ELEMENTS OF FILM STUDIES
PART
– A
1. Production assistant
· He is known as PA, is the member of the film crew.
· He is assisting the director in various aspects, of production – scripting, shooting, and organizing.
2. Cinema Varite
· It is a style of film making, characterized by realistic.
· It avoids artificial and artistic effects. Ex – documentary
3. Sound recordist
· He is a film crew, recording sound during film making (shooting).
· He is arranging all the necessary recording equipment – mic, speaker, etc.
4. Dissolve
· It is one kind of transition applied between two shots.
· One shot is gradually fades out while another image is fading in.
5. Fluorescent lamp
· It is used in film production which produce visible light.
· It produces light which is glowing in nature – fluorescent red, yellow, green.
6. Key light
· It is the main source of light used to illuminate the object.
· In indoor shoot, the key light is lamp and in outdoor, the sun is key light.
7. Fill light
· It is placed at the opposite side of key light.
· It controls the shadow produced by key light.
8. 16mm film
· It refers to the width size of film.
· It is used for low budget motion picture.
9. Dolly shot
· Moving the entire camera forward and backward is dolly.
· Move the camera towards the subject is dolly in, backward the camera is dolly out.
10. Comedian
· The person who is making the audience laugh is comedian.
· He is using joke, acting as fool to create comedy.
11. Villain
· He is known as antagonist who is a bad character in a story.
· He is doing negative character – creating trouble to hero, heroine and public.
12. Voice over
· The recorded audio is placed over the film.
· It is mainly used in documentaries to explain information.
13. Dubbing
· The voice of the character is recorded and synchronized with the lip movement.
· The voice can be given by the same artist or by other person.
14. OTS (Over The Shoulder Shot)
· The camera is placed to show the side face of the character and the mid shot of another character during conversation.
· It should follow 180 degree rule.
15. POV (Point of View)
· It is a kind of shot shows what a character is looking at.
· It is also showing the characters reaction.
16. Jump cut
· Two sequential shots of the same subject are taken from camera positions that vary slightly.
· It is a cut used in film editing.
17. Documentary
· Life history of a person or any living and non living things portrayed in actual manner.
· No imagination, exaggeration and dramatization in documentary.
· Eg – about a river, product manufacturing, etc.
18. Docudrama
· It is dramatized reenactments of actual events.
· It is to know historical fact. Eg – make up a man like Netaji to act in his way.
19. Trolley shot
· Moving the entire camera left or right in an arc shaped path.
· It is used to follow the object.
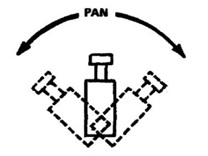
20. Pan
· Turning the camera left to right is pane right and right to left is pan left.
· It is used to follow the subject.
21. Jimmy jib or crane
· It is to lift the camera from low to height.
· It is used to take top view shot.
22. Cut
· It is one of the transitions used to clarify the event.
· The abrupt change over from one shot to another shot is cut.
23. Production house or company
· The company which produces media content is called production house.
· It makes film, programs for different television channels.
· Ex – Radan media, AVM production.
24. Song sequence
· Sequence is the restatement of a longer melody.
· It can be higher or lower pitch in the same voice.
25. 35mm
· It is the common name for 36 x 24 film format used in film making.
· It has an aspect ratio of 3:2
26. Softbox
· It is a type of photographic lighting device used to produce soft light.
· White umbrella or any white surface used to soften the light.
27. BGM (Background Music)
· Music that is played at a low volume at the background of dialogue.
· It is to support the dialogue and the mood of scene.
28. 19:9
· It is an aspect ratio with a width of 16 units and height of 9.
· It is the international standard format of HDTV.
29. Box office
· It is a place where tickets are sold to public to watch the show.
· In film industry it is the amount of business of film.
30. Suggestion
· An idea or plan put forward for consideration.
· The suggestion can be taken or denied.
31. Supporting role (actor)
· The person who is supporting the leading actors hero or heroine.
· The film industry give separate award for supporting actor to recognize their importance.
32. Framing
· It is the placement of visual elements in an image.
· It can make an image more pleasing and keep the viewer focus on the framed object.
33. Auteur
· He is a film director who influences the film so much.
· He controls all aspects of creative work.
34. Budget
· The financial planning for taking a film is called budget.
· It is prepared by above the line and below the line budget or pre-production, production and post production budget.
35. Genre
· Different types of film are called genre.
· Different genres are love film, sports film, action film, etc.
36. Aerial shot
· Taking photograph of ground from an elevated position is called aerial shot.
· Taking photo from helicopter or taller building.
37. Fade in
· It is a transition which changes the screen gradually from black to visual.
· It is used at the starting of the program to indicate that it starts.
38. Fade out
· It is a transition which changes the screen gradually from visual to black.
· It is used at the end of program to indicate that it ends.
39. Cross fade
· When one visual fade out and another visual fade in simultaneously is called cross fade.
· It is used between the end of first visual and starting of another visual.
40. XCU (Extreme close up) shot
· Framing the important part of character or the object – face, eyes.
· This shot creates intense mood.
41. Flash forward
· It is a scene that temporarily takes the story forward in time from the current point of story.
· That is one character think of what will happen in future.
42. Flash back
· It is a scene that temporarily takes the story backward in time from the current point of tory.
· That character thinks of what happened in past.
43. Rack focus
· Changing the focus of lens during shooting is called rack focus.
· Showing the front object clear and back object blur and changing the focus to show back object clear and front object blur.
44. Outline
· It is the shorter form of story told in a paragraph.
· It is to understand one line story.
45. One line story
· The whole story is told in single line.
· Outline, treatment, plot are derived from one line story.
46. Treatment
· It is longer and more detailed paragraph of story.
· It is told in the present tense and describes events.
47. Plot
· Building the story from beginning to end is plot.
· Exposition, rising action, conflict, climax and solution are elements of plot.
48. Psychoanalysis
· It was founded by Sigmund Freud.
· It is a set of philosophical descriptions of human nature.
· A theory of personality which is developed through different stages in life.
49. Running gag
· It is also called running joke, and is a form of funny joke.
· It begins with an unintentional humor that appears repeatedly.
50. Cinemascope
· It is a lens used to shoot side screen movies.
· The image size is up to 2.66:1 aspect ratio.
51. Alam Ara
· It is the first Indian talkie film.
· It is a love story between a prince and gypsy girl.
52. Raja Harish Chandra
· It is the first Indian movie directed by Dada Saheb Phalke.
· It is a silent film. In India the highest award in film industry is Dada Saheb Phalke award.
53. Laurel and Hardy
· It is a comedy double act of American cinema.
· The team was compost of thin English man Laural and heavy man American Hardy.
54. Mise-en-scene
· It is French word means placing on stage.
· It is the design aspect of stage which includes set design, costume, make up, lighting, camera movement, etc.
55. Slapstick comedy
· It is a style of humor involving exaggerated physical activity of the comedian.
· Charlie Chaplin comedy is the example for slapstick comedy.
56. Melodrama – Melody + Drama
· It is a dramatic work in which the plot is sensational.
· It is designed to appeal strongly to emotions such as sadness, anger.
57. National film Archive
· It is to trace, acquire and preserve the Indian cinema.
· To act as a center for dissemination of film culture.
58. In-cinema editing
· Editing is done during shooting itself.
· Instead of editing shots into sequence after shooting, the cinematographer shoots the sequence in order.
59. Concept
· The important message in the story is called concept.
· The story is developed based on concept.
60. Shot
· It is defined as capturing the video between camera on and off.
· It is made up of many frames.
61. Sequence
· It is collection of scenes.
· Scenes are placed in order to make sequence.
62. Music
· It is a sound created by musical instrument.
· It is to compose songs and to create feel to scene.
63. 70mm film
· It is a wide high resolution film more than 35 mm.
· The aspect ratio is 2.20:1
64. 180 degree rule
· It is a cinematography guideline that states that two characters in a scene should maintain the same left / right relationship to one another.
· When the camera passes over 180 degree rule is called reverse angle.
65. Montage
· It is a technique in film editing.
· Series of short shots are edited into a sequence to reduce space, time.
66. Take
· It is a single continuous recorded performance of film.
· It is numbered as take one, take two, take three and so an.
67. Slug line
· It is called as master scene heading which occurs at the start of every scene.
· It is made up of 3 parts such as interior, exterior and both.
68. Morphing
· It is a special effect in film that changes smoothly from one image into another.
· It is used to show one person turning into another.
69. Foreshadowing
· An important plot point is mentioned early in the story is foreshadowing.
· It is used to get the attention of viewer.
70. Chromakey
· It is a special effect techniques for composting two videos.
· Removing background of one video and joining with another video – ex – news reading.
71. Superimposition (Super)
· Showing two videos simultaneously is called superimposition.
· It can be achieved by reducing opacity of top video layer.
72. Incandescent
· It is an electric light with a wire filament.
· It is filled with inert gas.
73. Harsh light
· It is a high contrast hard shadow light.
· Mid-day sunlight is the example for harsh light.
74. Soft light
· It is very soft because of the light getting diffused.
· It tends to wrap around object.
75. Realism
· The reality of the character and events shown in film is realism.
· There is no exaggeration and fantasy in the film.
76. Screenplay
· It is a written work by screen writer for a film.
· The moment, actions, expressions and dialogues of the character are mentioned in it.
77. Available light
· The light which is available in the shooting place is available light
· Ex – sun light
78. Aspect ratio
· The width and height measurement of screen is aspect ratio.
· 4:3, 16:9 are general aspect ratio of screen.
79. Dutch angle
· It is a type of camera angle framing the subject nearly 45 degree angle.
· It is used to show the confusion mood of characters.
80. Steadycam
· It is a camera mounting device which is fixed on the cameraman body.
· It is used to capture the shot in an irregular surface.
81. Nose room
· It is the space in front of the moving object.
· It is to clarify the audience that the character is moving in the particular direction.
82. Protagonist
· He/She is the main character in story hero or heroine.
· It is at the center of the story and moves it forward.
83. Art director
· He is responsible for the visual style in movies.
· He creates the overall visual design of the film.
84. Blue matte and green matte
· It is a special effects film making to combine two or more videos into one.
· Mattes are used to combine foreground image with background image.
85. Linear editing
· It is a post production process of selecting, arranging and modifying images and sound in an ordered sequence.
· The principle of linear editing is copy and paste on to tape.
86. Non-linear editing (NLE)
· It is a computer based post production editing.
· The principle is arranging and rearranging the shots.
87. Storyboard
· It is in the form of illustrations or images displayed in sequential order.
· The purpose of storyboard is to pre-visualize the story.
88. Composition
· The arrangement of element in a shot is composition.
· It includes framing shot, depth of field, to communicate the story.
89. VFX (Visual Effects)
· The image is manipulated with some effects such as bouncing ball, page curl, etc.
· The VFX can be done during shooting or after.
90. Synchronization
· The proper arrangement of sound with visual is called synchronization.
· It is to match the sound with the lip movement of the character.
PART B & C
1. FILM GENRE - A film genre is a motion-picture category based on similarities either in the narrative elements or in the emotional response to the film. Genre consists of four elements or parts: character, story, plot and setting. An equation for remembering the genre is: Story (Action) + Plot + Character + Setting = Genre. This becomes an easy way to remember the elements of a genre.
Action
film
Action films usually
include high energy, big-budget physical stunts and chases, possibly with
rescues, battles, fights, escapes, destructive crises (floods, explosions,
natural disasters, fires, etc.), spectacular rhythm and pacing, and
adventurous, often two-dimensional 'good-guy' heroes or heroines battling 'bad
guys'.
Adventure
film
Adventure films are
usually exciting stories, with new experiences or exotic locales, very similar
to or often paired with the action film genre. They can include
"jungle" and "desert" epics, treasure hunts, disaster
films, or searches for the unknown.
Comedy
film
Comedies are
light-hearted plots consistently and deliberately designed to amuse and provoke
laughter by exaggerating the situation, the language, action, relationships and
characters. Various forms of comedy include slapstic, screwball, spoofs and
parodies, romantic comedies, black comedy and more.
Crime
film
Crime (gangster) films
are developed around the disturbing actions of criminals particularly bank
robbers, underworld figures, or ruthless hoodlums who operate outside the law,
stealing and murdering their way through life. The criminals or gangsters are
often counteracted by a detective-protagonist. This category also includes
various 'serial killer' films
Drama
film
Dramas are serious,
plot-driven presentations, portraying realistic characters, settings, life
situations, and stories involving intense character development and
interaction. Usually, they are not focused on special-effects; comedy, or
action. Melodramas, epics, courtroom dramas, romantic are examples of this
genre.
Epic
film
Epics include costume
dramas, historical dramas, war films that often cover a large expanse of
time set against a vast, panoramic backdrop. Epics often share elements of the
elaborate adventure films genre. Epics take an historical or imagined event,
mythic, legendary, or heroic figure, and add an extravagant setting or period,
lavish costumes, and accompany everything with grandeur and spectacle, dramatic
scope, high production values, and a sweeping musical score.
Horror
film
Horror films are
designed to frighten and to invoke our hidden worst fears, often in a
terrifying, shocking finale, while captivating and entertaining us at the same
time in a cathartic experience. Horror films are often combined with science
fiction when the monster is related to a corruption of technology, or when
Earth is threatened by aliens. There are many sub-genres of horror:
psychological, survival, serial killers, zombies, monsters, Dracula, etc.
Musical
/ Dance film
Musical/dance films are
cinematic forms that emphasize full-scale scores or song and dance routines in
a significant way (usually with a musical or dance performance integrated as
part of the film narrative), or they are films that are centered on
combinations of music, dance, song or choreography.
Science
fiction film
Sci-fi films are often
quasi-scientific, visionary and imaginative - complete with heroes, aliens,
distant planets, impossible quests, improbable settings, fantastic places,
great dark and shadowy villains, futuristic technology, unknown and unknowable
forces, and extraordinary monsters ('things or creatures from space'), created
by mad scientists. Science fiction often expresses the potential of technology
to destroy humankind.
War
film
War films acknowledge the horror and heartbreak of war, letting the actual combat fighting (against nations or humankind) on land, sea, or in the air provide the primary plot or background for the action of the film. War films are often paired with other genres, such as action, adventure, drama, romance, comedy, suspense. They may include stories of military operations, and training.
2. Film production stages
Pre-production
·
This stage is finalizing the preparations for
film production.
·
The budget of the film is prepared
·
Important cast members, director and
cinematographer are selected.
·
The screenplay is finalized
·
The script is broken down into individual
scenes.
·
Storyboard creations, location search, props,
costumes, special effects and visual effects are identified.
·
Detailed schedule is prepared and distributed
to the team members.
· Sets are constructed
Production
·
It is the stage of film shooting
·
More crew will be recruited such as property
master, script supervisor, assistant directors and still photographers.
·
The crew and the actors are present in the
location on time.
·
The actors are well dressed and go to the
hair and make-up departments.
·
The actors rehearse script
·
Finally the action is shot
· Assistant and associate directors are helping directors during shooting.
Post – production
·
It is done after the shooting
·
The film editor edits the footage in a
sequential order
·
The sound is recorded edited and music tracks
are scored
·
Sound effects are designed and recorded
· Computer graphic, visual effects, titling are digitally added
· Finally all sound elements are mixed which are added to picture and the film is fully ready for distribution.
3. Types of camera movements
The way a camera moves can give meaning to what's happening on screen.
1. Pan
· Turning the camera lens horizontally from left to right or right to left.
· Moving the camera from left to right is called pan right.
· Moving the camera from right to left is called pan left.
· It is used to follow the objects.
2. Tilt
· Moving the camera lens up or down is called tilt.
· Tilt up means that the camera is made to point up and tilt down means made to point down.
· Tilt down is used to show the character weak and tilt up is to show the character strong.
3. Zoom
· Here the camera is static, only the lens moves.
· Zoom in means showing the object in big size, zoom out means showing it in small size.
· Zoom in used to show emotions of the character
· A zoom shot gives the viewer feeling that the subject or object is coming toward or away to the viewer.
4. Dolly
· Moving the camera toward or away from the subject is dolly.
· Move the camera closer to the object is dolly in and away from object is dolly out.
· A dolly shot gives the viewer feeling that they are moving toward or away from the subject.
5. Trucking
· Moving the camera laterally.
· The camera moves left to right (or right to left)
· It maintains the same distance from the subject.
· We would need to have the camera in the street, moving parallel with our subject.
6. Pedestal
· Moving the camera up or down, while keeping the lens at a constant angle.
· Pedestal up means raise the camera, pedestal down means lowering the cameras.
· The whole time keeping the camera’s lens at a 90° angle to the ground.
7. Jimmy jib
· It is a triangular crane system which uses an arm supporting a camera at one end and a counterweight at the other.
· The crane can swing from the ground to the cranes maximum reach of 40ft and can swing 360 degrees.
4. Frame, shot, scene, and sequence
Frame
· The smallest unit of visual film structure is a frame.
· A frame is one of the many still images which compose the complete moving picture.
· If you looked at reel of film, you would see that it was a series of images. Each image is a frame of film.
Shot
· The shot is defined as the action captured between camera on and off
· It is made up of frames
· In filmmaking and video production, a shot is a series of frames that runs for an uninterrupted period of time.
· For instance, in a shot kitten playing with a toy mouse. Then you might see a shot of its brother kitten watching from behind a chair. Then a shot of the brother kitten as he pounces on the toy mouse from behind the chair. Then a shot of the first kitten hissing in anger as his brother carries the toy mouse off in his mouth.
Scene
· Scene is defined as the collection of shots
· A scene is defined as action that takes place in the same location or the same time.
· There are exceptions to this, such as if a character has a flashback, or flashforward, or the scene intercuts or crosscuts between two locations with action happening at the same time.
· For example, parts of an action film at the same location, that play at different times can also consist of several scenes. Likewise, there can be parallel action scenes at different locations usually in separate scenes
Sequence
·
· It forms a distinct narrative unit, which is usually connected either by a unity of location or a unity of time.
· For example, the leader of the gang collects together the conspirators, a robbery sequence, an escape sequence, and so on. The sequence is one of a hierarchy of structural units used to describe the structure of films.
5. Types of camera shots
Shot in filmmaking is a series of frames that runs for an uninterrupted period of time.
Extreme Long Shot
· The extreme wide shot or extreme long shot is all about showing the world in which the story takes place.
· In an extreme wide we will see large landscapes in the frame.
· Whether it is the desert or outer space, the audience should get a feel for the time and the place they are about to spend the next two hours.
· Though characters can be introduced in an extreme wide, they would be very tiny in context to the backdrop
· An extreme wide shot is often an establishing shot.
Long Shot
· A wide shot, often referred to as a long shot
· The characters can be seen from head to toe
· This shot is used to show how the character is small in relation to the vast surroundings.
· When the term long shot is emphasized, it can mean that the camera is farther away from the subject, making them even smaller.
· A wide shot can also be a master shot, which is used to introduce a new location like a dining room or restaurant.
· It gives the audience a sense of geography so when the camera goes in tighter, they can understand who is where.
Medium Shot
· The medium shot shows the character from the waist up.
· Medium shots are often used in dialog scenes.
· It is also known as a cowboy shot.
· This shot is about revealing information.
· You can see more detail than you can in a wide shot.
Close-Up Shot
· A close-up frames the character’s face.
· It gives more detail that tells us how a character feels.
· A close-up highlights emotional clues in the eyes.
· It is more intimate so the audience can feel what the character is feeling.
Medium Close-Up Shot
· Halfway between the close-up and the medium shot is the medium close-up
· It frames the subject from the shoulders up.
· This shot might be used to show more body language, some emotion and facial expressions.
· Medium close-up can reveal more information, but it is not as intimate as a close-up.
Extreme Close-Up Shot
· An extreme close-up frames even tighter on a face (or subject), highlighting facial features more.
· It usually frames a particular part of the face like the eyes or the mouth.
· It is even more intimate than the close-up
· It is used to show more intense emotion.
Two Shot
Over-the-Shoulder Shot
In addition to subject size within a frame, shot types can also indicate where a camera is placed in relation to the subject. Here are some commonly used terms:
Eye Level Angle
High Angle
Low Angle
· The camera lens is facing up (from below the eye level) to capture the video
· This can have the effect of making the subject look powerful, heroic, or dangerous.
· Taking a photograph from a low angle, also know as a ‘worm’s-eye view’, makes subjects appear larger than normal.
Dutch Angle
· It is often used to show a disoriented or uneasy psychological state.
· That is the subject is not entirely right.
· Dutch angles can be artfully utilized to tell us that something is wrong.
· Maybe the subject is in danger, or their state of mind isn’t properly grounded.
Bird eye angle
· The Bird's Eye photos are angled at 40 degrees rather than being straight down.
· Satellite imaging programs and photos have been described as offering a viewer the opportunity to "fly over" and observe the world from this specific angle.
7. Mise-en-scene
It is a French word which means placing on stage.
It is an expression used to describe the design aspects of film production.
Set design – The setting of a scene and
properties visible in a scene. Set design is used to amplify character emotion
which has physical social cultural significance in film
Lighting – It can influence the audiences
understanding of characters, actions and mood. Light and shade emphasize
texture, shape, time (day or night), season, etc.
Space – It affects the reading of film. It is
the distance between characters, camera, lighting, properties, etc.
Composition – The organization of object,
actors and space within the frame. Equal distribution of light, color and
objects in a shot is important in composition.
Costume – It refers to the clothes, that
characters wear. Using certain colors or designs, costumes are used to signify
the character.
Make-up and hair style – It gives beautiful
appearance to the character. It establishes the characters attitude.
Acting – The performance on the stage is
called acting. Different characterS perform on stage. Through acting, actors
convey story, emotions, feeling, etc.
Aspect ratio – The relationship between the width and height of the image. It gives different way of looking at the world.
8. Methods of film promotion
Promotion is the practice especially in the film industry is a kind of advertisement to inform people about film.
Television promotion – Film advertisements are shown in television between programs. It can be before or after releasing of film. Songs, fight, dialogue, music, are used to promote film through television advertising.
Print advertisement – Poster of a film is printed on newspaper and magazines. Theatre name, producer, director names are printed in it.
Radio advertisement – Film advertisements are done orally through radio. Film name, cast, crew name, music, dialogue, are come in radio promotion
Theatre advertisement – The new film going to be released soon is shown on theatre. It is shown to the theatre goers during break.
Promotion through internet – Films and songs are available in the internet to access for public. It is an effective way of promotion to reach globally.
Teaser – Before releasing the film, teaser is shown in TV, radio, internet and theatres. Important song clips, catchy dialogues, music are used to prepare teaser. It is very important to attract and get the attention of people.
Cast and crew interview – Cast and crew interviewed by a TV presenter. The story location, songs, interesting moments and problems faced during shooting are discussed.
Sponsor – Film sponsors programs of any event. During the event film name and its information’s are announced by the event person.
Poster – It is a big sized printed material displayed in theatre and road side walls. Film name, hero, heroine faces are printed in big size.
Audio launching – This function is done before releasing the film. It is covered by the print and electronic medias shown to public.
9. Film as a medium of mass communication
·
Film performs the functions of mass media. It
reaches millions of people.
·
It informs, educate, and entertain the people
through its content.
·
It transforms culture from one generation to
another
·
Since film is a audio visual medium, it
provides social messages effectively.
·
Movie helps us to perceive the world around
us. Songs are taken in different countries.
·
Film provides us to conceive of our society.
It shows what is happening around us.
·
Film uses varieties of stories such as love,
comedy, action, etc. to attract the audience.
·
Film appeal to people’s sentiments and
emotions. Happiness, sadness, anger are shown in the film
·
Film leaves lasting impression of the
message.
·
The films generate fashion styles and
mannerisms. Youths do what their hero does.
· Some films try to show breaking stereo type’s role. K. Balachander films are given more importance to female characters.
10. Three point lighting
Lighting
is the deliberate use of light to achieve practical or aesthetical effects.
Lighting includes the use of both artificial light sources like lamps and light
as well as natural illumination by capturing daylight.
Key
light - It is the main source of light used to illuminate the object. It shines
directly upon object. The placement of key light determines the shoot. In
indoor shoot the key light is lamp and in outdoor the sun is key light.
Fill
light – It is also shines upon the object. It is placed at the opposite side of
key light. It is placed lower position than key light. It controls the shadow
produced by the key light.
Back
light – It shines from the back side of object. It separates the object from
background. It is placing either one side or both side of object.
11. Importance of dialogue in film
·
The spoken word of the actor or actress is
called dialogue.
·
Through dialogue we can identify the
characters
·
Dialogue gives necessary information about
the story
·
Dialogue move the story forward
·
Dialogue can show what one character thinks of
another character
·
Dialogue can reveal conflict and build
tension in the story
·
Dialogue conveys feelings of the character
12. Importance of sound in film
·
Background music, dialogue and special
effects are the forms of sound
·
It communicates information happening in
various situations to the audience.
·
It creates feelings such as sadness,
happiness, anger etc
·
It is used to communicate the mood of scene.
·
Dialogue is used to reveal the character,
communicating information etc
·
Background music is used to communicate the
feelings, create tension and thrilling moment
·
Sound establishes time and moves the film
forward
·
It establishes the environment where the
action is taken place. Train sound indicates that the action is taken place in
railway station.
·
Doubtful contents of a movie
can be pushed into the “right” direction by music
·
Music can also work very
well to establish a certain time or period. Music that sounds very baroque will
put us back into the 18th century
·
Anything that gives the
feeling of not being real can be greatly enhanced by the music.
·
Music that sounds like
something that is not expected in a certain scene will create a feeling of
“something is not right”.
·
Music can help the audience
to understand or develop character.
·
One of the most obvious case
of such a function of music are national anthems whose function of course also
is, to unite the “nation”.
13. Importance of lighting in film
·
Lighting is used to illuminate the object and
show the character on screen
·
Lightings are used in different situations
such as early morning, afternoon, evening and night
·
It is used to establish time, season and
environment
·
Audience get thrilling mood if there is no
light or less light in scene
·
Artificial lights and available lights are
used to make film
·
Different lightings used in different
situations such as office environment, discotheque, festivals, horror, etc.
14. Factors determining the success of a movie
·
The popularity of the film content. Eg – Multiple
personality in Anyan film
·
The current popularity of the film genre
·
The current popularity of the film star.
People running towards the theatre to watch Rajini, Kamal, Ajith, and Vijai.
·
The strength of the films marketing campaign,
continuous advertisement of a film done through TV, radio, or newspaper.
·
The strength of the film distribution and its
release date is also important. Releasing film during Diwali, Pongal, and
summer holidays makes the box office hit.
·
The competition during the film release
period, that is releasing the film on the same date of famous film star film
·
Factors such as weather, holidays,
distracting news events that can limit the film audience to go to theatre.
·
Critical reviews affect the success of movie –
Thirai Vimarsanam, Magazine and Newsper reviews
·
The location where the film was shot also a
factor of its success
·
The characterization of an actor is an
another important factor makes the audience watch the film
·
Screenplay, songs and music play vital role
for the success of movie
·
Nowadays teaser is used as an important tool
to promote a movie
15. Importance of make-up in film
·
Makeup is done with the help of cosmetics
·
Generally it is used to enhance the
appearance of an actor / actress
·
It is done by makeup artist
·
It plays major role in drama, television,
film making, fashion and modeling industry to portray the actor to appear in a
particular character
·
It helps to communicate the personality of
the character to viewers
·
It creates various appearances for a
character such as black eye, bloody wounds.
16. Importance of costume in film
·
It is the clothing information of character
in film
·
It gives overall appearance of character
·
It refers to the style of dress for rich and
poor people
·
Costume designs are produced to denote
status, class, etc
·
Costume differs from genre to genre such as Historical,
Fantacy, Dance, and Drama, Epic, etc.
·
Costume designer is in-charge in preparing
costume for character
·
It differentiate hero and heroine from the
background dancers
17. Italian Neo-Realism
·
Realism refers to the believability of its
characters and events in a film
·
Italian neo-realism is also known as golden
age of Italian cinema
·
Italian films showed the conditions of people
everyday life including poverty, etc
·
It was a sign of cultural change and social
progress in Italy
·
Film presented new stories and ideas deviated
from the existing concept
·
Films were shot in streets, since film
studios had been damaged during world war
·
Neo realist films were filmed with
non-professional actors
·
Well known actors were acted in leading roles
in front of the available background
·
Italians shot film on location mostly in
cities and rural areas.
·
These films explore the conditions of poor
and lower working class
·
These films were made for the development of
Italy
18. German expressionism
·
It was initially restricted to Germany, due
to isolation after world war I
·
In 1916, the German government had banned
foreign films
·
Creative movement in cinema began in Germany
·
It was a direct reaction against realism
·
German expressionism used extreme distortions
in expression to show an inner emotion of the character
·
The story dealt with madness, intellectual
topics, etc
·
It is to enhance the mood of a film
·
It influences on modern film making
particularly in horror films
19. Narrative structure or Three act structure of film
It is a model used in screen writing that divides story into three parts
First act
·
It is usually used for exposition to
establish the main character, their relationship and the world they live in
·
Later in the first act an incident that meet
the main character whose attempt to deal with this incident and lead to
dramatic situation
·
It ensures life will never be the same again
for the protagonist (Hero) and raises dramatic question that is will be
answered at the climax of film
·
It occurs approximately 30 to 40 minutes into
film
Second act
·
It is referred to raising action
·
Protagonist attempt to resolve the problem
initiated in first act
·
Protagonist seem unable to resolve their
problems, because he does not has the skill to deal with antagonist
·
Protagonist finds a different way to defeat
antagonist
·
Different supporting characters help
protagonist to solve the problem
Third act
·
It features the resolution of story
·
The climax is a scene in which the main
tension of story is released and the dramatic question was answered
20. French new wave films
·
Director is the author of the movie
·
The new wave film makers attacked classic
literary style of French cinema
·
This film experimenting with different
filming techniques and method of editing
·
They use jump cut to create interest in film
·
They used improvised dialogue in the film to
create emotions
·
They record sound during shooting itself
·
They used natural lighting (sun and moon) for
shooting
·
They shoot film on location
·
The budget of film is low
·
New wave films spread to countries like
Britain, Germany.
21. Lip sync (lip synchronization)
·
The appropriate matching of lip movement in
visual with recorded audio is called lip sync
·
It is coming in dubbing of film
·
The lip sync in animation movie is between
the sound and animated character
·
It is important in television program such as
serial, game show
·
In music video, the movement of artist is
match with audio
·
Dubbing of foreign films needs proper
synchronization
·
If lip sync is not done well in any program creates
confusion to viewers, because both audio and video plays in different speed
22. Continuity editing
Rearranging the shots in a sequential order is editing.
Maintaining continuity between the shot is continuity editing
Subject identification
Subject should be identified by the audience without confusion. The shot must be gradually changed. If we show extreme long shot, the next shot should be long shot, then mid shot and close up shot. Don’t show close up shot immediately after extreme long shot which makes confusion to the audience.
Mental map
Our mind automatically fill up the object
which is out of screen. In an interview, if interviewee is in on the screen,
interviewer out of screen, our mind automatically fulfills the visual of out of
screen person.
1.
Vectors
Graphic, index and motion vectors are used to establish
or maintain the viewer’s mental on-and off-screen map.
a. Graphic vector – It is created
by lines on screen to lead the eye in a general direction. Graphical Vectors are vectors that are inherent in the inanimate objects of the
scene. One important way to maintain continuity between video clips is to maintain the Graphic Vectors by making sure
that lines and angles remain the same
b. Index vector – It shows the direction. Once the camera
shot is set, the next should not exceed 180 degree angle. Also called crossing
the line and action axis
To maintain the screen positions of person A and B in over-the-shoulder shooting, the cameras must be on the same side of the vector line
c. Motion vector – If a subject exists a frame to the right they should
enter the next frame from the left
When crossing the motion vector line with cameras, the object motion will be reversed in each shot
1. Movement - Try to continue action as much as possible from shot
to shot by cutting on the action. For example if a subject is rising from a
chair, cut to a wider shot just he has started to rise.
2. Color – The dress color and the background color in a shot to another shot in a scene must be same. If color continuity missing the audience get confusion
. Sound – The music and BGM must be appropriately cut to avoid
confusion. If sound continuity is not good, it disturb the mood of scene. When
editing dialogue or commentary, make sure to preserve the general speech
rhythm.
23. Editing
Arranging the shot in a sequential order is called
editing
Linear editing – It is a video editing
process done in post production stage. It is the process of selecting,
arranging, modifying images and sound in a sequential order. It is called tape
to tape editing. The selected footage is copied from source tape and pasted in
recording (output) tape.
Non-linear - It is computer based editing. It
is a video editing method which enables direct access to any video frame. It is
the concept of cut and paste technique. Premiere, FCP, AVID are the software’s
used for non-linear editing process.
Montage editing – Montage is a technique in
film editing in which a series of short shots are edited into a sequence. It is
to condense space, time and information. It is used to suggest the passage of
time
24. Dubbing
·
Dubbing is the post production process in
filmmaking
·
It is recording and replacing voices on a
motion picture to original shooting
·
It refers to the substitution of voices of
the actors
·
It is practiced in musicals when the actor is
not able to sing
·
It is done in other language films
·
It is to improve audio quality. The audio
recorded in shooting is not having the projection quality.
·
Films, videos and video game are dubbed into
local language of foreign market.
25. 180 degree rule
·
The 180-degree rule is a cinematography guideline that states that
two characters in a scene should maintain the same left/right relationship to
one another.
·
When the camera passes over
the invisible axis connecting the two subjects, it is called crossing the line
and the shot becomes what is called a reverse angle.
·
180 degree rule is a basic rule to be
followed when shoot film
·
It is to convey story without any confusion
·
While shooting film, it is the work of script
assistant, director and cinematographer to follow screen direction
·
Screen direction means keeping subjects which
are right to right throughout the scene
· Draw a imaginary line between two characters, eye contact, now place all the cameras only on one side of line
26. Types of transitions
CUT - The cut is an instantaneous change from one image (shot) to another. It is assuming that the preceding and following shots show some continuity. The cut itself is not visible; all you see are the preceding and following shots. It resembles most closely the changing field of the human eye. The cut is basically used for the clarification and intensification of an event. Clarification - For example, in an interview show the guest holds up the book she has written. To help the viewer identify the book, you cut to a close-up of it. Intensification - for example, a football tackle might look quite tame; by cutting to the close-up, the action has been intensified.
DISSOLVE - The dissolve is a gradual transition from shot to shot, the two images temporarily overlapping. The dissolve is a clearly visible transition. Dissolves are often used to provide a smooth bridge for action or to indicate the passage of time. When you hold the dissolve in the middle, you will create a superimposition, or super.
WIPE - The wipe tells the viewers that they are definitely going to see something else, or it injects some interest or fun into the shot sequence. Top, bottom, right, left, peel, diamond, door are some of the types wipes used as transitions.
FADE - In a fade the picture either goes gradually to black (fadeout) or appears gradually on the screen from black (fade-in). You use the fade to signal a definite beginning (fade-in) or end (fade-out) of a scene. Cross-fade for a quick fade to black followed immediately by a fade-in to the next image. The cross-fade is also called a dip to black.
27. Functions or Need or importance of editing
Editing
is done for different reasons. Sometimes you need to arrange shots so that they
tell a story. Other times you may have to eliminate extraneous material to make
a story fit a given time slot. These different reasons are all examples of the
four basic editing functions: (1) combine, (2) shorten, (3) correct, and (4)
build.
COMBINE
- The simplest editing is combining program portions by hooking the various
video-recorded pieces together in the proper sequence. For example, select
various shots taken at a friend's wedding and simply combine them in the order
in which they occurred.
SHORTEN
- Many editing assignments involve cutting the available material to make the
final videotape fit a given time slot or to eliminate extraneous material. For
example the whole T20 cricket match is shown on television news for 2 to 3
minutes only.
CORRECT
- Much editing time is spent on correcting mistakes, either by eliminating
unacceptable portions of a scene or by replacing them with better ones. This
type of editing can be simple—merely cutting out the part during which the
talent coughed and replacing it with a retake.
BUILD - The most difficult, but also the most satisfying, editing assignments are when you can build a show from a great many takes. For example, when you use a single camcorder during a film style field production, you need to select the best shots and put them in the proper sequence in postproduction editing to build the story.
28. Ambient sound
·
Ambient
sound (ambient audio, ambience, atmosphere, atmos or
background noise) means the
background sounds which
are present in a scene or location.
·
Common ambient sounds include wind,
water, birds, crowds, office noises, traffic, etc.
· Ambient
sound is very important in video and film work. It performs a number of
functions including:
- Providing
audio continuity between shots.
- Preventing
an unnatural silence when no other sound is present.
- Establishing
or reinforcing the mood.
·
It is the opposite of "silence". Ambience is
similar to presence, but is distinguished by the existence of explicit
background noise in ambience recordings, as opposed to the perceived
"silence" of presence recordings.
·
Every location has distinct and subtle sounds created by
its environment. These sound sources can include wildlife, wind, music, rain,
running water, thunder, rustling leaves, distant traffic, aircraft and
machinery noise, the sound of distant human movement and speech, creaks from
thermal contraction, air conditioning and plumbing noises, fan and motor
noises, and harmonics of mains power.
·
Ambience is normally recorded in stereo by
the sound department during the production stage of filmmaking.
·
It is used to provide a movie location with sonic space
and normally occupies a separate track in the sound edit
29. BGM (Back Ground Music)
·
BGM sets the tone for a movie. It gives the audience an idea about
the genre, level of intensity and the kind of movie it is.
·
It is possible to create music contrary to the scene, which gives
the audience a different perspective. This is often used in plots which have a
twist. For example, imagine that a villain character is actually a hero and the
film maker wants to convey that towards the end of the story.
·
There is also scope for thematic development, as in it is possible
to use a couple of musical themes and then develop them as the story
progresses.
·
Character themes help the audience to understand and connect the
dots as far as the plot is concerned. For example, if there’s a bad guy in the
story and we have his character theme, every time he is about to come if that
music is played, the audience gets a hint that something bad is going to
happen.
·
The pallet of sound used in a movie can be the collective decision
of the director, producer and music director. Creating a unique blend of
instruments and sounds give the film an aural personality.
· The perception of time can be manipulated by varying the tempo of the music according to the intensity of the scene.
·
Every good film has dynamics. There are scenes which are lighter
and some are more intense. Sometimes silence acts a powerful tool to help
create dynamics.
·
BGM can make you think and feel in a certain way about the
characters, their dialogues and the storyline.
·
Music gives the audience a better idea of how montage scenes
connect with each other and with the story.
·
Music helps to smoothen the video edit and blend scenes together
to make the story flow better.
·
Music can also be used to enhance the characteristics of a
location or time period.
30. Film form
Narrative cinema
·
Narrative films tell a story
·
These films screened in theatre broadcast on
TV and sold as DVD
·
It is also called fiction film
·
The film maker has the freedom to create
story
·
Fictional films are composed by a string of
events
·
It follows three act structure of story
telling
·
The introduction of characters at first then
the conflict and finally tells solution. Ex – Anniyan
Documentary (non-narrative film)
·
Documentary film making is concerned with the
real facts and historical event – ex – life history of Mahatma Gandhi
·
It is called non - fiction films
·
It has voice over to demonstrate the visual
·
The film maker must produce the evidence for
source of information is documented
·
Interviews with the people is part of
documentary
·
An expert witness in the concerned subject is
important for documentary
Experimental film
·
This type of movie is trying something new
and different
·
These films are rare and unpopular
·
It is neither narrative nor documentary
·
These films are not following three act story
structures.
·
An experimental film is often characterized by the
absence of linear narrative, the use of various abstracting
techniques—out-of-focus, painting or scratching on film, rapid editing or even
the absence of any sound track.
·
The goal is often to place the viewer in a more active
and more thoughtful relationship to the film.
· Most such films are made on very low budgets, self-financed or financed through small grants, with a minimal crew or, often a crew of only one person, the filmmaker.
31. Hollywood cinema
·
Hollywood is the world’s leading centre of
film production
·
MGM and Paramount are the important film
making companies in America
·
The popular comedian of American film industry
was Charlie Chaplin. His film was sentimental and less technical
·
Hollywood responded to the success of foreign
film makers by inviting them to work in America
·
Famous film stars also moved to Hollywood to
act in that film
·
Musicals were popular genre of film after
invention of sound
·
Laurel and Hardy were the famous characters
in American films
·
The horror film had gained importance after
invention of sound and technology
·
Gangster film were successful in America
·
Animated films had become part of Hollywood films
·
The contribution of Disney world and Warner
brothers to American films was appreciatable.
32. Soviet film
·
It reflect Soviet culture, language and
history
·
It is regulated by central government in
Moscow
·
The government fund only for short film and
educational films
·
Documentary is a film form of Soviet Russia
·
The directors and writers were dominated
Soviet film industry
33. Film realism
·
Realistic fiction typically involves a story whose basic
setting is real
·
Events could feasibly happen in a real-world setting
·
Non-realistic fiction involves a story being set in an
imaginary setting.
·
All types of fiction arguably invite their audience to
explore real ideas, issues, etc.
·
Fiction usually has elements of truth.
·
Non-fiction if it is people, places, and events are all
historically or factually real.
·
It refers to the believability of film character and
story
·
It is evident in classical Hollywood cinema
·
It is neither a rigid nor specific subject matter
·
It is about the nature of photographic images
·
The originality of people and their life style is shown
in film as it is
34. Surrealism
·
It is opposite to realism
·
The story is imaginary
·
Surrealism used new techniques in filmmaking
·
It breaks down traditional way of film making
·
It is made for entertainment purpose
·
Film moves by love, action, emotions, etc
35. Film language
Telling the story effectively using various
elements of film is film language. It involves shot, camera angle, sound,
editing, etc.
Shot – An XLS establishes the environment and
the close up details the parts of the subject
Composition
- Arrangement of elements in a frame which make things look natural is
composition.
Camera position and angle – Placing the
camera in different places, move forward and backward to capture image
Movement – Shots need some movement in the
frame. Movement such as pan, track, tilt are used to follow action.
Lens – Normal lens, Wide angle lens,
Telephoto lens, Fish eye lens are used in different situations to capture the
visual. Filters are also used in front of the lens to create effects.
Light and color – It makes the mood happy,
sad, scary using day light or room light
Sound – It creates more impact. The sound
includes music, dialogue and natural sound which communicate stories.
Editing – Arranging the shots sequentially to
convey story effectively
Continuity – Film different shots, add sound
and music and put it together to flow naturally
36. Trilogy
·
It means series of three complete films that
are related in same theme
·
The series of three matrix movies is an
example of trilogy
·
The trilogy represents three parts to story –
beginning, middle, end
·
It enhances a story and gives it more depth
·
Main characters are same and some new
characters are introduced in trilogy
·
Satyajit Ray’s Appu Trilogy is the best
example for trilogy film
37. Apu trilogy
Trilogy is
a series of three complete books, films or creative works that are related in
theme. The Apu Trilogy comprises three Bengali films directed by Satyajit Ray:
Pather Panchali, Aparajito and The World of Apu. The three films showed childhood,
education and early maturity of a young Bengali named Apu
Pather Panchali - Apu's early
experiences in rural Bengal as the son of a poor but high caste family are
presented. Apu's father Harihar, a Brahmin, has difficulty in supporting his
family. After the death of Apu's sister, Durga, the family moves to the holy
city of Benares.
Aparajito - The family's
finances are still precarious. After his father dies there, Apu and his mother
Sarbajaya come back to a village in Bengal. Despite unrelenting poverty, Apu
manages to get formal schooling and turns out to be a brilliant student. The
growing Apu comes into conflict with his mother. Later, when his mother dies
too, he has to learn to live alone.
Apur Sansar - Attempting to become a writer, Apu unexpectedly finds himself pressured to marry a girl whose mother rejected her mentally ill bridegroom on the day of their wedding. Their blossoming marriage ends in her death in childbirth, after which the despairing Apu abandons his child, but eventually returns to accept his responsibilities.
38. Casting
·
Casting
in film is a pre-production
process for selecting an actor, dancer, and singer.
·
The casting process involves a series of
auditions before a casting panel, composed of film producer, film director,
and/or choreographer.
·
These auditions are videotaped, then shared with film
producers, film directors.
·
The casting panel examines both the individual actor
perfomance, and the combination of two or more actors.
·
Casting director is in charge of the process of casting.
·
He is comes under above the line staff
·
Casting director is sometimes assisted by a casting
associate
39. Roles and responsibilities of director
·
Director is a person who is responsible for
film
·
Film director is like captain of ship
·
They select actors and control them
·
Director is also selecting technical persons
such as music director, camera man, etc
·
He / she writes story for film
·
He prepares budget for film
·
Director is co-ordinating with the whole
produciton team
·
Some directors do other functions such as
music, editing, etc
·
Director is involved in pre-production to
till the release of movie
40. Characteristics of film media
· It is an audio visual medium because it has both video as well as audio in it.
· It reaches mass audience hence it is a mass medium of entertainment.
· The story of the film is imaginary and narrative. It follows three act structure namely first act, second act and third act.
· It comes in various genres such as action, thriller, romance, war, science fiction, etc.
· It is approximately the length of 2 to 3 hours of running time in the theatre.
· It is made in different languages depends upon the language the audience speak. In India it is made in Tamil, Telugu, Malayalam, Kannada, Hindi, Bengali, Marathi, etc.
· Either the film is made in the own language of the people or it is dubbed from other languages.
· It is one way communication medium. There is no interaction between the medium and the viewer.
· Film is projected in 35 mm and 70 mm screen
· It creates more impact on public
· Graphics and animations are part of cinema
41. Special effects (VFX)
·
It is called as visual effects
·
It is a visual trick used in film
·
VFX categories are optical effect and
mechanical effects
·
It is one of the post production works
·
Creating wind effect, rain, fog, snow, are
some of the example for mechanical effects
·
An optical effect is created by camera lens
such as multiple exposure, rack focus.
·
Various special effects in the computer
editing software are used to create special effects.
·
Bouncing ball, bubbles, fire effects can be
created using computer
·
Special effects can be used during live production
42. Write the role of graphics in film
Special effects
·
Special effects are visual
tricks used in film to simulate the imagined events in a story or virtual
world.
·
Mechanical effects includes the creation of physical
wind, rain, fog, snow, clouds, making a car appear to drive by itself and
blowing up a building, etc.
·
Optical effects are techniques in which images or film
frames are created photographically, either "in-camera" using
multiple exposure, blue or green mattes, etc.
Digital effects
· It covers the various processes by which imagery is created or manipulated with or from photographic assets.
· Digital Effects often involve the integration of still photography and computer generated imagery (CGI) to create environments which look realistic but would be dangerous, costly, or impossible to capture in camera.
Matte painting
· A matte painting is a painted representation of a landscape, set, or distant location that allows filmmakers to create the illusion of an environment that is not present at the filming location.
· Matte paintings are either filmed on set, where they are framed to look like a physical set piece, or they are combined with live footage in post production
·
In the scenes the painting
part is static and movements are integrated on it.
Motion capture
· The process of recording the movements of objects and or people.
· It can be used to track the facial movements and expressions of an actor and transfer them to a 3d model.
·
The movement of the camera
is also recorded, which allows editors to use this data to enhance the
environment the motion captured set is imagined in.
Modeling
· 3D modeling is the process of creating a 3D representation of any surface or object
· 3D modeling software produces three-dimensional digital effects.
·
It produces a digital object
capable of being fully animated, making it an essential process for character
animation and special effects
Animation
· Computer animation is the art of creating moving images via the use of computers
·
It speeds up the process
of creating the many images needed for such a sequence
Compositing
· Compositing is the combining of visual elements from separate sources into single images
·
Live-action shooting
for compositing is
called "chroma key", "blue screen", "green
screen".
VFX
· Visual effects are the processes by which imagery is created and/or manipulated outside the context of a live action shot.
· Visual effects make use of graphic design, animation, modeling, etc. using software such as After Effects, Maya, Cinema4D, and NUKE
43. Hero worship culture in India
·
The four south Indian States and the Union Territory of
Puducherry are home to a unique variant of fandom.
·
Each State—and every region within the State—has its own
variant of the fan club.
·
Across the southern States we see the signs of activities
by fan clubs on the streets. These range from leaflets, wall posters and giant
plywood cut-outs of screen idols.
·
Fan club know as Rasigar manram (Tamil) and abhimana sangha/sangham (Kannada/Telugu),
formed by a group of 10-25 young men between 20 to 30 years of age who are poor
or from the lower middle class.
·
Fans of female stars are not impossible to find, but it
is usually the male star that is the centre of fan activity.
·
The Tamil superstar Rajinikanth alone reportedly has a
hundred thousand clubs with a total of million-plus members.
·
Fan activity is carried out in the name of the star to
promote him. It is a myth that fans are remote-controlled by stars or their
offices.
·
When the Tamil superstar M.G. Ramachandran (MGR) died, as
many as 31 people reportedly committed suicide.
·
Kannada star Rajkumar death from natural causes brought
Bangalore to a complete standstill and several people died.
·
Often we can see clash with the fans of two hero’s
generally placing cutout in front of the theatre.
·
Fans are, of course, movie buffs who spend the better
part of their evenings in and around cinema halls: watching films, decorating
them or simply hanging around talking about cinema and its stars.
·
Fans also participate in a wide range of activities such
as feeding the poor, blood donation, disaster relief work, etc, that are
completely unrelated to film watching.
44. Portrayal of women in Indian cinema
· It is true that the number of movies that have meaningful roles for women is increasing.
· Mother India is the first Indian cinema in which female actor is in the lead role.
· Roughly upto the 1980s, lead actresses have significant roles. Movies at that time used to have wonderful stories which totally reflected the society. But at the same time, filmmakers used to add ‘vamp’ characters in the movies to provide sexually explicit entertainment.
· This culture has not changed even now. Producers are adding item songs to gain commercial success.
· Since 1980 the role of lead actress started reducing to just an add-on to the hero-centric film.
· In recent times, many lead actresses are doing strong roles. As more and more women are joining in the film industry as directors, producers, actresses etc., the situation of female characters portrayal is improving.
· Most of the mainstream movies are male-centric. Lead actresses are treated as glam dolls in these movies.
· In many movies of present times, female characters are needlessly sexualized. Along with that, adding vulgar lyrics and dances in the name of item songs is very derogatory towards women.
· Lead actors are always shown as saviors. Women are shown as either helpless victims or cunning villains. In general, hero is the one who solves everyone’s including heroine’s problems.
· Movies depict actresses as unrealistically beautiful. This causes a lot of trauma and insecurity issues.
· Stalking (irritating) and eve-teasing are depicted as love in Indian movies. In many mainstream movies, female characters fall in love with these abusers.
· Heroines were portrayed as submissive, prefer to be homemaker, not career oriented and bears the brunt of abusive husband silently.
· Now the female characters in movies are more realistic and are many actresses are not doing such kind of meaningless roles.
45. How to review a film?
·
Introduction:
Include the name of the movie/documentary, its release date, and background
information.
·
Summary:
Provide a brief overview of the story.
·
Analysis
of the events: Analyze the plot and important events like action, climax.
·
Creative
elements: Describe the characters, dialogues, camera work, costumes, use of
colors, genre, tone, symbols, or anything that adds to or misses from the
overall story.
·
Opinion:
Support your opinion with facts and examples from the story
·
Conclusion:
Announce whether the filmmaker succeeded in his/her goal, paraphrase your
evidence. Also, explain how the film helped in developing a deeper
understanding of the course topic
46. Cinema is cathartic in nature (Catharsis)
· Catharsis refers to an emotional release for the characters in a film
· Catharsis is a concept in psychoanalytic theory wherein the emotions associated with traumatic events come to the surface. The word has its origin in a Greek term for cleansing or purging.
· Catharsis is associated with the elimination of negative emotions, affect, or behaviors associated with unacknowledged trauma
· Playing the piano is a catharsis for a tired, busy mother after a long day of work.
· Crying is a great catharsis for releasing pain and anger
· Emotional catharsis is an important factor in a person's well-being.
· Laughter can be a catharsis for expressing joy and amusement
47. Montage
Montage is a technique in film editing in which a series of short shots are edited into a sequence to condense space, time, and information. It was introduced to cinema primarily by Sergei Eisenstein and early Soviet directors used it as a synonym for creative editing.
Types of Montages
1. Metric montage - Metric montage refers to the length of the shots
relative to one another. Regardless of their content, shortening the shots
abbreviates the time the audience has to absorb the information in each shot.
This increases the tension resulting from the scene. The use of close-ups with
shorter shots creates a more intense sequence.
2.
Rhythmic montage - Rhythmic
montage refers to continuity arising from the visual pattern within the shots.
Continuity based on matching action and screen direction are examples
of rhythmic montage. This type of montage has considerable potential for
portraying conflict because opposing forces can be presented in terms of
opposing screen directions as well as parts of the frame.
3. Tonal montage - Tonal montage refers to editing decisions made to
establish the emotional character of a scene, which may change in the course of
the scene. Tone or mood is used as a guideline for interpreting tonal montage.
4. Overtonal montage - Overtonal montage is the interplay of metric,
rhythmic, and tonal montages. That interplay mixes pace, ideas, and emotions to
induce the desired effect from the audience.
5. Intellectual montage
- Intellectual montage refers to
the introduction of ideas into a highly charged and emotionalized sequence. The practice of cutting according to the shot’s
relationship to an intellectual concept.
48. Importance of script
· A screenplay or script is a written work by screenwriters for film
· It can be original work or adaptation from existing pieces of writing
· In them the movement, action, expression and dialogues of the characters are also narrated
· It includes as much detail as possible about most aspects in the scene.
· Without the script it would be difficult to complete further tasks later on such as the storyboard and the shot list.
· The script help us to give a rough idea of the length of the film
· An explainer video stimulates audio and visual senses simultaneously, helping viewers retain information longer and more effectively
49. Importance of cinematography / cinematographer
·
Cinematography is called as the art of moving
photography
·
Cinematographer decides which camera and
lighting effects should be used while filming.
·
This is the part of movie making that test
the creativity of cinematographer
·
If the cinematography of a film is not right
then the film may not really work
·
Cinematographer chooses required equipment
and recording devices
·
He use filters for making dramatic effect for
specific scene in a movie
·
The lens choosen by the cinematographer has
an impact on look, field and the effect of movie.
·
Skilled cinematographer chooses the right
framing and aspect ratio
·
Suitable lights used in cinematography to
evoke the right emotions
·
Cinematographer conveys feelings through
camera shots, angle and movement
50. Basics of script writing
Create a logline - A logline is a brief summary of the story, usually no more than a single sentence. It describes the protagonists and their goal, as well as the antagonists and their conflict. It conveys both the ideas of the story and its emotional undertones.
Write a treatment - A treatment is a longer 2-5 page summary that includes the titles of the screenplay, the logline, a list of main characters and a short synopsis. It is mostly used for marketing purposes. A producer may read the treatment first before deciding if the script is worth their time. The synopsis should highlight the main beats and turning point of the story
Develop the characters - Create characters who will create problem and who is going to solve it. Makes the character empathetic and interesting. Even the bad guy should have a reason he is bad
Plot - Plot refers to the storyline of the text. The plot is the sequence of events in the story or drama. The conclusion is the final resolution – either good or bad of the conflict and the end of the story
Outline - Outline the plot of the story means you will write a summary of the story, a short description of what the story will be about, what will happen, who will do what etc from beginning to end.
Write a first draft - Using the outline as a map, write the script scene by scene, including the dialogue and descriptive action. It creates interest to the producer to read the script if it has interesting characters and the proper structure elements.
Rewrite - If
the draft is ready go through once again for review. Refine the action, shorten
the dialogue and edit the script. This stage helps the writer to reduce the
error at the maximum
51. Art film
·
An art film is typically a serious,
independent film, aimed at a niche market rather than a mass market
audience
·
It
is "intended to be a serious, artistic work, often experimental and not
designed for mass appeal"
·
It
is "made primarily for aesthetic reasons rather than commercial
profit", and contains "unconventional or highly symbolic
content".
·
Film
critics and film studies scholars typically define an art film as
possessing "formal qualities that mark them as different from mainstream
Hollywood films".
·
These
qualities can include : a sense of social realism; an emphasis on the authorial
expressiveness of the director; and a focus on the thoughts, dreams, or
motivations of characters
·
Art
film producers usually present their films at special theaters and at film
festivals.
·
The
term art film is much
more widely used in North America, the United Kingdom, and Australia
·
Such
films are geared more towards linear storytelling and entertainment.
· For promotion, art films rely on the publicity generated from film critics' reviews; discussion of the film by arts columnists, commentators, and bloggers; and word-of-mouth promotion by audience members.
52. Role of production manager in filmmaking
· The main job of the film production manager is to organize all the needs of a production
· He is responsible for setting budgets for the needs of every film production aspects, which include paying all workers or staff of the production, incurring props, hiring catering services and other expenses used daily
·
He is responsible for solving problems that
may arise during filming, setting schedule of meetings and shooting, preparing
and submitting all types of paper work needed before deadline and making sure
all equipment's are set up properly and working well
·
He hires workers, assign people daily tasks,
assist in the set and administrative work, and oversee video editing.
·
He must know how to handle people and can
multi task.
·
Film production managers are excellent In
communication skills, both oral and written.
·
They must be very knowledgeable in all
aspects of film production, such as directing and editing
·
Also have advanced computer skills, and basic
knowledge in accounting, management and administration
53. Cinema and politics in Tamilnadu
·
Tamil people have always held two things
close to their hearts, film and politics
·
Tamilnadu Chief Minister C.N. Annadurai along
with Dr. K. Karunanidhi were the first script writer who pushed forth the
agenda of Dravidian ideologies
·
Sivaji Ganesan and S.S.Rajendran kept the
messages of Dravidian movement rolling in their films
·
Karunanidhi’s son M.K.Muthu formed ADMK which
is now called AIADMK
·
Assembly election in 1977 paved the wave to
MGR to enter the politics
·
MGR’s demise thrust the light upon another
film star Dr.J.Jayalalitha
·
Vijayakanth, Tamil film hero launched DMDK a
regional political party
·
Leading Tamil heros like Kamal Hassan,
Rjinikanth with the film background entered politics
·
Another Tamil hero Sarathkumar launched his
own political party All India Smathuva Makkal Katchi
·
Many film artist in Tamilnadu belongs to
political party nowadays
·
Some political parties have their own
production house.
54. Dubbing
· Dubbing, in filmmaking, the process of adding new dialogue or other sounds to the sound track of a motion picture that has already been shot.
·
Dubbing is most familiar to
audiences as a means of translating foreign-language films into the audience’s
language.
· When a foreign language is dubbed, the translation of the original dialogue is carefully matched to the lip movements of the actors in the film.
· Dubbing is often employed in the original-language version of a sound track for technical reasons.
· Synchronously recorded dialogue may be unclear or inaudible in a long-distance shot. Dubbing allows the filmmaker to obtain high-quality dialogue.
· Dubbing is also used to add sound effects to the original sound track.
· It may also be used in musicals to substitute a more pleasing voice for that of an actor who performs a song on camera.
55. Western movies
·
Western is a genre of
various arts which tell stories set primarily in the latter half of the 19th
century in the American Old West
·
Often centering on the life of a nomadic cowboy or
gunfighter armed with a revolver and a rifle who rides a horse.
·
Cowboys and gunslingers typically wear Stetson hats,
neckerchief bandannas, vests, spurs, cowboy boots and buckskins.
·
Recurring characters include the aforementioned cowboys,
Native Americans, bandits, lawmen, bounty hunters, outlaws, gamblers, soldiers
and settlers.
·
The ambience is usually punctuated with a Western music
score, including American and Mexican folk music such as country, Native
American Music, New Mexico music, and ranchers.
·
Often, the vast landscape plays an important role,
presenting a " mythic vision of the plains and deserts of the American
West".
·
Specific settings include ranches, small frontier towns,
saloons, railways and isolated military forts of the Wild West.
Common plots include:
·
The construction of a railroad or a telegraph
line on the wild frontier.
·
Ranchers protecting their family ranch from
rustlers or large landowners or who build a ranch empire.
·
Revenge stories, which hinge on the chase and
pursuit by someone who has been wronged.
·
Stories about cavalry fighting Native
Americans.
·
Outlaw gang plots.
·
Stories about a lawman or bounty hunter
tracking down his quarry.
56. Shooting script
·
The shooting script is more elaborate, precise,
overwritten version of the screenplay.
·
The shooting script is not written by the screenwriter.
It is written by the director alongside his cinematographer, while both discuss
their ideas and shot plan desired for the movie.
·
The main difference between the screenplay and the
shooting script is that the screenplay is a selling tool, whereas the shooting
script is a production tool.
·
The shooting script is normally broken into shots,
featuring precise cinematography terminology such as close-ups, dolly
in, overexposed.
·
The idea here is to inform the crew what is going on.
·
Before shooting starts, the shooting script will be
divided into dates, so everyone knows what is being shot when.
·
The goal is to let all the crew members know what they
will need to bring or arrange beforehand.
57. Elements of film
Theme - The theme in a story is its underlying
message, or 'big idea.' In other words, what critical belief about life is
the author trying to
convey in the writing of a novel, play, short story or poem
Plot - Plot is a literary term used to describe the events
that make up a story, or the
main part of a story. These
events relate to each other in a pattern or a sequence. The structure of a
novel depends on the organization of events in the plot of the story.
Script - A screenplay, or script,
is a written work by screenwriters for a film. These screenplays can be original works or adaptations
from existing pieces of writing. In them, the movement, actions, expression and
dialogues of the characters are also narrated.
Acting - Acting is an activity in which a story is told by means
of its enactment by an actor or actress who adopts a character—in
theatre, television, film, radio.
Setting - Settings locate the film & its narrative in a
time & place, giving it specificity, context & a unique flavour. It
anchors the film.
"A setting is
anywhere a scene takes place & it could be anywhere from a desert, to space
to even virtual reality.
Costume - "Costume"
often refers to a particular style of clothing worn
to portray the wearer as a character or type of character at a social event in
a film
Make-up - Makeup artists that work in film help communicate the
personality of all characters to the viewer. They use makeup as a way to improve,
enhance, or alter the appearance of the actors/actresses
Sound - “Sound”
refers to everything we hear in a movie —
words, sound effects,
and music. Sound is
used in film to heighten a
mood, provide us with information about the location of a scene, advance the
plot, and tell us about the characters in the story.
There
are two categories of sound:
Diegetic sound is a sound which has a source on-screen
(actual sound). Non-diegetic sound is a sound which does
not have a source on-screen, they have been added in.
Dialogue - Any piece of a
conversation or comment or speech has to elaborate on the plot or reveal
something about a character (a form of exposition).
Cinematography - Cinematography can make or
break a film. The person in
charge of the cinematography called
the cinematographer/camera
man or D.O.P (Director of Photography) is largely responsible for the film turning out what it is.
Lighting - Lighting includes the
use of both artificial light sources like lamps and light fixtures, as well as
natural illumination by capturing daylight. Day lighting (using windows,
skylights, or light shelves) is sometimes used
as the main source of light during daytime in buildings.
Direction - A film director
controls a film's artistic and dramatic aspects and visualizes the screenplay
(or script) while guiding
the technical crew and actors in the fulfillment of that vision. The director has a key role in
choosing the cast members, production design, and the creative aspects of
filmmaking.
58. Growth and development of cinema or History of cinema
· The Edison Company in the USA successfully demonstrated Kinetoscope, which enabled one person at a time to view moving pictures.
·
The
first to present projected moving pictures to a paying audience were Lumiere
Brothers in Paris.
·
At
first, films were very short, sometimes only a few minutes or less. They were
shown at fairgrounds and music halls or anywhere a screen could be set up and a
room darkened.
·
The
films were accompanied by lecturers, music and a lot of audience
participation— although they did not have synchronized dialogue.
·
Several
national film industries Europe, Russia were established. Films became longer,
and storytelling, or narrative, became the dominant form.
·
Large
studios were established and special cinemas built.
·
Colour
was first added to black-and-white movies through tinting, toning and
stencilling.
·
The
principles of colour separation were used to produce ‘natural colour’ moving
images.
·
The
first attempts to add synchronised sound to projected pictures used
phonographic cylinders or discs.
·
The
first feature-length movie incorporating synchronised dialogue was The Jazz
Singer, by Warner Brothers.
·
By
the early 1930s, nearly all feature-length movies were presented with
synchronised sound with color.
·
The
advent of sound gave rise to the ‘Golden Age of Hollywood’.
·
Thomas
Edison had used 35mm film in the Kinetoscope with the aspect ratio of 1:1.33,
later adjusted to 1.37:1.
·
Eadweard Muy bridge – he became the first man
in history to record continuous live action by using multiple still cameras. He
used a row of 12 cameras equally spaced along the race track to record the
movement of a horse.
·
Jules Mary – developed a camera called
Chronophotography or photographic gun that could take 12 snaps per second of
moving animals in a single camera.
·
George Melies – he developed fantasy films
with help of magic and special effects. A trip to the moon – special effects was
used including the image of rocket ship landing and man walking in moon.