FILM LANGUAGE
PART – A
1. Production house
·
A production house is that
organization which gets a movie made.
·
They also provide the
necessary finances that are required to make the film.
· It can encompass anything and everything that is required to get the movie released in a theater.
2. Dolly
·
Moving the camera toward / away from an
object or subject
· Moving the camera closer to the subject is dolly in and away is dolly out.
3. Key light
·
It is the main source of light which is used
to illuminate the object
· This directly shines on the object
4. BGM
·
BGM stands for back ground music
· This is played for supporting the scene
5. Comedian
·
The person who creates humor in a scene is
comedian
· Vadivelu, Vivek, Santhanam are some of the comedians in Tamil film industry
6. Cut
·
It is the basic type of transition. It is an
abrupt transition from one sequence to another
· A cut happens when one shot replaces the other shot
7. Voice over
·
A piece of narration in a
film or broadcast, not accompanied by an image of the speaker.
·
The voice-over is read from
a script and may be spoken by someone who appears elsewhere in the production
or by a specialist voice actor.
· It is mainly used in documentaries to explain information
8. POV
·
It is a shot that shows what a character is
looking at
· When the character looking at something or to show the character reaction POV shot is used
9. Fluorescent light
·
Fluorescent
lamps are a specific type of
gas-charged luminaire that produce light through
a chemical reaction that involves gases and mercury vapor interacting to
produce UV light inside
of a glass tube.
· This is used in film production, which produce visible light
10. Auteur
·
He is a film director who influences the film
so much
· He controls all aspect of creative work
11.
·
It refers to the clothes that characters wear
· Using certain colors / designs costumes signify the character
12. Sequence
·
It is a collection of scenes
· A sequence is a series of scenes that form a distinct narrative unit, which is usually connected either by a unity of location or a unity of time.
13. Lighting
·
Lighting means controlling the light and
shadows
· Three point and four point lighting techniques are used in video production
14. Montage
·
The technique of selecting, editing and
joining together various sections of film
· It conveys story using short shots
15. Voyeurism
·
It is often used to indicate
a general interest in spying at other people’s private activities or moments.
· In fact, watching a movie itself may also be a voyeuristic activity in its nature in that the audience seeks pleasure in looking at lives of other people.
16. Animation
·
It is a method in which pictures are
manipulated to appear as moving images
· They are graphics, 2D and 3D animation
17. Surrealism
·
It is characterized by juxtaposition and
frequent use of shocking imagery
· Surrealists films created a revolution in cinema by providing with linear narrative and plots
18.
·
It is a scene that temporarily takes the
story backward in time from the current point of story
· The character think / tell others of what happened in past
19. Melodrama
·
It is a dramatic work in which the plot is
sensational
· It is designed to appeal strongly to emotions such as sad, angry, etc.
20. Aspect ratio
·
The relationship between the width and height
of the image is aspect ratio
· It gives different way of looking at the world (4:3, 19:9)
21. Scene
·
Scene is the collection of shots
·
A scene is generally thought of as the action
in a single location
· It is a part of a film, as well as an act, a sequence and a setting
22. Adaptation
·
It is the transfer of a written work, in
whole / in part to a film
· A common form of film adaptation is the use of a novel as the basis of a feature film
23. Parallel cinema
·
It was a film movement in Indian cinema that
originated in the state of West Bengal
· Parallel cinema is known for its serious content, realism and naturalism
24. NLE (Non-Linear Editing)
·
It is system based editing. The editing is
done in computer using some software’s
· The shots are randomly picked up and rearranged in a sequential order
25. Alfred Hitchcock
·
He was an English film director and producer
· He is one of the most influential filmmaker in the history of cinema
26. Sign
·
· Sign could also mean a usage of gesture to convey information or instruction
27. Film noir
·
It is a cinematic term used primarily to
describe stylish Hollywood crime dramas
· The term Film Noir, French for black / dark film was first applied to Hollywood films
28. Film realism
·
The common attribute of neo realism is
location shooting and the dubbing of dialogue
· Principal character would be portrayed by trained actors while supporting members would be non-actors
29. Dialect
·
Dialects are linguistic varieties that may
differ in pronunciation, vocabulary, spelling and grammar.
· A form of a language that is spoken in a particular area and that uses some of its own words, grammar, and pronunciations.
30. Non fiction
·
It is any document or content that maintain
in good faith to represent truth and accuracy regarding information, events or
people
· It is usually filmed on the actual scene, with the actual people, without sets, costumes, written dialogue, or created sound effects
31. Stereotype
·
Any commonly know public belief, about the
certain social group or the type of individual
· Example – Many commercial films are male centric in which women are portrayed as sexual object
32. Imaginary line
·
The 180 degree sets an imaginary access or
eye line between two characters or between a character and an object
· By keeping the camera on one side of imaginary access, the characters maintain the same left right relationship to each other
33.
·
A film or book illustrated lecture about the
places visited by a traveler
· Example – An art teacher slideshow of his trip to Mahabalipuram
34. 70MM
·
70mm is a wide high resolution film gauge for
motion picture
· For projection the 65mm film is printed on 70mm film
35. Psychoanalysis
·
It is a set of psychological theories framed
by Sigmund Freud
· It is the belief that all people posses unconscious thoughts, feelings, desires and memories
36. B-roll
·
It is the extra footage captured to enrich
the story telling
· The term A-roll referring to the main footage
37. Symbolism
·
The use of symbols to represent ideas
· It is the way of indirect suggestion to express ideas, emotions and states of mind
38. Characterization
·
It refers to the portrayal of character in
cinema
· It tells the audience what the personality of the character is
39. Paradigmatic connotation
· The film has a paradigmatic connotation when the director has chosen specific cinematic aids to portray an effect such as camera angle, shot, movement, etc
40. Expressionism
·
It is a modernist movement initially in
poetry and painting
· In cinema it is associated with titling, impossible sets, high angles, etc
41. Virtual arts
·
· It includes human-machine interfaces such as visualization, digital painting, sculpture, etc
42. Linear / non linear
·
Linear tells the events of a story in the
order in which they occurred
· Non-linear story which present some or all of the events in a non-chronological order
43. Perception
·
The ability to see, hear, listen, taste and
smell
· It is the way in which something is understood or interpreted
44. Fiction
·
It refers to plot, settings and characters
created from imagination
· An example of fiction is a book, that is not based on a true story
45. Idea
·
It is a thought that generate in the mind
· Ideas often form during brainstorming sessions or through discussions
46. Twist
·
It is a technique that introduces a radical
change in the fiction
· When it happens near the end of the story is known as twist or surprise ending
47. Male gaze
·
It is the act of depicting women and the
world from a masculine perspective
· It represents women as sexual objects for the pleasure of the male viewer
48. French New Wave
·
It is a French film movement and is a form of
European art cinema
· It includes radical experimentation with editing, visual style, narrative, etc
49. Narration
·
The action or process of narrating a story
· It is a set of representational and organizational cues that deliver the story information to audience
50. Myth
·
It is a folklore genre consisting of stories
that play a fundamental role in society
· The main characters in myths are gods, supernatural humans, etc
51. Follow focus
·
A follow focus system is a set of
parts that work together to help focus more
precisely and conveniently for video work.
· Its primary function is to allow focus to follow the action.
52. 35MM
·
It is a film gauge used for motion picture
· It refers to the width of a film which is low resolution than 70mm
53. Jimmy jib
·
It is a light weight modular camera crane
system
· It is a smaller size which allows for easy transportation and set up in any location
54. Music
·
An art of sound in that expresses ideas and
emotions
· It is conveyed through the elements of rhythm, melody and harmony
55. Feminism
·
It is a range of social movement, political movement
and ideologies that share the common goal
· It is to establish and achieve the political, economic, personal and social equality of men and women
56. Cinema verite
·
· It combines improvisation with the use of the camera to unveil truth or highlight subjects hidden behind crude reality.
57. SFX
·
Special effects are
illusions or visual tricks used in the theatre, film, television, and video
game to simulate the imagined events in a story or virtual world.
· Special effects are traditionally divided into the categories of mechanical effects and optical effects
58. VFX
·
In filmmaking, visual effects (VFX) is the creation or manipulation
of any on-screen imagery that does not
physically exist in real life.
· VFX allows filmmakers to create environments, objects, creatures, and even people that would otherwise be impractical or impossible to film in the context of a live-action.
59. Villain
·
He is known as antagonist who is a bad
character in story
· He does negative role and creating trouble to hero and others
60. EDL
·
An edit decision list is the post production
process of film editing
· Video clips can be obtained in order to confirm the final cut
61. Spatial relationship
·
The establishing shot or sequence serves to
situate the audience within a particular environment or setting
· It is to introduce an important character in a movie
62. Icon
·
These are the literal signs and codes: a cop
(police officer) means a cop. They are mean to appear like the thing itself
· When we see a cop, we also associate this with our cultural ideas of justice, the law
63. Codes
·
They are group of signs that seem to fit
together naturally. Together they create meaning
· Example – The sign of a broken heart means lost love and if you add the broken heart to the signs of two people the signs together the code, anyone will read into it that the couple has broken off their relationship
64. Production manager
·
A film production manager who oversees the
overall operations of film production
· He / she are tasked to organize all the necessary needs of a production staff, handle project budget, prepare permits and documents. He also assists in daily production tasks and ensures the production schedules are met
65. Semiotics
·
The study of signs, codes and conventions in
film is called semiotics or semiotic analysis
· Semiotic analysis is a way to explain how an audience makes meaning from codes. It is to read and understand a film and its text
66. Syntax (Grammar)
·
Written language uses letters, words,
sentences and paragraphs to convey narrative
· Cinema uses shots, shot sequences, scenes and dramatic sequences.
67. Film perception
·
It refers to the sensory and cognitive
processes employed when viewing scenes, events and narratives presented in
movie
·
PART B & C
1.
Film
form
Narrative cinema
·
Narrative films tell a story
·
These films screened in theatre broadcast on
TV and sold as DVD
·
It is also called fiction (imaginary tale) film
·
The film maker has the freedom to create
story
·
Fictional films are composed by a string of
events
·
It follows three act structure of story
telling
·
The introduction of characters at first then
the conflict and finally tells solution.
Documentary (non-narrative film)
·
Documentary film making is concerned with the
real facts and historical event – ex – life history of Mahatma Gandhi
·
It is called non - fiction films
·
It has voice over to demonstrate the visual
·
The film maker must produce the evidence for
source of information is documented
·
Interviews with the people is part of
documentary
·
An expert witness in the concerned subject is
important for documentary
Experimental film
·
This type of movie is trying something new
and different
·
These films are rare and unpopular
·
It is neither narrative nor documentary
·
These films are not following three act story
structures.
·
·
The goal is often to place the viewer in a more active
and more thoughtful relationship to the film.
·
Most such films are made on very low budgets,
self-financed or financed through small grants, with a minimal crew or, often a
crew of only one person, the filmmaker.
2.
Film
genre
FILM GENRE - A film genre is a motion-picture category based on similarities either in the narrative elements or in the emotional response to the film. Genre consists of four elements or parts: character, story, plot and setting.
1. Action
film
Action films usually
include high energy, big-budget physical stunts and chases, possibly with
rescues, battles, fights, escapes, destructive crises (floods, explosions,
natural disasters, fires, etc.), spectacular rhythm and pacing, and
adventurous, often two-dimensional 'good-guy' heroes or heroines battling 'bad
guys'.
2. Adventure
film
Adventure films are
usually exciting stories, with new experiences, very similar to or often paired
with the action film genre. They can include "jungle" and
"desert" epics, treasure hunts, disaster films, or searches for the
unknown.
3.
Comedies are
light-hearted plots consistently and deliberately designed to amuse and provoke
laughter by exaggerating the situation, the language, action, relationships and
characters. Various forms of comedy include slapstick, screwball, spoofs and
parodies, romantic comedies, black comedy and more.
4. Crime
film
Crime (gangster) films
are developed around the disturbing actions of criminals particularly bank
robbers, underworld figures, or ruthless hoodlums who operate outside the law,
stealing and murdering their way through life. The criminals or gangsters are
often counteracted by a detective-protagonist. This category also includes
various 'serial killer' films
5. Drama
film
Dramas are serious, plot-driven presentations, portraying realistic characters, settings, life situations, and stories involving intense character development and interaction. Usually, they are not focused on special-effects; comedy, or action. Melodramas, epics, courtroom dramas, romantic are examples of this genre.
6. Epic
film
Epics include costume
dramas, historical dramas, war films that often cover a large expanse of
time set against a vast, panoramic backdrop. Epics often share elements of the
elaborate adventure films genre. Epics take an historical or imagined
event, mythic, legendary, or heroic figure, and add an extravagant setting or
period, lavish costumes, and accompany everything with grandeur and spectacle,
dramatic scope, high production values, and a sweeping musical score.
7. Horror
film
Horror films are
designed to frighten and to invoke our hidden worst fears, often in a
terrifying, shocking finale, while captivating and entertaining us at the same
time in a cathartic experience. Horror films are often combined with science
fiction when the monster is related to a corruption of technology, or when
Earth is threatened by aliens. There are many sub-genres of horror:
psychological, survival, serial killers, zombies, monsters, Dracula, etc.
8.
Musical/dance films are
cinematic forms that emphasize full-scale scores or song and dance routines in
a significant way (usually with a musical or dance performance integrated as
part of the film narrative), or they are films that are centered on
combinations of music, dance, song or choreography.
9. Science
fiction film
Sci-fi films are often
quasi-scientific, visionary and imaginative - complete with heroes, aliens,
distant planets, impossible quests, improbable settings, fantastic places,
great dark and shadowy villains, futuristic technology, unknown and unknowable
forces, and extraordinary monsters ('things or creatures from space'), created
by mad scientists. Science fiction often expresses the potential of technology
to destroy humankind.
10. War
film
War films acknowledge the horror and heartbreak of war, letting the actual combat fighting (against nations or humankind) on land, sea, or in the air provide the primary plot or background for the action of the film. War films are often paired with other genres, such as action, adventure, drama, romance, comedy, suspense. They may include stories of military operations, and training.
3. Types of camera shots
Shot in filmmaking is a series of frames that runs for an uninterrupted period of time.
Extreme Long Shot
· The extreme wide shot or extreme long shot is all about showing the world in which the story takes place.
· In an extreme wide we will see large landscapes in the frame.
· Whether it is the desert or outer space, the audience should get a feel for the time and the place they are about to spend the next two hours.
· Though characters can be introduced in an extreme wide, they would be very tiny in context to the backdrop
· An extreme wide shot is often an establishing shot.
Long Shot
· A wide shot, often referred to as a long shot
· The characters can be seen from head to toe
· This shot is used to show how the character is small in relation to the vast surroundings.
· When the term long shot is emphasized, it can mean that the camera is farther away from the subject, making them even smaller.
· A wide shot can also be a master shot, which is used to introduce a new location like a dining room or restaurant.
· It gives the audience a sense of geography so when the camera goes in tighter, they can understand who is where.
Medium Shot
· The medium shot shows the character from the waist up.
· Medium shots are often used in dialog scenes.
· It is also known as a cowboy shot.
· This shot is about revealing information.
· You can see more detail than you can in a wide shot.
Close-Up Shot
· A close-up frames the character’s face.
· It gives more detail that tells us how a character feels.
· A close-up highlights emotional clues in the eyes.
· It is more intimate so the audience can feel what the character is feeling.
Medium Close-Up Shot
· Halfway between the close-up and the medium shot is the medium close-up
· It frames the subject from the shoulders up.
· This shot might be used to show more body language, some emotion and facial expressions.
· Medium close-up can reveal more information, but it is not as intimate as a close-up.
Extreme Close-Up Shot
· An extreme close-up frames even tighter on a face (or subject), highlighting facial features more.
· It usually frames a particular part of the face like the eyes or the mouth.
· It is even more intimate than the close-up
· It is used to show more intense emotion.
Two Shot
Over-the-Shoulder Shot
In addition to subject size within a frame, shot types can also indicate where a camera is placed in relation to the subject. Here are some commonly used terms:
Eye Level Angle
High Angle
Low Angle
· The camera lens is facing up (from below the eye level) to capture the video
· This can have the effect of making the subject look powerful, heroic, or dangerous.
· Taking a photograph from a low angle, also know as a ‘worm’s-eye view’, makes subjects appear larger than normal.
Dutch Angle
· It is often used to show a disoriented or uneasy psychological state.
· That is the subject is not entirely right.
· Dutch angles can be artfully utilized to tell us that something is wrong.
· Maybe the subject is in danger, or their state of mind isn’t properly grounded.
Bird eye angle
· The Bird's Eye photos are angled at 40 degrees rather than being straight down. · Satellite imaging programs and photos have been described as offering a viewer the opportunity to "fly over" and observe the world from this specific angle.
5. Types of camera movements
The way a camera moves can give meaning to what's happening on screen.
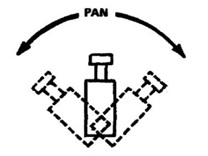
1. Pan
· Turning the camera lens horizontally from left to right or right to left.
· Moving the camera from left to right is called pan right.
· Moving the camera from right to left is called pan left.
· It is used to follow the objects.
2. Tilt
· Moving the camera lens up or down is called tilt.
· Tilt up means that the camera is made to point up and tilt down means made to point down.
· Tilt down is used to show the character weak and tilt up is to show the character strong.
3. Zoom
· Here the camera is static, only the lens moves.
· Zoom in means showing the object in big size, zoom out means showing it in small size.
· Zoom in used to show emotions of the character
· A zoom shot gives the viewer feeling that the subject or object is coming toward or away to the viewer.
4. Dolly
· Moving the camera toward or away from the subject is dolly.
· Move the camera closer to the object is dolly in and away from object is dolly out.
· A dolly shot gives the viewer feeling that they are moving toward or away from the subject.
5. Trucking
· Moving the camera laterally.
· The camera moves left to right (or right to left)
· It maintains the same distance from the subject.
· We would need to have the camera in the street, moving parallel with our subject.
6. Pedestal
· Moving the camera up or down, while keeping the lens at a constant angle.
· Pedestal up means raise the camera, pedestal down means lowering the cameras.
· The whole time keeping the camera’s lens at a 90° angle to the ground.
7. Jimmy jib
· It is a triangular crane system which uses an arm supporting a camera at one end and a counterweight at the other.
· The crane can swing from the ground to the cranes maximum reach of 40ft and can swing 360 degrees.
6. Importance of editing / Functions of editing
Editing
is done for different reasons. It is needed to arrange shots to tell a story
and also to eliminate extraneous material to make a story fit a given time
slot. Four basic editing functions are: (1) combine, (2) shorten, (3) correct,
and (4) build.
COMBINE
- The simplest editing is combining program portions by hooking the various
video-recorded pieces together in the proper sequence. For example, select
various shots taken at a friend's wedding and simply combine them in the order
in which they occurred.
SHORTEN
- Many editing assignments involve cutting the available material to make the
final videotape fit a given time slot or to eliminate extraneous material. For
example the whole T20 cricket match is shown on television news for 2 to 3
minutes only.
CORRECT
- Much editing time is spent on correcting mistakes, either by eliminating
unacceptable portions of a scene or by replacing them with better ones. This
type of editing can be simple—merely cutting out the part during which the
talent coughed and replacing it with a retake.
BUILD -
The most difficult, but also the most satisfying, editing assignments are when
you can build a show from a great many takes. For example, when you use a
single camcorder during a field production, you need to select the best shots
and put them in the proper sequence in postproduction editing to build the
story.
7. Three point lighting
Lighting
is the deliberate use of light to achieve practical or aesthetical effects.
Lighting includes the use of both artificial light sources like lamps and light
as well as natural illumination by capturing daylight.
Key
light - It is the main source of light used to illuminate the object. It shines
directly upon object. The placement of key light determines the shoot. In
indoor shoot the key light is lamp and in outdoor the sun is key light.
Fill
light – It is also shines upon the object. It is placed at the opposite side of
key light. It is placed lower position than key light. It controls the shadow
produced by the key light.
Back
light – It shines from the back side of object. It separates the object from
background. It is placing either one side or both side of object.
8.
Mise-en-scene
It is a
French word which means placing on stage. It is an expression used to describe
the design aspects of film production.
Set
design – The setting of a scene and properties visible in a scene. Set design
is used to amplify character emotion which has physical social cultural
significance in film
Lighting – It can influence the audiences understanding of characters, actions and mood. Light and shade emphasize texture, shape, time (day or night), season, etc.
Space –
It affects the reading of film. It is the distance between characters, camera,
lighting, properties, etc.
Composition
– The organization of object, actors and space within the frame. Equal
distribution of light, color and objects in a shot is important in composition.
Costume
– It refers to the clothes, that characters wear. Using certain colors or
designs, costumes are used to signify the character.
Make-up
and hair style – It gives beautiful appearance to the character. It establishes
the characters attitude.
Acting – The performance on the stage is called acting. Different characters perform on stage. Through acting, actors convey story, emotions, feeling, etc.
Aspect ratio – The relationship between the width and height of the image. It gives different way of looking at the world.
9. Types of transitions
CUT - The cut is an instantaneous change from one image (shot) to another. It is assuming that the preceding and following shots show some continuity. The cut itself is not visible; all you see are the preceding and following shots. It resembles most closely the changing field of the human eye. The cut is basically used for the clarification and intensification of an event. Clarification - For example, in an interview show the guest holds up the book she has written. To help the viewer identify the book, you cut to a close-up of it. Intensification - for example, a football tackle might look quite tame; by cutting to the close-up, the action has been intensified.
DISSOLVE - The dissolve is a gradual transition from shot to shot, the two images temporarily overlapping. The dissolve is a clearly visible transition. Dissolves are often used to provide a smooth bridge for action or to indicate the passage of time. When you hold the dissolve in the middle, you will create a superimposition, or super.
FADE - In a fade the picture either goes gradually to black (fadeout) or appears gradually on the screen from black (fade-in). You use the fade to signal a definite beginning (fade-in) or end (fade-out) of a scene. Cross-fade for a quick fade to black followed immediately by a fade-in to the next image.
10. Film as a medium of communication
·
It performs the functions of mass media such
as inform, educate and entertain.
·
It is used for transmission of culture from
one generation to another
·
They generate mass mediated culture arising
from elite, folk, popular and mass origins. Audiences follow their hero /
heroine’s dress code, attitude, etc.
·
Through cinema we perceive the world around
us. Story based on various locations help us to know their language, habit,
behavior, etc.
·
It provides ideas to visualize our society.
·
Films appeal to their primary emotions and
sentiments of the viewer with its content such as happy, sad, etc.
·
Information spread through cinema still fresh
in minds of people
·
Films combine visualize, movement, sound,
theatre, music all in one to communicate the message effectively.
·
Cinema language is universal which helps in
breaking social and cultural barriers. Without understanding the language
people understand the message with the help of visuals and music
·
It educates even an illiterate people through
dialogue, concept, music, shots, angle.
·
Films have been effective in projecting
social evils such as bribe, corruption, theft, robbery, etc.
·
Films have been exposing under world
elements, bureaucrats, unemployment problem, etc.
·
It can stimulate values of good life and
citizenship through its content.
11. Film is a mass communication
·
Film performs the functions of mass media. It
reaches millions of people.
·
It informs, educate, and entertain the people
through its content.
·
It transforms culture from one generation to
another
·
Since film is an audio visual medium, it
provides social messages
·
Movie helps us to perceive the world around
us. Songs are taken in different countries.
·
Film provides us to conceive of our society.
It shows what is happening around us.
·
Film uses varieties of stories such as love,
comedy, action, etc. to attract the audience.
·
Film appeal to people’s sentiments and
emotions. Happiness, sadness, anger are shown in the film
·
Film leaves lasting impression of the
message.
·
The films generate fashion styles and
mannerisms. Youths do what their hero does.
·
Some films try to show breaking stereo type’s
role. K. Balachander films are given more importance to female characters.