mal-administration or a violation of rights
· Press ombudsman is a person whose role is to determine whether the actions of a newspaper is in line with good journalistic practice
67. Impact assessment
· Impact assessment is about goals; how news informs, connects and engages communities; and how best to maintain journalistic integrity in the process.
· Media impact can be characterized as whether individual media users had their attitudes, beliefs, cognitions, or behaviors.
68. Horizontal ownership
· Horizontal Integration is a Media Company's Ownership of several businesses of the same value.
· A Media Company can own a Magazine, Radio, Newspaper, Television and Books.
· Almost all Media companies have horizontal integration.
· It helps to create more money and makes the company more popular among readers
69. Hero worship
· Hero worship is defined as 'excessive admiration for someone', an idea that they are special or perfect, and is commonly directed at people in the public eye.
· People need heroes because heroes save or improve lives and because heroes are inspiring.
· Heroes elevate us emotionally; they heal our psychological ills; they build connections between people; they encourage us to transform ourselves for the better; and they call us to become heroes and help others.
· The NRS is a survey on all media, but especially the print medium, conducted by the National Readership Survey Council.
· This body consists of members from the INS (Indian Newspaper Society), AAAI (Advertising Associations of India) and ABC (Audit Bureau of Circulation).
71. Governance
· Media Governance refers to the entire system of rules and regulation and informal societal, ideological and economical processes that influence the behavior of our media.
· Governance provides a framework for identifying the network of actors, the blurred boundary between the private and the public sector, and the relationship between different socio-political dimensions. In
72. Popular culture
· Culture based on the tastes of ordinary people rather than an educated elite.
· The most common pop-culture categories are: entertainment (such as movies, music, television and video games), sports, news, politics, fashion, technology, and slang
73. Integrated marketing
· It is a process designed to ensure that all messaging and communications strategies are consistent across all channels and are centered on the customer.
· It attempts to meld all aspects of marketing communication such as advertising, sales promotion, public relations, direct marketing, and social media, through their respective mix of tactics, methods, channels, media, and activities, so that all work together as a unified force.
74. Risk assessment
· Risk assessment is a thorough examination and documentation of all risks the institution faces and the measures in place to help prevent them.
· It outlines a list of threats and a measurement of the likelihood of the risk occurring and the potential severity of the threat’s impact.
75. Negotiation
· Negotiation is a core leadership and management skill
· Media buyer focuses on locating the desired vehicles and negotiate and maintain satisfactory schedule and rates
76. Project management
· Project management as 'the application of knowledge, skills, tools, and techniques to project activities to meet the project requirements.
· Similarly, a producer is usually responsible for taking the project from development through to production and distribution
77. Scheduling
· Media scheduling is one of the important decisions in advertising programme. Company should carefully decide on media timing for a maximum market response.
· The frequency to advertise the message through different media – how many times in a year (or specified time period) the message should be advertised in each of the media.
78. Cost analysis
· The practice of utilizing the cost of media to the broadcast time or print/internet space occupied by a client
· Cost analysis is comparative analysis against historical performance, against objectives, or against competitors.
79. Content analysis
· Media content analysis is a specialized sub set of content analysis, a well established research methodology.
· It is used to study a broad range of text from films, TV programs, and the editorial and advertising content of newspapers and magazines
80. Group behavior
· Group behavior in organizations tends to follow the organizational norms and rules wherein the employees are expected to be disciplined, follow orders, and work to the requirements of the organization rather than their own whims and fancies.
81. Decentralization
· Decentralization is the process by which the activities of an organization, particularly those regarding planning and decision making are distributed or delegated away from a central, authoritative location or group.
82. Slot
· Part of a time segment bought by an advertiser for the airing of a commercial on radio or television is slot.
· From 7pm-10pm seem to be the prime time slots.
83. Buyer
· Product manufacturers are called buyers because they buy space and time in newspaper, magazine, television and radio to publish and broadcast their media content.
84. Revenue model
· The advertising model is often used by Media businesses which use their platforms where content is provided to the customer as an advertising space.
· Possible examples are newspapers and magazines which generate revenue through the various advertisements.
85. Public broadcasting
· Public broadcasting involves radio, television and other electronic-media outlets whose primary mission is public service.
· Public broadcasting may be nationally or locally operated, depending on the country and the station.
PART - B & C
1. Job opportunities in Indian media industry
(1) News editor
·
He is responsible for the overall news
production
·
He decides which news item has to be
published or broadcasted
(2) Designer
·
He designs creative layout for print such as
advertisement, brochure, poster, etc
·
He uses suitable font, color, and picture to
create attractive design
(3) Animator
·
They do animation using 2D and 3D animation
software
·
Animation is used in television
advertisements, title animation, in cinema industry, cartoon animation, etc.
(4) Reporter
·
He collects news information’s for newspaper,
magazine, television.
·
The news items includes sports, political,
health tips, cinema, share market, etc
(5) Program producer
·
He plans various programs for television
·
He involved in all the activities involved
from pre-production to post-production.
(6) Costume designer
·
He designs costume for the character in
television programs, advertisement, etc
·
He designs suitable dress for the artist
(7) Make-up artist
·
He puts make-up to the performer as per the
requirement of director
·
The artist looks like a particular character
after make-up is done
(8) Script writer
·
The person who writes the script for program
is script writer
·
Creative script decides the success of the
program
(9) Camera man
·
He is called as director of photography (DOP)
·
He shoots video for serials, advertisements,
news, film, etc.
(10)
Video editor
·
The person who is editing various television
programs, film is called editor
·
He combines, condense, correct the mistakes
and give final shape to program
Students can write about sound engineer, VFX artist, art director, director, production manager, floor manager, etc.
2. Types of production budget
It determines how much money will be spent for a television programs or a film. The budget is prepared by any one of the following methods
(1) Above the line and below the line budget
The budget for creative persons involved in production is called above the line budget. It includes script writer, producer, director, actor, etc.
The budget for production team such as camera man, production assistant, floor and production manager, is called below the line budget. These persons are all not involved in creative work but in technical work.
(2) Production budget
The budget is prepared based on pre-production, production and post-production
Pre – production – budget prepared for the persons involved in pre-production such as script writer, director, actor, etc.,
Production – budget prepared for production personnel’s such as camera man, light men, make-up artist, costume designer, etc. It includes transport, room rent, food, etc.
Post-production - budget prepared for post production activities such as audio and video editing, dubbing, SFX, and VFX, graphics and animation, etc.
3. Sources of revenue (income) in media organization (or) Media as business
(1) Print media
(a) Circulation (sales of newspaper)
·
Print media earns money from the sales of
newspaper and magazine
·
It gains considerable amount from sales. The
cost for each newspaper and magazine is not same.
(b) Advertisement
·
It is the main and major source of income for
pint media organization
·
The rate for the advertisement differs based
on the size, color or black and white, and the place of advertisement.
(c) Classified ad
·
It is a kind of advertisement in newspaper
which earn money for the organization.
·
It’s size very small, has small amount of
text generally used for job opportunity, matrimonial, real estate, etc.
(d) Inserts
·
It is a separate advertisement put in a
newspaper publication
·
A single sheet of advertisement is inserted
inside the newspaper
(2) Electronic media
(a) Commercial
·
It is the main and major source of income for
radio and television
·
The rate for the advertisement is fixed based
on the time duration, the time of broadcasting.
(b) Sponsorship
· It includes program sponsor, event sponsor, dress sponsor, etc.
·
The sponsors pay money to the channel for the
program.
·
Example – Airtel is the sponsor for super
singer
(c) Subscription
When subscribe a particular channel either on
cable or DTH then the operator has to pay subscription fee to channel.
(d) Content royalty fee
If a television wanted to use by other
television channels they have to pay money for the content.
4. Production process in newspaper organization
(1) News gathering
·
Reporters and correspondents are gathering
news for their organization.
·
They collect various news items such as
politics, sports, share market, etc.
·
Some domestic and international news agencies
also supply news for newspaper.
·
Freelance journalist, public also give news
to newspaper.
(2) News editing
·
It is done by sub-editor and editor of
newspaper
·
Reporters submit the gathered news to the
sub-editor
·
Sub-editor edits the news, giving heading and
show it to the editor for final approval
·
The truthfulness of the news item is verified
during editing
(3) Designing
·
The designer designs the newspaper pages.
·
Sub-editor sends edited text and photograph
to the designer
·
Designer designs the page with the help of
software
·
He gets help from sub-editor to fit the
content within given space
(4) Printing
·
Offset printing method is used for printing
newspaper.
·
Required positive, printing plate and ink are
arranged for printing
·
Black and white, color printings are done
here
(5) Distribution
· Distributing the newspaper to the distributor
· The number of newspaper for each area bundled and dispatched
5. Measurements of audience rating
(1) People’s meter
·
It is also called as Television Rating Point
(TRP)
·
It is measuring which program is watched by
most of people
·
People’s meter is a digital device attached with
the television set
·
This meter reads and records the duration of
each program watched by people
·
After a week the measurements are calculated
to know which programs are viewed by most
·
INTAM – Indian National Television Audience
Measurement is an organization calculating TRP.
(2) Diaries
·
It was the first method of recording
information
·
A diary is given to particular number of
families in a area
·
They are instructed to record the programs
name, duration of watching, number of viewers.
·
After a month all the diaries were collected
and calculated the viewership
(3) GTAM
·
It stands for Global Television Audience
Metering
·
It is advanced method of people meter used to
measure viewership across multiple platforms such as television, internet, and
mobile.
·
It reads and record the audio tracks of
particular program
6. Types of media ownership
Types of Newspaper Ownership in India
There are various types of media ownership. There are many media organization in the country that are owned and controlled by a wide variety of entities including corporate bodies, societies and trusts and individuals. There are four major types of ownership of mass media. Chain, cross media, conglomerate and vertical integration.
1. Chain Ownership
Chain ownership means the same media company owns numerous outlets in a single medium, a chain of newspaper, a series of radio stations, a string of television stations or several book publishing companies. Chain ownership in India applies mostly to newspapers. There are many publishing groups in India which fall into this category such as the group headed by the Times of India, Hindustan Times, Indian Express, Statesman, Ananda bazar Patrika, Hindu, Telegraph and living media foundations.
2. Cross Media Ownership
Cross media ownership is when the same company owns several along with newspaper, magazines, musical labels, and publishers and so on. Cross-media ownership across the various carriers such as television, radio or print; consolidation, including vertical integration among media operations of content, carrier and distributor within a media segment such as television or radio; and market share dominance in a given geography within each media segment.
3. Conglomerate Ownership
Conglomerate ownership means the ownership of several business one of which a media business. For example when a publishing company owns a newspaper along with chemical, fertilizer, cement rubber or plastics factories, or a liquor brewery or distillery or a major corporation has controlling shares in a number of media related business, the pattern is conglomerate. In a conglomerate, there will be interlocking of directorships, which means the same persons will be director of a media company as well as of manufacturing industries or financial corporations. Infact several transport or lorry company directors are directing the destiny of newspaper, television or film production companies. Their main business will be a high profit industry, but they run a media company for prestige or to exercise social and political influence on decision makers in the private or public sector and in the government of the day. Such a conglomeration may not always support an unbiased or dispassionate presentation of events, issues and personalities.
4. Vertical Integration
Vertical integration indicates that a media company monopolizes the production of the ingredients that go into the making of media products. For example a newspaper publisher may own several hundred areas of forests where the major components of a newspaper namely wood for newsprints cultivated. Some other newspaper company may own a factory that produces the bulk of the printing ink or processed used in the industry. Certain film companies may own studies or industrial units producing film stocks or even a chain of theatres where the films are exhibited.
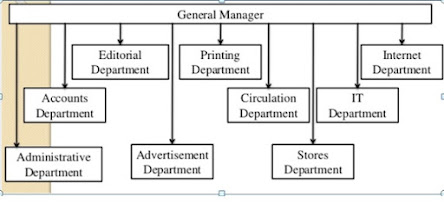
7. Organizational structure of newspaper
(1) Editorial department
This department is headed by the Editor who is responsible for collection of news, selection of news and features, editing of news and features and interpretation of news. The editor of the newspaper alone cannot handle the editing work and is therefore assisted by Chief correspondent. Resident editors, Managing editors, Deputy editors, Assistant editors, News editor, sub-editors and other functionaries like photographers, cartoonists, features writers and reviewers. Various types of correspondents are engaged in collection and supply of news to the newspaper’s Editorial department.
(2) Advertising department
Advertising is the major source of revenue for a newspaper. As such, the work of collection and publication of advertisements becomes crucial in a newspaper organization. The advertising department looks after this work. There can be several sections in this department one to look after local advertising, one for classified ads, one for general / national advertising, one for legal advertising, and yet another one for preparing copy and so on.
(3) Circulation department
As circulation is the life blood of a newspaper, this department assumes great importance. The main responsibilities of the circulation department are selling the newspaper, delivering it and collection from subscribers.
(4) Printing department
It looks after all the work of printing including installation of machines, plant layout, composing, processing, loading, scheduling, maintenance of machines, etc.
(5) Administrative department
This department looks after the general administrative work pertaining to personnel their selection, training, promotion, allotment of work, maintaining leave record, liaison with government departments, general facilities and all such work that facilitates working of other departments. In the absence of a separate legal department the administrative department also handles the work pertaining to legal matters.
(6) Accounting department
This department looks after all the accounting work like maintaining books of accounts, preparing balance sheet and other financial statements, payment, receipt, preparation of budget, financial planning, cost control, etc.
(7) Stores department
It is charged with the responsibility of proper storage of raw material and other material used in the newspaper office.
(8) IT department
It is charged with the responsibilities of IT affairs in the news paper
(9) Internet department
Now days internet and social media is very popular platform to share the news, so the newspapers are started to have a separate department for dealing with internet affairs
8. Organizational structure of Doordarshan
· Director General of Doordarshan is responsible for the overall administration of the Doordarshan network.
· Doordarshan is divided into four wings: Programme, News, Engineering and Administration and Finance.
· Programme wing deals with all aspects relating to programme conception, production and procurement at the national, regional and local level
· News wing puts out news bulletins and other current affairs programmes at the national and regional level.
· Engineering wing deals with all the hardware requirements of the entire network including the space segment and the studios, transmitters etc.
· Administration and Finance using deals with the administrative and financial aspects including general administration, personal management, budget and plan coordination.
· The overall head of all the departments in Doordarshan is Director General.
· In Doordarshan, the Director General heads the Department of programme and Administration.
· His main job is to supervise, guide, govern and control the entire functioning of the department.
He is assisted by
· Additional Director General and Deputy Director General (Development)
· Deputy Director General (News and current affairs)
· Deputy Director General (Communication and film)
· Director (Finance and Personnel control).
· Deputy Director general (Production and Transmission)
In addition to that there is a large number of staff in Doordarshan which are directly associated with pre-production, production and post production.
These staff members are- Programme producer,
programme executive, video engineer, vision control operator, Lighting
engineer, cameraman, vision mixer, studio engineers, Make-up supervisors,
script designer, program Assistant, production assistant, Audio control
manager, MIC boom operator, script writer etc.
9. Organizational structure of a private television channel
The organization of a television station depends on the size of the market in which it operates and the type of ownership under which it exists. For example, small-market television stations may only retain skeleton crews for each department whereas large-market stations may have as many as fifty employees on the payroll for a given department. In addition, larger stations may necessitate the division of departments into smaller branches in order to increase efficiency.
General administration operations manage and distribute the revenue received from station sales of advertising time. This includes the appropriation of available funds to each department as well as the billing of supplies and services both inter-departmentally and externally to clients and advertising agencies. In short, the general administrative function supports and maintains the operations of the entire station. Under the general administration division are the general manager or station manager, the business manager, the accountants, the secretaries, and other administrative and office staff.
Sales
The sales department at
a television station is responsible for generating the revenue for the station
to survive. A general sales manager leads a team that is comprised of a
national/regional sales manager, a local sales manager, account executives, and
at times, a traffic manager. However, the
salespeople of television must negotiate advertising sales using a rate card, a
definitive list of airtime costs during the various time periods and television
programs. Furthermore, the television account executive can also offer to
create the advertisement for a client if the client so chooses, in which case
the sales department cooperates with the production and programming departments
for this venture.
Programming
The programming
department, in conjunction with the production and news departments, acquires
and schedules the product that the audience consumes, which in turn allows the
sales department to create revenue, which in turn allows the general
administration department to facilitate station operations. The programming
department is responsible for filling the entire broadcast day with programming
and is therefore saddled with arguably the most challenging job in television.
Consequently, this department also works closely with the traffic department in
structuring the daily programming schedule.
Production
The production department works closely with the programming, news, engineering, and sales divisions. Its sole responsibility is to produce the various programs, be they news packages, newscasts, public-affairs programs, station promotional spots, client commercials, or other productions that a station may require.
News
The news department is
primarily responsible for creating news programming such as newscasts and news
interview shows, although sometimes members of the news team will participate
in the production of public-affairs programs. The news department is headed by
the news director, who oversees all news operations and produces the final
program. Assignment editors coordinate with the news director and assign
stories to available reporters. Copy editors may also be employed to review and
edit the written stories, and videotape editors may be employed to edit footage
together. The remaining staff may consist of news anchors and reporters, sports
anchors and reporters, and meteorologists.
Advertising and Promotions
Advertising and
promotions is where a station creates its own promotional spots and
advertisements in an attempt to gain more viewership, and therefore more
advertising dollars from local, regional, and national companies.
Engineering
It is the duty of this
department to transmit the programming product of a station to its audience. The employees include the chief engineer, who
oversees all technical operations, the broadcast technicians, who help maintain
the equipment, and the master control operators, who actually put the
programming on air. The two main areas of responsibility for engineering are
master control and technical supervision.
10. Television channel news department
11. All India Radio
(1) Director General (DG)
He is responsible for the overall administration of All India Radio
(2) Program division
·
This division is responsible for production
of various radio programs
·
The DG is assisted by additional DG’s for
making program
(3) Audience Research Unit
·
It surveys the listening habits and program
preferences of people
·
It is to planning effective programs
(4) New division
·
They are collecting various news information
and broadcast to public
·
It is headed by the DG news service
(5) Engineering division
·
This division is responsible for broadcasting
radio programs
·
The DG is assisted by editor – in - chief
(6) Administrative division
This department deals the matters of
administration, finance and security
12. Greiner’s development model of organization
(1) Growth through creativity
·
The company is young and small in size
·
The organization is informal and the
employees are loyal
·
The organization structure is flat
·
Here one person is controlling everything, so
leadership crisis arises
(2) Growth through direction
·
Rules and procedures are formalized and
standardized
·
The coordination remains in the hands of
company owner
·
Because of further growth the coordination
may become too big for owner
(3) Growth through delegation
·
The entrepreneur delegate the important task
to his middle management
·
A division structure is created with
individual manager
·
The middle managers are responsible for
achieving objectives
·
It is difficult for management to coordinate
all the departments, thus there is a risk of management crisis
(4) Growth through coordination
·
More emphasis is put on the coordination
between various departments
·
The rules have made the company to rigid thus
red tape crisis arises
(5) Growth through cooperation
·
In this phase cooperation
between line and staff departments is aimed at and this creates a break-up of
the hierarchical coordination.
·
This phase is characterized
by much mutual contact between employees via all kinds of consultation groups.
·
There is little
formalization and standardization.
(6) Growth through alliances
·
The organization acquires good external
contacts and alliances
·
This can be found in merging or alliancing
other companies
·
Organization is more focused on alliances
than its own main business, thus identity crisis will arise.
13. Media as social institution
(1) Promoting National Integration
·
Media creates the feeling of togetherness as
Indian irrespective of religion, caste, color, etc.
·
People joining together to help people during
flood earthquake is an example for national integration
(2) Safeguarding citizen rights
·
Mass medias protect human rights of Indian
citizens
·
Each and every person of India can get the
government information, getting education, and work anywhere in India.
(3) Education
·
Quiz program, distance education programs are
educating people
·
To attend the public exams newspapers publish
10th and 12th standard model question and answer for
students.
(4) Agriculture
·
Many programs related to agricultural in
radio, television, newspaper and magazine educate farmers.
·
People get awareness about organic food
through mass media
(5) Environmental exposure
·
Mass media keep on insisting people, keep the
surrounding clean not burning tyres and plastics, save water and electricity,
plant trees, etc. to have healthy life.
(6) Health and family welfare
·
Mass media informs people about the disease,
reason and protection by broadcasting doctors programs.
·
Dietitian programs give tips about food
habits
(7) Science and technology
·
It informs people about the new inventions of
home appliances, communication technologies, machineries, etc.
14. Production Project Cycle (PPC)
(1) Initiation
·
A concept is required to start a production
·
We can get concept from a book, an idea,
brainstorming, etc.
·
The concept is assessed and evaluated for
production
(2) Pre-production
·
It is the first stage of production
·
Budget is prepared in this stage
·
Detailed planning of the production takes
place
·
Responsibilities are assigned to each person
·
Script is prepared for production
(3) Production
·
It is stage of executing the script
·
The actors are performing and the actions are
videographed
·
Script is distributed to the various
production department
·
Transport, staying, food, place for rehearsal
are arranged
(4) Post production
·
Videos are edited and dubbing is done
·
Background music, SFX, VFX are added to
videos
·
Titling, adding graphic and animation to the
visuals are done
(5) Completion
·
The program is previewed for distribution
·
After preview, the program is sent to channel
for broadcasting
·
The response of the audiences are monitored
15. Types or models of organizational culture
(1) Power culture
·
Control radiate from the center
·
Power is held with few individuals
·
There are few rules and regulations in a
power cultures
·
Employees are judged by what they achieve
(2) Role culture
·
It is based on roles
·
Everyone in the organization know their roles
and responsibilities
·
Power in a role culture is determined by a
person’s position in the organizational culture.
·
Decision making is slow in this culture
(3) Task culture
·
Teams are formed to solve particular problems
·
Power derives from experts
·
Team may develop own objectives
·
With the right mix of skills, leadership,
working in teams can be productive and creative.
(4) Personal culture
·
Individuals very much see themselves as
superior to the organization
·
The organization exists in order for people
to work
·
It is a collection of individuals who are
working for same organization
16. Functions of circulation department - Circulation department is headed by circulation manager. He is responsible for delivering the publication from press to readers home.
(1) City circulation
·
It involves the maintenance of circulation
records for the city of publication
·
The supervision of district men who oversee
circulation by the sub-division of city.
(2) Area circulation
·
Delivering publication for the surrounding
area
·
Post, taxis are used to distribute the
publication
(3) Sales promotion
·
It involves office staff to keep records, subscription,
renewing, handling complaints over the counter by post.
· Public relations department is responsible for promotion of sales
17. Contract in media industry (for its workers)
(1) Full time permanent
·
The job roles are managerial, editorial,
financial, creative, sales and marketing
·
Workers has to work for 39 hours a week
·
Worker is a regular member of staff can get
the benefits including pension, sick, pay, maternity leave and holiday pay
(2) Part time permanent
·
The job roles are financial, sales and
marketing
·
The worker can get same benefits as full time
permanent but on reduced basis due to fewer working hours
(3) Fixed term and freelance
·
The job roles are technical, creative, sales
and marketing
·
Fixed term contract may get company benefits
if mentioned in contract, but it is not applicable for freelancer
(4) Shift work
·
The working hours are set to a certain time
of a day
·
It include late or night work
(5) Office hours
·
The job roles are financial sales and
marketing and some assistance job
·
Usually the working time will be 9am to 5pm
(6) Irregular hours
·
Working extra hours in the organization
·
The worker is paid extra money for his extra
time work
(7) Salaried
·
A person is a permanent worker of an
organization who gets salary on every month
·
His job roles are managerial, technical and
creative
(8) On completion
·
This people work for commission basis
·
He is not a permanent employee of an
organization
18. Contracts (agreement) in media industry
Media contract means any written, oral or other agreement, contract, subcontract, lease, understanding, instrument, note, warranty, license, sublicense or legally binding commitment or undertaking of any nature, whether express or implied, related to the Media Assets.
Intellectual Property
No matter the type of contract that is used, there is typically a clause stating who owns the publishing rights, potential royalties, and the piece as a whole. These clauses are used most often when contracting with written content providers, script writers, video producers, publications, and advertising agencies.
Such agreements require
an increased level of visibility and accountability. Deadlines, reminders,
contract expiration and renewal dates, and any other terms of the contract must
be monitored closely for precise compliance. Contract management systems allows
to draft contracts, collaborate with others, and set email alerts to remind you
of deadlines, payment dates, and any other reminder that you might need.
Freelance Agreements
A common contract for
media producers is a freelancer contract, or an independent contractor
agreement. Freelance writers, videographers, musicians, and various other
entertainers are often brought on to help with a single project, and then
released back into the wild.
Media companies need to
be able to manage dozens of freelance contracts simultaneously, facing the same
problems of managing deadlines, dates, and terms, but with the added difficulty
of multiplying the need by however many active contracts they have. Companies
should also be able to renew easily.
International Contracts
Media companies,
particularly news agencies and those in the film industry, constantly transfer
content internationally. They will often employ foreigners to do the work in
different countries, meaning that their contracts must comply with
international law. This makes it imperative that media companies monitor
closely to see that regulations are being met perfectly.
Technology Agreements
The media industry
thrives on the use of technology, particularly newer media, such as social
media. Technology comes with various types of contracts, however, each of which
has its own set of terms and conditions. Each of these varying contracts comes
with expiration dates, renewal dates, payment cycles, and a whole host of other
things.
19. Functions of media organization
(1) Planning
·
It involves selecting the appropriate media
for campaign
·
Choosing the target audience is important
·
Right place, right time, right medium and
right communication message are planned
·
Media planning involves how frequently a
message should reach the audience
(2) Organizing
·
Controlling the overall structure of the
company
·
It involves assigning jobs and
responsibilities to employees
·
It develops the organizational structure and
chain of command
(3) Staffing
·
Selecting staff for the right job
·
It involves training and development,
performance appraisal, promotions and transfer.
(4) Coordinative
·
Control all the organizing, planning and
staffing activities of the company
·
In ensures all activities function together
for the welfare of the organization
·
Meeting and planning sessions take place with
department heads
·
It involves communication, supervision, and
direction by management
(5) Controlling
·
Ensuring all the functions of organization
are operating successfully
·
It involves establishing performance
standards and monitoring the output of employees
·
It leads to the identification of problems
that need to be solved
20. Status of Indian media industry
(1) Television industry
·
It is a mass media which has thousands of
channels and programs
·
Today India is the second largest television
market in the world
·
Television serials are popular with housewife
and working women
·
Approximately half of all Indian households
own a television
·
India has highest television viewership in
the world
(2) Radio industry
·
All India Radio is one of the largest radio
networks in world
·
It includes AM, FM and satellite radio
·
Industry gains more profit
·
Many private FM radio such as Suryan FM,
Radio Mirchi, Hello FM broadcast various programs
(3) Print industry
·
Indian print industry is growing strong
·
It is moving towards digitalization
·
India is world second largest industry with
over 90 million copies in circulation per day
·
Most newspaper has an online presence
·
Newspaper gains more revenue through
advertisement
·
Newspapers have launched area specific
newspaper – Example – Kodambakkam Times, Anna Nagar Times, Etc.
(4) Film industry
·
It is the most important form of
entertainment in India
·
India produced more number of films than
other countries
·
Films come in Tamil, Telugu, Malayalam,
Kannada, Hindi and many regional languages
·
Approximately 23 million Indians go to see
film everyday
·
Bollywood earns 46 percentage of total Indian
film industry revenue
·
Nearly 6 million people employ in this
industry
21. Leisure time activity
It is time when a person is not working – free time
Free
time is used for enjoyment using radio, television, etc.
(1) Go to cinema - Cinema is one of the entertainment medium
where people go to watch movie on big screen. Usually people go to theatre
during weekends.
(2) Watching TV - Television provides various entertainment
programs such as songs, comedy, cartoon, news, etc. People watch television
everyday to relax after their work
(3) Spending time with family and friends - Talking with
family members make the relationship closer. Going out to cinema, restaurant,
coffee shop with fiends to spend time
(4) Play video games - Some spend time on video games through
computer, play station, etc. We can play video games individually or with
family and fiends
(5) Listen to music - Songs are important stress releasing
element in human life. People listen to songs, carnatic music, and instrumental
music
(6) Playing - People
play at free time to stay fit and healthy. Playing football, cricket, swimming,
volleyball keeps man healthy
(7) Gardening - Plant flowers, vegetables, herbs, and
maintain garden by watering it and feeding it with fertilizer.
(8) Shopping - People like to go to shopping malls to buy
clothes, play games and buying household items
(9) Go to park - People go to park alone or with family and
fiends. There we can walk, talk, play, etc
(10)
Art and craft - Many people draw and paint
during free time. Children spend time happily by doing craft
22. Cost factors in different media
(1) Film production
·
Major amount is spent for actor and actress
salary
·
Amount also spent for pre-production
processes such as location searching, script writing, storyboard, etc.
·
It takes more money for post production processes
such as editing, dubbing.
·
Nowadays animation and visual effects include
in film expenses
·
Hiring equipments for shooting is another
expenses
·
Set design, costumes, clothes, food and other
expenses are there in film production
·
Film companies spend money for insurance,
permits and other expenses
(2) Television channel
·
Television channels pay salary for their
employees
·
They spend money to buy broadcasting devices
·
They pay money for getting satellite space
·
They pay tax to the government
·
They construct set design for various
programs
·
They spend money for food, transport, space
rental for studios, etc
(3) Newspaper
·
Newspaper organization pays salary for their
employees
·
Small newspapers pay rental for office,
printing press and store room
·
They spend money for buying printing machine,
news print papers, ink, printing plate, etc.
·
Newspaper pays amount to news agencies for
their service
·
Transportation, circulation also the cost
factors of newspaper
·
Newspaper pays amount for insurance and
tax
23. Buyer seller relationship in media
Seller – the media companies are called sellers, because they sell space and time for advertising, programs and information. Newspaper, magazine, radio and television media are doing the selling function.
Buyer – product manufacturers are called buyers because they buy space and time in newspaper, magazine, television and radio to publish and broadcast their media content.
Relationship
·
Buyers expect quick responses from sellers
·
Delayed response leads to misunderstanding
between them
·
Relationship includes patient listening
·
Both buyer and seller should be honest when
they make mistake
·
They should have meetings to solve
communication gap
·
Telephonic conversation makes them to clarify
doubts
24. 4 Ps of marketing
(1) Product
·
Product is a goods manufactured by an
organization to satisfy the customer needs
·
Different products are perishable and
non-perishable such as electronic goods, cosmetics, FMCG products
·
The benefits and main features of the product
should be understood by the customer
·
The USP of the product need to be studied
(2) Price
·
It is the rate of the product
·
If the product rate is high, the sale will be
less
·
If the product rate is low the sale will be
high
·
People ready to buy high price product if it
is branded
(3) Promotion
·
It is an activity to increase the sale of
product
·
It includes advertising, sales promotion,
offers and public relations
·
Appropriate media channels to be used for
promotion
·
It is used to make the people to understand
about the product
(4) Place
·
Proper location should be identified to sell
the product
·
It is the way to provide service to customer
·
It includes the place of business and method
of delivery
·
The delivery can be done through distributor,
retailer, etc.
25. Production house / company
·
The media company which creates program for
radio, television and film called production house
·
AVM, Radan, Global Villagers are example for
production house
·
Production house is responsible for
fundraising for the production or through partner, private investors.
·
It handles budgeting, scheduling, scripting,
production, distribution and marketing
·
It can be owned by a person or under contract
with other organization
·
It is done by a producer or director
·
Production companies are ranked based on the
amount of funding it has for the production.
26. Entrepreneur
·
A person who starts his own business taking
on financial risks in the hope of profit
·
He is seen as an innovator, source of new
ideas and business
·
He plays a key role in economic management
·
Entrepreneur brings good new ideas to market
·
He is rewarded with profit, fame and growth
opportunities
·
They manufacture goods and provide service
·
He hires labour and provides leadership and
management for business
27. Stages of project management
(1) Project initiation - This is the first stage of project
life cycle. The value of the project is measured. This is an evaluation of
project goal, time and the cost
(2) Project planning - It is the plan to guide the team. It
is used to complete the project on time and within the budget. Proper planning
of the project leads to quality output
(3) Project execution - The project is done in this stage. It
is happened by allocating resources (men & material). It keep team members
focused on their assigned task
(4) Project monitoring and control - The project progress
must be constantly monitor. Monitoring and control helps to keep the project
moving smoothly
(5) Project closure - Once the project is completed the
finished project is delivered to customer. It allows the team to evaluate and
document the project. Mistakes are identified and rectified in the next
projects
28. Strategic management (5Ps)
(1) Plan - It is an idea used to develop business. It
includes how the product is going to sell, the cost, etc
(2) Ploy - It is a plan to complete with other products. Bu
using specific ploy one can success in his business. The successful ploy may be
able to take control market segmentation
(3) Pattern - It is a stream of actions. It tells about what
is going on in the business currently
(4) Position - Locating an organization in an environment. All
businesses fight for position in the market place. Position includes method of
sales, the quality and price
(5) Perspective - It means how an individual think about an
organization. It is shared by member of organization through their elections
29. Prime time (program)
·
It is also called as peak time
·
Prime time occurs between 7pm and 10.30pm
·
The program which is broadcasted during prime
time is called prime time program
·
Prime time program gets more advertisement
·
Prime time programs are television serials,
movies and other entertainments
·
The prime time programs designed to attract
children and families
·
Morning 6am to 10am and evening 3pm to 7pm
are prime times in radio
30. Legal issues in media
·
Copyright is a big issue the media industry
faces. It means a person cannot use original material (concept, story) of other
person.
·
It is also illegal to discriminate anyone on
grades of race, sex and disability
·
National security such as official secret
act, prevention of terrorism act is another legal issue filmmaker’s face.
·
Before filming it is important to ensure
everybody’s health and safety
·
One company trade mark should not be used by
other company
·
People should not work in two or more
television channels simultaneously
·
The media industry faces some ethical issues
such as privacy, truth and trust
·
The news reporter should not submit the
biased information
·
No two products should be compared in
advertisements
·
Publishing or broadcasting defamation
messages is a big issue the media faces.
31. Marketing process
Marketing is the process of communicating the value of product to customer to sell the product
(1) Situation analysis
·
The company identifies customer needs to
satisfy
·
It analysis external and internal environment
of a company
·
It includes past, present and future aspects
of company
(2) Marketing strategy
·
Market research will provide specific market
information
·
Research helps to select the target market
·
It includes targeting, segmentation and
positioning of product
(3) Marketing mix
·
Specifying designing and producing the
product
·
It includes pricing decisions, distribution
and promotional contracts.
(4) Implementation and control
·
The product has been launched
·
The result of the marketing effort should be
monitored closely
·
As the market changes the marketing mix can
be adjusted
32. Sponsor
·
Any kind of support given by a person or an
organization to an event or program is called sponsor
·
Airtel is the main sponsor for the program
super singer in Vijay TV
·
Sponsorship increase awareness and used for
brand building
·
There is a contract between sponsor and the
sponsored party
·
It is a kind of promotion which is cheaper
and more effective than advertising
·
It can be in the form of money, print out,
media support, etc
33. Behaviour
(1) Group behavior
·
Two or more individuals who have come
together to achieve particular objectives is called group behavior
·
Here verbal and non verbal communication
takes place
·
All members agree that they are part of group
·
There is a chance to become a leader
·
A distinguished work group defined by
organization structure is called formal group
·
A group that is neither formally structured
nor organizationally structured is informal group
(2) Individual behavior
It can be defined as how an individual
behaves at work
Factors influencing individual behavior are
(a) Perception – it is the respects of various senses like
feeling, seeing, hearing, etc.
(b) Attitude – it can be negative or positive. I like my job
is a positive attitude towards my work.
(c) Personality – some people seem to be very friendly and
some others not
(d) Emotions – there are happy moment we cherish and the sad
moments like anger, frustrations that we try to forget.
(3) Organizational behavior
·
It is the study of both group and individual
performance activity within an organization
·
It examines human behavior in a work environment,
performance, communication, etc.
·
Organization is a combination of humanity and
technology
·
People within the organization woks based on
the structure
·
It is a system of cooperative activities
·
It helps the manager to manage human
resources effectively
·
It helps individual to understand about
organization
34. organizational structure
It is how works are formally divided, grouped and coordinated within an organization
(1) Work specialization
·
An entire job is broken down into steps and
each step is completed by a different person
·
The job is assigned based on expert and
experiences
·
It increases productivity
·
Employees have defined roles and standardized
work processes
(2) Departmentalization
·
Departmentalization is the dividing of
organizational functions into separate departments
·
Department is divided based on its functions
·
Similar skill experts are working in a
department
(3) Chain of command
·
It refers to a company’s hierarchy of
reporting relationships who must answer to whom
·
It lays out a lines of authority and decision
making power
·
Authority, responsibility, accountability are
included in chain of command
(4) Span of control
·
It means the number of subordinate that can
be managed effectively by a superior
·
Narrow span of control means a single manager
oversees few subordinates
·
Wide span of control means a single manager
oversees a large number subordinates
(5) Centralization and decentralization
·
In a centralized organizational structure
decision making authority is concentrated at the top and only a few people are
responsible for decision making.
·
In a decentralized organization, authority is
delegated to all levels of management
(6) Formalization
·
It is a process in which managers specify
procedures, rules and responsibilities for the individual employees
·
It leads to the development of relationship
and operating procedures
35. Organizational design
(1) Traditional organizational design
Simple structure – It consists of owner and
employees. The authority is centralized in a single person
Functional structure – It groups similar
experts together. Example – functions of operations, finance, research and
development
Divisional structure – Each division has
limited authority. Divisional manager is responsible for performance of that
particular division.
(2) Contemporary organizational design
Team structure – The entire organization is
made up of teams. Teams design their work and responsible for it.
Matrix and project structure – It assign
specialist from different functional department to work. In project structure
the employees continuously work on projects.
Virtual organization – It is a recent
development in information technology to get work done. It composed of full
time employees and employees who can work from their home
Network organization – It minimizes or
eliminates organizational boundaries. It outsources major business functions
36. Organizational design issues and challenges
·
The process constructing and adjusting an
organizational structure to achieve its goal is called organizational design.
·
Small space in organization provides poor facility
to work and difficult in employees movement.
·
It is difficult to connect employees in
virtual and network organization
·
Most organizations are not providing
opportunity to learn, acquire and share new knowledge
·
In today’s business environment managers need
to be familiar with the issues surrounding.
37. Principles of media management
·
It is a money management
·
They sell space and time
·
Having contract with all media are important
·
Cost efficiency – less production cost and
more profit.
·
Creating appropriate media plan and
monitoring it is important.
·
Media plan must reflect the overall marketing
strategy
·
Keep the media door open to media suppliers
·
Everyone in the media organization should be
kept informed all the activities
38. Innovation and creativity in media
(1) Innovation
·
It is defined as a new idea, device or method
·
In media innovative ideas are used in program
to attract the audience
·
It includes digital magazines, websites,
apps, blogs, etc
·
Audience watches programs which have
innovative ideas and concept
·
Advertisement with innovative ideas gets more
audience attention
(2) Creativity
·
The use of imagination or idea to create
something new
·
Creativity is used in video games as new
ideas are being developed for games.
·
It is highly used on youtube as people use
their own ideas to create a video of their choice and upload onto youtube for
other people to see.
·
Creativity is used on facebook, whatsapp by
changing photos.
·
Artists use creativity when making music
videos
·
Creativity is widely used in advertisement
while copy writing, composing music, etc.
·
Creativity is used in film in developing
stories, characters, editing, sound, special effects, etc.
·
Creativity used in fashions by the magazines
focusing highly on people’s image
39. Audience trends
·
An individual or collective group of people
who read or consume any media text is audience. Example – Radio listener,
Television viewers, and Magazine and Newspaper readers
·
People use to access new media such as
internet, whatsapp, facebook, than old medias.
·
More people use digital media nowadays.
·
Since mobile media provides more
information’s it dominate other media.
·
People use mobile media for playing games,
watching movies, listening to songs, reading newspaper, etc.
40. Media consumer and behavior
·
Social media influences buying behavior
·
Media changed re - inforce individual belief
·
Media changes behavior, attitude of their
consumer by watching the program
·
Media content influences their uses in many
situation
·
Media users tend to dress, speak, behave, act
like media person
·
Some people involved in illegal and
misbehavior because of media
41. Functions of media management
Any task that relates to processing your media is considered to be media management, such as capturing, compression, copying, moving, or deleting media files. It also refers to keeping track of the media files via clip properties such as log notes, scene number, shot/take number, and so on. The functions of media management are
1. Plan
·
It is the base upon which all the areas of
management should be built
·
Planning requires administration to assess
where the company is presently set, and where it would be in the future.
·
From there an appropriate course of action is
determined and implemented to attain the company’s goals and objectives
·
Depending on the conditions, a company may
have to alter its course of action in accomplishing certain goals which is
known as strategic planning
·
In strategic planning, management analyzes
inside and outside factors that may affect the company and so objectives and
goals.
·
Here they should study of strengths and
weaknesses, opportunities and threats
2. Organize
·
Management must organize all its resources
well before in hand to put into practice the course of action to decide that
has been planned in the base function
·
Through this process, management will now
determine the inside directorial configuration establish and maintain
relationships and also assign require resources
·
They also see to the harmonization of staff,
and try to find out the best way to handle the important tasks and expenditure
of information within the company
·
Management determines the division of work
according to its need. It also has to decide for suitable departments to hand
over authority and responsibilities
3. Direct
·
This function helps the management to control
and supervise the actions of the staff
·
This helps them to assist the staff in
achieving the company’s goals and also accomplishing their personal or career
goals which can be powered by motivation, communication, department dynamics,
and department leadership
·
They come about with prize and incentive
programs based on job performance and geared in the direction of the employees
requirements.
·
It is important to maintain a productive
working environment, building positive interpersonal relationships, and problem
solving. And this can be done with effective communication
·
The finest technique of finding the areas
that requires improvement is to ask themselves and other at regular intervals,
how well they are doing. This leads to better relationship and helps the
managers for better directing plans
4. Control
·
It includes establishing performance
standards which are of course based on the company’s objective
·
It also involves evaluating the reporting of
actual job performance.
·
In an effort of solving performance problems,
they should straightforwardly speak to the employee or department having
problem
42. Structure of local media organization (Structure of a Typical Small Magazine)
Editor
in Chief
The chief editor oversees the whole content and makes sure the flow of the magazine is seamless. As a top editor, this person is responsible for making all the final decisions and is constantly getting reports from the managing editor, creative director and the executive editor.
Executive Editor
The executive editor selects the writers, assigns them stories and edits their articles. He or she usually writes the larger stories and the cover headlines that must be short, sweet and catchy. However, in larger magazines, the executive editor may have a staff of editors to oversee such as the features editor and a specializing editor.
Writers/contributing editors
These people are paid staff members and are expected to produce certain kinds of copy and articles for each issue of the magazine. Most magazines have relatively free writers on staff.
Assistants
An editorial assistant writes small sections, answers calls, makes the coffee and does whatever the editor assigns on a day-to-day basis. An assistant editor has more experience, is given more responsibilities and gets paid higher but is still in the assisting role.
Staff writer
The
staff writer is the immediate target-partner because she/he combines the
function of a reporter with that of a feature writer.
43. Proposal – prepare a dummy proposal to a funding agent
·
A social media proposal is a document that you present to
your prospective client outlining how you can help them achieve their goals.
·
A proposal is neither a pitch nor a contract. But it is a
key part of the client acquisition process that converts a prospect into a
customer.
·
It’s used after a consultation and research into what
your potential client needs. But before you’ve signed contracts.
·
Your prospect needs to know what you can do for them, and
a proposal is the medium for you to convey your message.
Preparing proposal
1. Introduction
·
You want to set your prospective client’s expectations
and show you understand what they require.
·
Use words like you, yours and we to
address the prospective customer directly and establish a relationship
·
Use the tone that matches your agency. Be authentic and
build trust.
·
Next, you can go into a little more detail matching their
business goals to social media goals and objectives.
·
For example, if the prospective client indicated they
wanted to grow their audience on social media, you could say:
·
Goal
1 -
Increase the number of Instagram followers in the age range 35-45 by 20% over
the next six months.
2. Scope of work
·
Here’s where you state what activities you’re going to
perform for your prospective client. It’s worth adding why you’re proposing to
do each item, so they understand the reason behind it.
·
Creating a social media content calendar,
creating images, taking photographs, recording videos, writing captions, and
curating industry-related content.
·
Outline why you’ve chosen specific social networks; e.g.
they are more suited to the target audience, their competitors are active
there.
·
Include a schedule of review overall performance.
3. Project milestones and deadlines
Use this section to define how you’ll measure
a project’s success. Don’t forget to benchmark current performance levels so you
can measure the growth.
4. Proof of work
·
It’s highly likely that your prospective client will
review several proposals. So aside from explaining what you plan to do, you
should show why you’re the best option.
·
An excellent way to show your value is to use results,
case studies, and testimonials from other clients.
5. Terms of agreement
·
Use this section to propose your fees and payment terms.
·
Fees: Depending on the scope of the
work there may be several components including a fixed project or an hourly or
monthly retainer.
·
Payment: Specify how you
invoice and what your payment terms are.
·
Termination: Include how
either party may end the agreement.
6. Next steps for the client
Draw your proposal to a conclusion by
outlining the next steps for the client in the process. For example
- Accept the proposal as-is
- Discuss any changes
- Request and sign the contract
- Submit an initial payment
44. Stages of television production
Pre-production
·
This stage is finalizing the preparations for
film production.
·
The budget of the film is prepared
·
Important cast members, director and
cinematographer are selected.
·
The screenplay is finalized
·
The script is broken down into individual scenes.
·
Storyboard creations, location search, props,
costumes, special effects and visual effects are identified.
·
Detailed schedule is prepared and distributed
to the team members.
·
Sets are constructed
Production
· It is the stage of film shooting
·
More crew will be recruited such as property
master, script supervisor, assistant directors and still photographers.
·
The crew and the actors are present in the
location on time.
·
The actors are well dressed and go to the
hair and make-up departments.
·
The actors rehearse script
·
Finally the action is shot
·
Assistant and associate directors are helping
directors during shooting.
Post – production
· It is done after the shooting
·
The film editor edits the footage in a
sequential order
·
The sound is recorded edited and music tracks
are scored
·
Sound effects are designed and recorded
·
Computer graphic, visual effects, titling are
digitally added
·
Finally all sound elements are mixed which
are added to picture and the film is fully ready for distribution.
45. Process of evaluation
· Media evaluation is a tool used to measure corporate or brand reputation.
·
Media evaluation is very important to understand the idea
of a particular media type for a product or service.
·
Media evaluation is the analysis
of media content based on tonal value and presence of key messages.
·
The International Association for Measurement and
Evaluation of Communication (AMEC) is the industry appointed trade body
for companies and individuals involved in research, measurement and evaluation
in editorial media coverage and related communications issues.
·
It
has become an integral part of the planning, research and evaluation process
used by PR practitioners.
·
There are different attributes of a product or service
for which different communication medium are chosen. Similar media strategy
cannot be followed for all types of products.
·
Once the medium to send the message is chosen, it is
necessary to evaluate the medium. The effectiveness of media determines the
reach the message will cover.
46. Recent trends in marketing (promotion) a program
·
Promos typically run from 15 to 60 seconds, with
30-second spots being the most common
·
Most promos show select video or audio clips of scenes or
segments from an upcoming program (such as a television or radio series, film or
special).
·
Some television promos (particularly for an upcoming
television series) utilize a monologue format in which a star or host of
the program
·
Most radio promos utilize this format as well,, with a
host of the program discussing the show itself
·
Broadcast television stations promote upcoming
newscasts by featuring teases of select story packages to be featured in the
broadcast, such as an investigative report or a special-interest feature
segment.
·
The airdate and time of the program's broadcast as well
as the name and/or logo of the station or network that the program will be
broadcast on are displayed either at the end of or throughout the promo
·
Types of promotional media:- 1) television 2) radio 3)
internet 4) billboards 5) newspapers, magazines 6) pamphlets 7) SMS 8)
brochures 9) word of mouth
·
An ad in the lower third of a TV screen during a show
helps to remind people what network they are watching. Called a snipe, this
type of promotion targets people.
47. Media enterprise
· Media enterprises are strategically organized economic unit whose central work is generating and marketing of media.
·
The generation of media is the bundling of internally and
externally generated content and its transformation into a medium. The
marketing is the direct or indirect distribution of media.
·
The term media in this connection is restricted to
one-to-many-communication with one sender and a large number of consumers. More
precisely, the focus is
on newspapers, magazines, books, music, television, films, internet and games.
·
Media enterprises operate in three different markets.
They sell their services in form of content like information and entertainment,
as well as in form of advertising space.
·
The content is offered to the consumer markets which
differ depending of the type of media and the way it is used by consumers. The
advertising spaces are traded on advertisement markets.
·
The third markets are procurement markets. They
do not produce all their offered content themselves but buy service packages of
both, information and entertainment, from procurement markets. For example,
authors and artists contracts or license and copyright deals can be acquired.
·
In fact, the three described media markets each media
enterprise can be active in are strongly interdependent. For example, there is
a strong relationship between advertisement and consumer markets as the success
among consumers drives advertising revenues.
·
Furthermore, there are geographic media markets.
Some firms operate in a national market while other companies, for example,
local radio stations operate in a regional area.
48. Project specification
Reason for project
specification
- For
project managers, it functions as a ‘one source of truth’ document, a
place where they can add all notes relating to the functionality
- For developers, the spec is an instructional
guide of what they are going to build and why
- For clients, the project spec is an agreement
of what they can expect from the final product
- For testers, the spec is a clear indication of
how the site should function
- New team members can be easily brought
up to speed on a project, whether they are client-side or in your own organization.
All they need to do is read the spec!
49. Define shooting schedule. Explain the importance
· A shooting schedule is a project plan that every film, tv show, and commercial follows to make sure the production goes smoothly.
· It's a simple breakdown of the scenes, talent, time, cast, company moves, and day breaks.
· It is normally created and managed by the assistant director, who reports to the production manager managing the production schedule.
· Both schedules represent a timeline stating where and when production resources are used.
· These days, a shooting schedule is often created on a computer. Scenes are inputted manually into a spreadsheet for reordering.
This
is an example of a Shooting schedule, it's clear to see that there is a lot of
information in this picture. For example; From left to right there is
Date,"Shot" Board, Ones/Twos, Location Set, Synopsis, Character,
Props, Lighting, and camera info. On this you can have anything from the
location, which is shown as being "A hospital Room", this is
important so that the actors know what scene they are filming and what kind
of environment that they are working in, also to back this up is that
they tell you exactly the times that they will be working and also
the specific scene that they will be filming. As it says at the top,
a production companies shooting schedule is the most important part of a
production company.
50. Production strategies (plan) for different media agencies
·
A media agency plans and buys the media necessary to advertise to that client's target
market.
·
A media agency is in charge of the strategic
recommendations of media activity for your campaigns. They specialise in
finding the right placement at the right time for the right price.
·
Media agencies advise
companies on how and where to advertise, and on how to present a positive
picture of themselves to the public.
·
Primary services include advertising, public
relations and other forms of media management.
1- Attracting clients
- Advertising agency needs
clients (advertisers). Without them, it cannot survive.
2-
Account Management
- Within an advertising agency
the account manager or account executive is tasked with handling all major
decisions related to a specific client.
- The account manager works
closely with the client to develop an advertising strategy.
3-
Creative Team
- Advertising agency put the
advertising-plan into action under its creative function. Creation of ads
is the most important function of an ad agency. Generally, it involves
activities like:
- Copy writing, Drawing
photographs, Making illustrations, layouts, an effective ad message,
etc.
- These jobs are done by experts
like copy writers, artists, designers, etc. These people are highly
skilled and creative. They make an advertisement more appealing.
Attractive ads help to increase the sales of the product.
4-
Researchers
- Full-service advertising
agencies employ market researchers who assess a client’s market situation,
including understanding customers and competitors, and also are used to
test creative ideas.
- Advertising agency gathers
information related to the client's product. It collects following
information about a product under its research function:
- Features, quality, advantages
and limitations of a product, Present and future market possibilities,
Competition in the market, Situation in the market, Distribution methods,
Buyers' preferences, so on
- Ad agency analyses (studies)
all this collected information properly and draws conclusions for its
research. It helps in planning an advertising campaign, selecting proper
media and creation function.
5-
Media Planners
- Advertising agency helps
an advertiser to select a proper media (ad platform) to promote his
advertisement effectively.
- Advertising agency plans the
entire ad campaign of its client. It is done when its research function is
completed. That is, after analyzing the client's product, its competitors,
market conditions, etc.
- Once an advertisement is
created, it must be placed through an appropriate advertising media.
6-
Advertising budget
- Advertising agency helps
an advertiser to prepare his ad budget. It helps him to use his budget
economically and make the best use of it.
- Without a proper advertising
budget, there is a risk of client's funds getting wasted or lost.
7-
Coordination
- Advertising agency brings a
good coordination between the advertiser, itself, media and
distributors.
8-
Sales promotion
- Advertising agency performs
sales promotion. It helps an advertiser to introduce sales promotion
measures for the dealers and consumers. This helps to increase the sales
of the product.
9-
Public relations
- Advertising agency does the
public relations (PR) work for its clients. It increases the goodwill
between its clients and other parties like consumers, employees,
middlemen, shareholders, etc. It also maintains good relations between the
client and media owner.
10-
Non-advertising functions
- Advertising agency also
performs many non-advertising functions:
- It fixes the prices of the
product, It determines the discounts, It designs the product, It also
designs its package, trademarks, labels, etc.
· They want freedom in everything they do, from freedom of choice to freedom of expression
· They love to customize, personalize
· They are the new scrutinizers
· They look for corporate integrity and openness when deciding what to buy and where to work
· They want entertainment and play in their work, education and social life
· They are the collaboration and relationship generation
· Has a need for speed and not just in video games
· They are the innovators
52. Communication as a process
Communication is a series of actions between people and between animals that transfers information or meaning from one to the other. In a broad sense every series of related actions is a process and thus, communication can be considered a process. In a narrower sense, the one that says a process is a set of predetermined actions in a predetermined order that achieves a predetermined goal, then only some communication experiences fit the definition. For example teacher is the sender in the class room who has content of the subject. The content of the subject he has what is called as message. The students are the receiver in this place who receives the message. The desired output of this process is to impart knowledge about the subject to the students. Thus communication is a process.
53. Market factors operating the Indian media industry
Budget - It determines everything. Unless a media person has sufficient money he / she cannot produce a film or run newspaper.
Star value – The name of the newspaper, program on famous television channels, famous magazine, well established star film are most important to withstand in the market
The taste of the audience – The program taste of the audience is most important thing to be considered because they need different as well as entertaining program. Stereotyped programs are not at all work out nowadays.
Concept of the program – Whether it is a film, television game show the concept is more important. It should be new and innovative or it should be presented in a new way.
Promotion (Advertising) – Advertising television program, film or even a new newspaper or magazine is most important. It informs people about their new arrivals.
54. Revenue models in media organization
Media revenue models
One
of the most important aspects of media is the fact that the media industry is
just that: an industry. Most media producers and outlets are commercial in
nature, with the main objective of making money. There are several methods or
"revenue models" that media companies use to make money. The four
most common revenue models are discussed below.
Advertising
Advertising
is the most common of all revenue models in traditional media and online. TV
shows, newspapers, and websites offer their content (programming, news stories,
etc.) at no charge (or at a low price) in order to attract a large audience.
Advertisers wanting to promote the products they're selling pay the media
outlets, which in turn place ads in between their content for the audience to
experience.
Subscription
Subscriptions
are great for media types that are continually being updated - think a
newspaper, a magazine, or cable TV - or have some kind of ongoing value - think
websites like LinkedIn or informational databases. Subscriptions are popular
with media companies because they provide steady revenues over time.
Pay-per-item
The
pay-per-item model works for media types that come in an individual package. An
example of this is a pay per view movie on cable, a movie ticket at your local
theater, or a CD or DVD.
Merchandising
Media
companies use merchandising (selling) as a secondary, or ancillary, income.
This is popular with recognizable media franchises whose fan base would want to
purchase related items. An example might be the merchandising efforts of a
company like Disney, which produces and sells merchandise for all of it's
big-budget movies and TV shows. For example, the original Star Wars movies
earned more income through merchandising than through ticket sales.
55. Characteristics of organizational behavior
“Organisational behaviour is the study and application of knowledge about how people act within an organisation. It applies broadly to the behaviour of people in all types of organisation.”
Organisational behaviour revolves around
two fundamental components: 1. The nature of the man. 2. The nature of the
organisation.
In other words,
organisational behaviour may be organisation of individual’s behaviour in
relation to physical means and resources so as to achieve the desired objective
of the organisation.
Characteristics
of Organisational Behavior:
1. Behavioural Approach to Management:
Organisational behaviour is that
part of whole management which represents the behavioural approach to
management. Organisational behaviour has emerged as a distinct field of study
because of the importance of human behaviour in organisations.
2. Cause and Effect Relationship:
Human behaviour is generally taken
in terms of cause and effect relationship. It helps in predicting the behaviour
of individuals. It provides generalizations that managers can use to anticipate
the effect of certain activities on human behaviour.
3. Organisational Behaviour is a Branch of Social Sciences:
·
Organization behavior uses various concepts of social
science in performing various researches required for understanding
organization structure. It is influenced by several social sciences. Sociology,
Anthropology and Psychology are some of important social science used by
organizational behavior. These disciplines provide organizational behavior with
rich information necessary for performing its function
·
Organization behavior is termed as both science and art.
It implies performing several researches and collecting data systematically
regarding behavior. The collected information is then used to control and
manage problems in the organization.
·
Collection of all relevant information systematically
about human behavior is termed as science. Application of collected behavioral
knowledge and skills in the organization is known as art
·
Organizational behavior is a term which is beneficial for
both organization and peoples working within the organization. It creates good
interpersonal relations among employer and employees in the organization.
Employers get full detailed information about their employees working with
them. This eventually reduces all conflicts within organization and results in
better interpersonal relations.
56. Programming strategies of television channel
All networks need to fill their air time with programming. The programming executives must figure out What new shows to develop, What new shows to greenlight, Which programs to keep and to cancel. Overall, they must develop a programming strategy and plan for implementation.
Programming
is divided into two major areas: development and scheduling. Development
involves choosing promising show ideas, purchasing them, and producing them
into viable TV shows. Scheduling involves planning a programming lineup to
maximize viewership.
To create a compelling
TV series, the principal components of the show must differentiate it from the
competition.
Since
television programming is strategic, network executives determine a programming
strategy by considering the following factors:
- A scheduling strategy including the
day and time a show should air, the line-up on a particular day (the order
of shows), and a programming block
- Target audience demographics for the
programming
- Audience flow--keeping the audience
tuned in from one show to the next
- Advertiser appeal
- Promotions for the program
- Production costs of a program
- Cost to purchase rights to
particular programs
- Type of program such as sitcom,
drama, reality, and talk show
- Television ratings
- The competitive landscape during
any particular day part
57. Supply and demand
·
Among other factors, a person's access to media
technology affects the amount and quality of his or her intake.
·
In the United States, in 2009 estimated the 'average'
American consumes 34 gigabytes of media a day."
·
The amount of media consumption among individuals is
increasing as new technologies are created.
·
The sum of media asked for and delivered to consumers on
mobile devices and their homes would take more than 15 hours a day to see or
hear.
·
With social media networks rapidly growing such
as Instagram, Facebook, and Twitter, our world of media consumption is reaching
a younger and younger age group, making our consumption that much larger as a
country.
·
With mobile devices such as smartphones, news,
entertainment, shopping and buying are all now at the tip of our fingers,
anytime, anywhere.[
·
In the world of TV advertising, some markets are short on
supply, while others have it in bucket loads.
·
But in reality, the application of programmatic
(according to a programme, schedule, or method) is not so dried.
·
Take France, for example. On the whole, there is very
little unsold TV inventory (list), meaning supply and demand are in natural
balance.
·
This is a market that will likely yield few buy- or
sell-side advantages in pricing or audience discovery within a programmatic TV
framework.
·
By contrast, the U.S. has roughly 70 ad-supported
channels available to the average household.
·
They (media owners) need the ability to manage inventory,
maximize yield and seamlessly fulfill campaign audience commitments across all
content distribution channels.
58. Project planning stages
Project Goals
A project is successful when it has met the needs of the stakeholders. A
stakeholder is anybody directly, or indirectly impacted by the project.
As a first step, it is important to identify the stakeholders in your
project. It is not always easy to determine the stakeholders of a project,
particularly those impacted indirectly. Examples of stakeholders are:
- The project sponsor
- The customer who receives the
deliverables
- The users of the project output
- The project manager and project
team
Once you have established a clear set of goals, they should be recorded
in the project plan. It can be useful also to include the needs and
expectations of your stakeholders.
Project
Deliverables
·
Using the goals you have defined, create a list of things
the project needs to deliver to meet those goals. Specify when and how to
deliver each item.
·
Add the deliverables to the project plan with an
estimated delivery date. You will establish more accurate delivery dates during
the scheduling phase, which is next.
Project Schedule
Create a list of tasks that need to be carried out for each deliverable.
For each task determine the following:
- The amount of effort (hours or
days) required for completing the task
- The resource who will carry out the
task
Once you have established the amount of effort for each task, you can
work out the effort required for each deliverable, and an accurate delivery
date. Update your deliverables section with the more precise delivery dates.
Human Resource Plan
·
Identify, by name, the individuals and organisations with
a leading role in the project. For each, describe their roles and
responsibilities on the project.
·
Next, specify the number and type of people needed to
carry out the project. For each resource detail start dates, the estimated duration
and the method you will use for obtaining them.
Communications Plan
Create
a document showing who is to be kept informed about the project and how they
will receive the information. The most common mechanism is a weekly or monthly
status report, describing how the project is performing, milestones achieved
and the work you've planned for the next period.
Risk Management Plan
Risk management is an important part of
project management. Although often overlooked, it is important to identify as
many risks to your project as possible and be prepared if something bad
happens.
Here are some examples of common project risks:
- Time and
cost estimate too optimistic
- Customer
review and feedback cycle too slow
- Unexpected
budget cuts
- Unclear
roles and responsibilities
- No
stakeholder input obtained
- Not clearly
understanding stakeholder needs
- Stakeholders
changing requirements after the project has started
- Stakeholders
adding new requirements after the project has started
- Poor
communication resulting in misunderstandings, quality problems and rework
- Lack of
resource commitment
59. Media organization
The term "media organization" means “a person or entity engaged in disseminating information to the general public through a newspaper, magazine, other publication, radio, television, cable television, or other medium of mass communication.” Media organizations have something to sell, and that the audiences are their customers
Gatekeeping
The
media product passes through many levels of organizational processing on its way
to the audience, and at each step in the process, the original data is filtered
reduced in length, edited for style, censored, and so on. Each step in the
process can be thought of as a gate through which the data must pass on its way
to the consumer, consequently this situation is known as gatekeeping.
Agenda
Setting
In
recent decades media researchers have been able to demonstrate an indirect, but
nonetheless powerful, connection between what the news media presents and what
people think. This connection has been dubbed agenda setting.
The media
tend to set the "agenda" -- the list of items that people will be
discussing. Thus, the power of the media may lie not in its ability to sway
people's opinions, but rather in its role of determining what issues will be
considered important enough to discuss.
CONTENT
The term content refers to the message that is distributed by the mass media organization by means of the mass communication channel. The content includes such as entertainment, advertisements, news, sports, etc.
The
content of each medium is subject to analysis and criticism by its readers.
"Literary criticism," "film criticism," and
"television criticism" are all well established fields of academic
study, and some members of mass media organizations make their livings by
publishing their critical views.
SOCIAL INSTITUTIONS
Typically, mass communication operates as a one way communication – messages flow from the media organizations to their audiences in a way that allows for very little immediate feedback. Those who work in media organizations are themselves a part of the society within which their audiences exist, there is a path by which audience response to mass communication messages can feed back to the producers of the messages
60. Media is service organization
· The word ‘media’ is derived from the word medium, signifying mode or carrier. Media is intended to reach and address a large target group or audience.
· The word was first used in respect of books and newspapers i.e. print media and with the advent of technology, media now encompasses television, movies, radio and internet.
· Media is the sword arm of democracy. Media acts as watchdog to protect public interest against malpractice and create public awareness.
61. Marketing process vs Sales
1.
Process
Whether you're writing a marketing
or sales plan, both will include details about the history of the company and
its goals and initiatives. Then the plans dive into the aspects of the plan
that are specific for each department.
The marketing plan lays
out what the product is, its price, who it'll be sold to, and where it will be
sold. This is also known as the 4Ps of marketing: product, price, place, and
promotion. Goals are set, marketing channels are chosen, and a budget is made
for the campaigns the marketing team plans to pursue.
Sales plans include
details about the sales process, team structure, target market, and goals. Plus,
the sales plan outlines the action plan, tools, and resources that will be
used to hit these targets.
2.
Goals
The primary goal of
marketing is to look big picture and promote the company, product or
service, and brand. Marketing departments are responsible for pricing the
products and communicating how the product fills customers' needs and wants.
3.
Tools and Resources
A CRM database is
a tool that can be used by sales, marketing, and the company as a whole. The
database helps all departments manage relationships with contacts, no matter
which stage of the customer lifecycle they're in.
Social media can also be leveraged
by both business units. For marketing, social media can be used to promote
content and for sales, it can be used as part of a social selling strategy.
Plus, there are tools that are specific to
each department.
Marketing tools
·
Search engine optimization (SEO) tool
·
Project management tool
·
Data reporting software
· Content creation tool
Sales Tools
Meetings app
Documents tools
Invoicing software
·
Email management tool
4.
Strategies
Marketing
teams can take different strategic approaches depending on the type of campaign
and customer they're targeting. Marketing strategies include:
·
Internet marketing
·
Print marketing
·
Blog marketing
·
Search engine optimization
·
Social media marketing
·
Video marketing
Similar
to marketing strategies, sales methods can vary depending on its industry,
products, market, and target customer. Some of the most popular sales
methodologies are:
·
Solution Selling
·
Conceptual Selling
·
CustomerCentric Selling
·
The Challenger Sale
62. Freedom of press
·
Freedom of the press or freedom
of the media is the principle that communication and expression
through various media, including printed and electronic media,
especially published materials, should be considered a right to be
exercised freely.
·
Such
freedom implies the absence of interference from an overreaching state;
its preservation may be sought through constitution or
other legal protection and security.
·
With
respect to governmental information, any government may distinguish which
materials are public or protected from disclosure to the public.
·
State
materials are protected due to either of 2 reasons: the classification of
information as sensitive, classified or secret, or the relevance of the
information to protecting the national interest.
·
The United
Nations' 1948 Universal Declaration of Human Rights states:
"Everyone has the right to freedom of opinion and expression; this right
includes freedom to hold opinions without interference, and to seek, receive,
and impart information and ideas through any media.
·
The
depth to which these laws are entrenched in a country's legal system can go as
far down as its constitution.
·
The
concept of freedom of speech is often covered by the same laws as
freedom of the press, thereby giving equal treatment to spoken and published
expression.
63. Impact of globalization on Indian media
· The Indian media and entertainment industry is one of the fastest growing industry in the world.
· India has many entertainment media. Its film and television sectors are dominating the entertainment industry.
· Film and television sectors are growing and globalisation has impacted entertainment and media sectors. India produces many films running at global level theatres, especially in Japan, Singapore, USA, and Canada.
· Indian films and televisions got very large audience all over the world.
· Indian film and television producers are improving the international marketability of large budget Indian movies by building partnership with international screenwriters and composers technicians.
· Indian film industry enjoys world fourth place and television industry is in the third place.
· The most important effect of Globalisation on film industries was that it enabled a bigger market for films worldwide.
· It was after the 1990’s that films started to get released worldwide. This increased the size of the film market and massive growth of revenue in result.
64. Characteristics of an effective budget
· Budget - how much a media company is going to spend for a program (Ex-Advertising)
· Budget is done in the pre-production stage and it is not same for every company
· Budget is prepared based on the program and its content.
· Different types of budgets are there in advertising such as affordable method, percentage of sales method, competitive parity method, objective and task method, judgment method
· In film production budget is prepared by above the line and below the line method and based on production (stages) method.
· New product has to spend more advertising than existing product
· Company’s which have high market share usually spend less amount for advertising. Example – Apple products
· The budget spend for the program should be worth for its output
· The factors that decides budget are the duration of advertisement, number of time it is advertised, the geographical area, etc.
65. Promotion department
· The circulation department takes care of everything after the newspaper is printed.
· This includes delivering the publication to homes through their own or third-party carriers, to the post office to be mailed into homes, as well as to newsstands, vending machines, and other places it's circulated.
· It is usually headed by a major executive, the circulation manager, since the newspaper ultimately stands or falls on the basis of the number of steady readers that can be enrolled.
· Sales Promotion:It involves the direction of an office staff to keep records, notifying subscribers when their subscriptions need renewing, the handling of complaints, new subscriptions and renewals over the counter, by mail, etc.
· Promotion is essentially the "public relations" department of the newspaper. Where a separate promotion department exists, it usually is responsible for initiating promotion policies, subject to the approval of the publisher, and usually coordinates the promotional activities of other departments.
66. Editorial department in newspaper organization
The editorial department forms the backbone of any newspaper organization. As the name implies, this department is the one responsible for content creation in any newspaper establishment. The main responsibilities of this department is the gathering of news, selecting which news and features get to be published in the paper, editing the news and features that have been selected for publication and then laying them out for print.
Publisher- The publisher is responsible for all of the operations of the newspaper, both editorial and business. The main job of the publisher is to see that the newspaper remains financially healthy.
Editor- The editor is responsible for all of the editorial content of the newspaper and for the budgets and money spent by the editorial side of the newspaper. Often in smaller papers, the publisher and editor is the same person.
Editorial page editor- The editorial page editor is responsible for the editorial page and the "op-ed" page of the newspaper. These pages are where the newspaper's editorials are printed as well as letters to the editor, columns by syndicated columnists and guest columns by local people.
Managing editor- This is the person who is in charge of the day-to-day production of the newspaper.
City Editor- The city editor -sometimes called the metro editor -is in charge of the news coverage of the area in which the newspaper is located. The city editor usually has the largest staff and assigns tasks to most of the local news reporters.
News reporter- A news reporter gathers information about news stories in the local area. There are generally two kinds of reporters: i) a beat reporter, and ii) a general assignment reporter.
A beat reporter covers the same subject or location all the time. The subject is generally of interest to the reporter. Various beats include legal reporting, parliamentary reporting, political reporting, etc. Ageneral assignment reporter, on the other hand, covers any story assigned by the city editor or assistant city editor.
Chief copy editor- The chief copy editor is in charge of the newspaper's copydesk. The people on the copydesk read news stories (and sometimes stories from other sections) to make sure they are written according to the newspaper's standards. The chief copy editor makes final decisions about the copy and is in charge of the staffing of the desk.
Copy editor- A copy editor is specially trained to read the stories that others have written and make sure they conform with the rules of grammar and style. A copy editor also writes headlines and performs other duties that help produce the newspaper every day.
Photo editor- A photo editor is not a photographer, although it is often the case that the photo editor is a former photographer. This editor assigns photographers and helps select the photos that the newspaper prints.
Graphics editor- The graphics editor is the head of the graphics department, sometimes called the "art department." This editor is in charge of all of the graphics and illustrations produced for the newspaper.
Graphics reporter- A graphics reporter researches and designs informational graphics that support news stories the paper. A graphics reporter is an expert in graphic forms and also must be able to local information that can be used to build graphics.
67. Duties and responsible of editor (in Newspaper)
· They represent the editorial team in important and controversial matters.
· Manage the editorial team since they have the most experience. However they do little writing and may from time to time contribute to an editorial pieces or editing content
· Ensuring the final draft is complete and there are no omissions or any form of plagiarism.
· They responsible for motivating and developing the editorial team. They may also help settle disputes and problems
· They also handle reader complaints and take responsibility for issues after publication
· Attends all and chairs the Editorial Board meetings and ensures that meeting are productive, run smoothly and end on time, with all business completed
· Sees that all stories for their media company are assigned and deadlines are established
· Enforces deadlines on news stories submission and production
· Responsible for design and layout of the front page and news sections in print edition
· In consultation with the adviser and / or lab-teaching assistant, he/she organizes production of the newspaper, including copyediting, computer inputting and formatting, and pagination, proofreading and prepress. Plans and directs weekly Editorial Board meetings throughout the semester
68. Media manager and his / her responsibilities
Media Managers are communication specialists who develop and implement all targeted content for various media platforms. They research, write, proofread and edit all media content, implement and manage media campaigns, and deliver public relations and communications plans. Media managers are expected to possess super project management and organizational skills with the ability to work comfortable under pressure in a fast – paced environment. To ensure success, media managers should demonstrate a wide degree of creativity and latitude with a keen interest in shaping an organization’s image and values through appropriate communication to the outside world.
Media manager responsibilities
· Identify press opportunities through evolving issues
· Develop content for dissemination via press releases, social media, websites and other distribution channels.
· Ensure that key messages align with vital business strategies
· Serve as the organization’s media liaison and formal spokesperson
· Conduct press conference and briefings.
· Scan media marketplace to keep up-to-date on the latest media trends
· Monitor online and offline campaigns and report on results
· Negotiate with media channels to close competitive deals
· Build and manage the organization’s social media profile and presence
· Promote additional projects to support new product launches
· Build long-term relationships with media influencers
· Appropriately manage the organization’s media budget
69. Problems faced by small newspaper organization
A small newspaper is a newspaper
with a circulation less than 2500. These papers cater to the needs of the
people living in one particular locality. Small newspapers play a more direct
role in forcing the accountability of the people's representatives and all in
influencing the people. They are also a good source of local, political and
commercial information, while at the same time satisfying the socio-cultural
interest of the readers and providing entertainment for them.
Problems of Small Newspapers
·
A small newspaper is a written publication containing
news and ads, usually printed on low costs newsprint often published on a daily
and weekly basis.
·
Small newspapers focus solely on one particular
geographical area where most of the readers live.
·
Subscriptions in small news papers generate a very low
revenue and is insufficient to run a newspaper efficiently.
·
Since ads generate a major amount of the organization's
revenue, the dearth of the ads greatly affect a small newspaper's finance
because of the boom in Electronic media
·
With a limited revenue, small newspapers cannot maintain
a large staff. The administration also finds it hard to pay for the basic
utilities like phone and electricity for its employees.
·
They also use low cost printing which is of much lower
quality, giving the newspaper a very cheap look.
·
Small newspaper has a very limited network because they
employ very few reporters. They do not have time to go out and widen their networks.
·
The paper faces a major problem in delivering newspapers
when there are no delivery boys available..
· The circulation figures of a small newspaper is very less since small newspaper are subscribed by people of only one locality.
· Small newspaper with their limited circulation figures cannot afford to participate with the big organization’s price wars.